Mod_1_Transformers1.ppt
- 2. What are transformers? ŌĆó Transformers are electrical devices used to convert or "transform" AC voltage from one level to another. (high to low or low to high) ŌĆó Input and output are AC ŌĆó They do this by the principle of electromagnetic induction
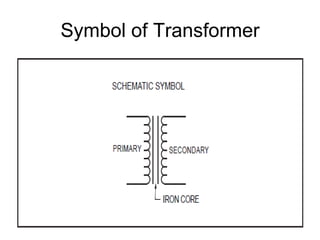
- 3. Transformer
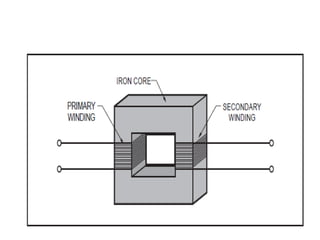
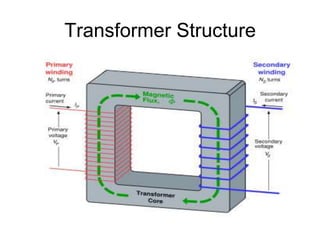
- 6. Parts of a Transformer A transformer consists of 3 basic components ŌĆó Primary Coil or Primary Winding : It is an electrical wire wrapped around the core on the input side ŌĆó Secondary Coil or Secondary Winding: It is an electrical wire wrapped around the core on the output side ŌĆó Core : A ferromagnetic material that can conduct a magnetic field through it. Example: Iron
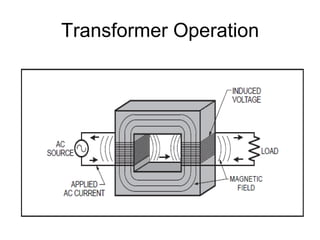
- 8. Transformer Operation ŌĆó An electrical transformer normally consists of a ferromagnetic core and two coils called "windings". ŌĆó A transformer uses the principle of mutual inductance to create an AC voltage in the secondary coil from the alternating electric current flowing through the primary coil. ŌĆó The voltage induced in the secondary can be used to drive a load.
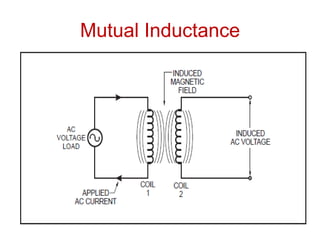
- 9. What is Mutual Inductance? ŌĆó The principle of mutual inductance says that when two electrical coils are placed near to each other, AC electrical current flowing in one coil induces an AC voltage in the other coil. ŌĆó This is because current in the first coil creates a magnetic field around the first coil which in turn induces a voltage in second coil
- 11. ŌĆó The transformer improves the efficiency of the transfer of energy from one coil to another by using a core to concentrate the magnetic field. ŌĆó The primary coil creates a magnetic field that is concentrated by the core and induces a voltage in the secondary coil
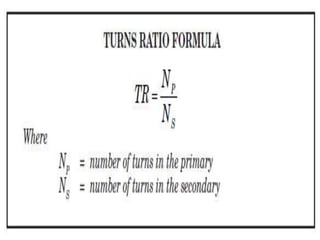
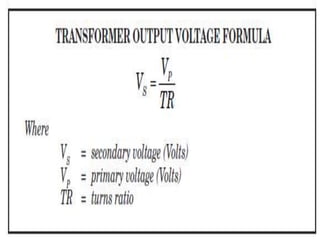
- 13. Turns Ratio ŌĆó The voltage at the secondary coil can be different from the voltage at the primary. This happens when the number of turns of the coil in primary and secondary are not the same ŌĆó The Turns Ratio (TR) is the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil
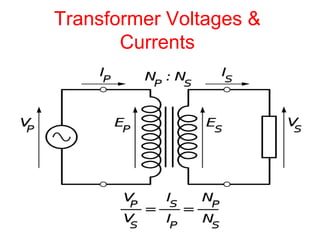
- 16. Formulas ŌĆóTR= Vp / Vs ŌĆóAlso TR= Np /Ns ŌĆóSo we can say Vp / Vs = Np /Ns Also Vp/Vs=Is /Ip
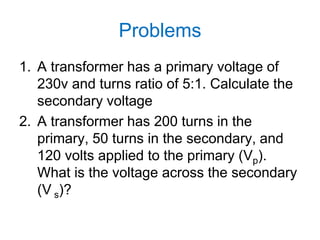
- 18. Problems 1. A transformer has a primary voltage of 230v and turns ratio of 5:1. Calculate the secondary voltage 2. A transformer has 200 turns in the primary, 50 turns in the secondary, and 120 volts applied to the primary (Vp). What is the voltage across the secondary (V s)?
