Model2Roo - ACME
- 1. Model2Roo: Web Application Development based on the Eclipse Modeling Framework and Spring Roo Juan CastrejĂłn, Genoveva Vargas-Solar, Rafael Lozano University of Grenoble, CNRS, TecnolĂłgico de Monterrey ACME 2012
- 2. 2 Background •  First version of the project presented in early 2011 Google Code Project Conference Paper http://code.google.com/p/model2roo http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/CONIELECOMP.2011.5749344
- 3. 3 Objective •  Generate web applications, by transforming Class diagrams into Spring Roo commands Ecore, UML2 ATL Queries Spring Roo commands Spring Roo details: Ecore Annotations, UML Profiles
- 4. 4 Related work •  Web application development based on MDE techniques is a widely studied topic •  Web Modeling Language (WebML), WebRatio •  UWE approach •  Acceleo generators •  However, Model2Roo provides an association to modern development tools, through the Spring Roo project •  Spring Roo is responsible for the actual code generation •  Access to a wide variety of SpringSource projects
- 5. 5 User-identified issues 1.  Insufficient support for graphical environments •  Limited support for complex UML editors, such as Papyrus •  Limited support for numeric data types 2.  Basic edition of Spring Roo properties •  Spring Roo properties could only be set as free text •  Users were required to know the domains for each property 3.  Troublesome installation procedure •  Tool deployed as a single plugin file •  Manual installation of the required dependencies (ATL, Papyrus)
- 6. 6 Technical issues 1.  Maintenance of ATL queries •  Not a standard Model-To-Text specification 2.  Output Spring Roo commands into a file •  ATL was designed primarily for M2M not for M2T •  In order to generate files, we had to modify ATL loggers •  Not an elegant solution, prone to subtle errors 3.  Invocation of ATL queries from Eclipse plugin •  Limited documentation
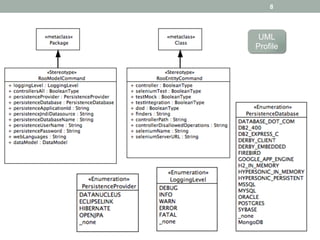
- 7. 7 Recent improvements 1.  Transformations implemented as Acceleo templates •  Standard notation (MOFM2T) •  Powerful syntax editors •  Automatic generation of UI Launcher projects (Eclipse plugin) 2.  Improved edition of Spring Roo properties •  Full support for Papyrus profiles (UML) •  Properties domains are specified in the UML profiles •  Fixed support for Ecore Annotations 3.  Improved installation procedure •  Eclipse update site containing all required dependencies
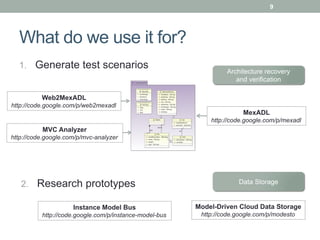
- 9. 9 What do we use it for? 1.  Generate test scenarios Architecture recovery and verification Web2MexADL http://code.google.com/p/web2mexadl MexADL http://code.google.com/p/mexadl MVC Analyzer http://code.google.com/p/mvc-analyzer 2.  Research prototypes Data Storage Instance Model Bus Model-Driven Cloud Data Storage http://code.google.com/p/instance-model-bus http://code.google.com/p/modesto
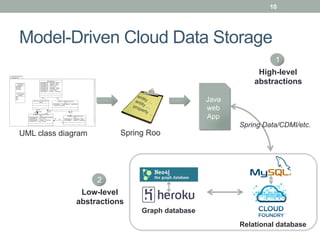
- 10. 10 Model-Driven Cloud Data Storage 1 High-level abstractions Java web App Spring Data/CDMI/etc. UML class diagram Spring Roo 2 Low-level abstractions Graph database Relational database
- 11. 11 Demonstration / Questions Contact: Juan.Castrejon@imag.fr