- 19. More ProblemsŌĆ”. 1. There are 400 turns of wire in an iron- core coil. If this coil is to be used as the primary of a transformer, how many turns must be wound on the coil to form the secondary winding of the transformer to have a secondary voltage of one volt if the primary voltage is five volts? 2. A 12 volts transformer has 20 turns in the primary, 5 turns in the secondary. What is the voltage across the primary side (VP)?
- 20. Lab Activity 2 ŌĆóComplete Pages 19 -22 of Module 1
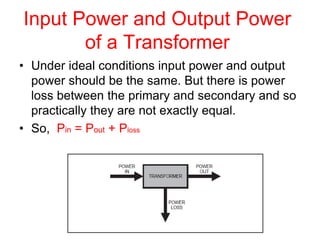
- 21. Input Power and Output Power of a Transformer ŌĆó Under ideal conditions input power and output power should be the same. But there is power loss between the primary and secondary and so practically they are not exactly equal. ŌĆó So, Pin = Pout + Ploss
- 22. Transformer Efficiency ŌĆó The power loss is converted to heat . The heat produced can be found by calculating the transformer efficiency.
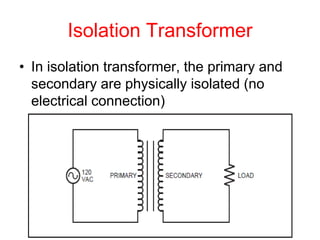
- 24. Isolation Transformer ŌĆó In isolation transformer, the primary and secondary are physically isolated (no electrical connection)
- 25. Advantages of Isolation Transformer ŌĆó Voltage spikes that might occur on the primary are greatly reduced or eliminated in the secondary ŌĆó If the primary is shorted somehow, any load connected to the secondary is not damaged ŌĆó Example: In TV monitors to protect the picture tube from voltage spikes in main power lines
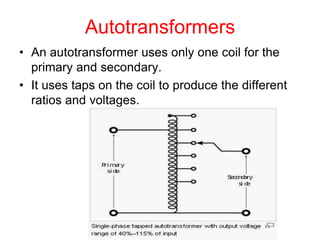
- 26. Autotransformers ŌĆó An autotransformer uses only one coil for the primary and secondary. ŌĆó It uses taps on the coil to produce the different ratios and voltages.
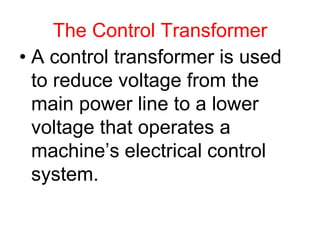
- 27. The Control Transformer ŌĆó A control transformer is used to reduce voltage from the main power line to a lower voltage that operates a machineŌĆÖs electrical control system.
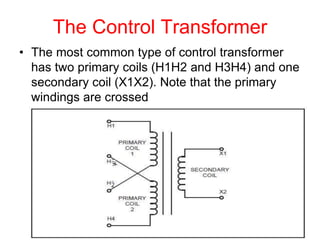
- 28. The Control Transformer ŌĆó The most common type of control transformer has two primary coils (H1H2 and H3H4) and one secondary coil (X1X2). Note that the primary windings are crossed
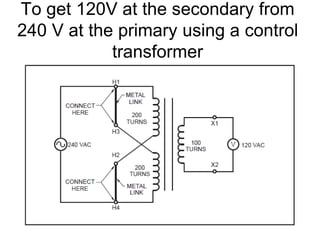
- 29. To get 120V at the secondary from 240 V at the primary using a control transformer
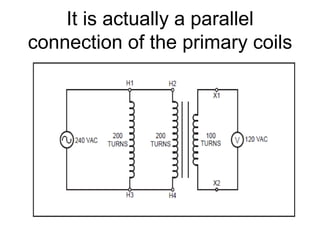
- 30. It is actually a parallel connection of the primary coils
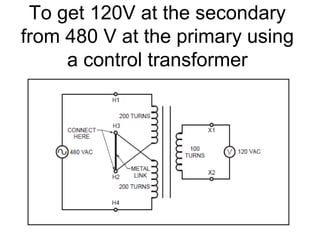
- 31. To get 120V at the secondary from 480 V at the primary using a control transformer
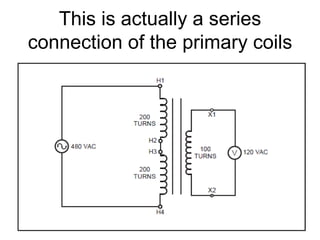
- 32. This is actually a series connection of the primary coils
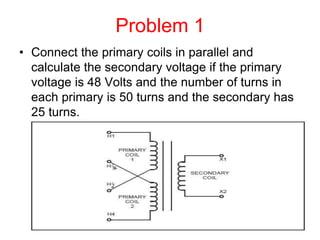
- 33. Problem 1 ŌĆó Connect the primary coils in parallel and calculate the secondary voltage if the primary voltage is 48 Volts and the number of turns in each primary is 50 turns and the secondary has 25 turns.
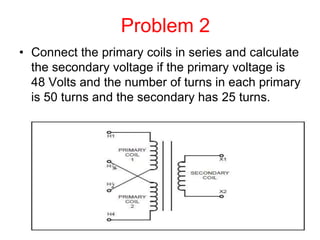
- 34. Problem 2 ŌĆó Connect the primary coils in series and calculate the secondary voltage if the primary voltage is 48 Volts and the number of turns in each primary is 50 turns and the secondary has 25 turns.
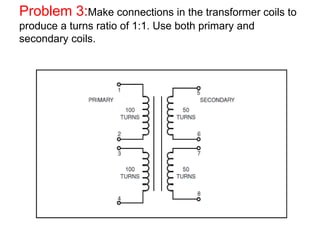
- 35. Problem 3:Make connections in the transformer coils to produce a turns ratio of 1:1. Use both primary and secondary coils.
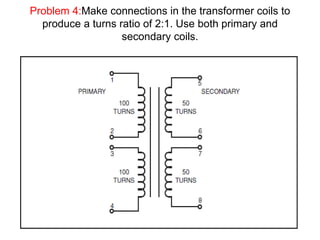
- 36. Problem 4:Make connections in the transformer coils to produce a turns ratio of 2:1. Use both primary and secondary coils.
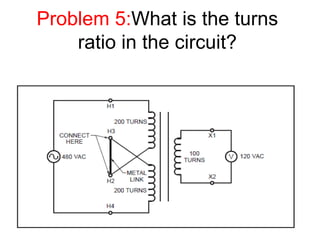
- 37. Problem 5:What is the turns ratio in the circuit?
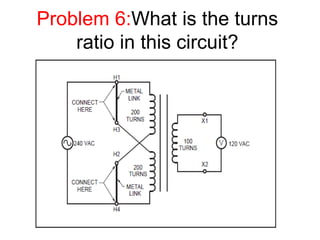
- 38. Problem 6:What is the turns ratio in this circuit?