Modeling and Design Optimisation of an Alternative Cost Effective Rain sensing wiper system
- 1. Modeling and Design Optimization of an Alternative Cost Effective Rain Sensing Wiper System Dr. Amol M Khatkhate Nitin Dhamal Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering PhD Student, Department of Production Engineering Rizvi College of Engineering (RCOE) Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute (VJTI) Bandra (W), Mumbai - 400050 Matunga(W), Mumbai - 400028
- 2. Motivation : Analogous to Classical Control Theory Classical control theory evolved with all the mathematics so as to model linear systems Further advancements took place to identify solutions for nonlinear systems Control of DC motor is well established using Arduino UNO microcontroller Modular software systems can be built on top of the same with advanced control algorithms to develop innovative solutions for auto industry
- 3. Motivation and Introduction v Rain sensing wipers form an important part of a vehicle which operates in a region where there is heavy rain and considerable reduction in visibility due to such events. This may also lead to accidents and may prove to be fatal. v Rain sensing wipers reduce the drivers distraction and his attention span so that he can focus on the driving and ensure the safety of the passengers in the vehicle. v In a place like Mumbai, there is heavy downpour and neck to neck traffic which requires a lot of alertness and energy of the driver to ensure smooth and controller driving. In such a scenario, rain sensing wipers and such units which are sensitive to rain will result in an alarm system which can be very useful for the driver to park his vehicle in case of heavy rainfall thus avoiding vehicle disability. v This work introduces a novel idea of making an modified electrochemical cell to work as a rain sensor and also to further utilise the rainwater for cooling purposes. This sensor has been adapted to suit the conditions of the tropical climate and hence provide good level of automation to the driver during the rain. v The work presented also shows that the system is very cost effective (66% less costly) as compared to the conventional one and achieves the same functionality as required.Also, the system is independant of the microcontroller or the current manufacturing process of the vehicle and can be installed with proper procedure as a seperate unit.
- 4. Electrochemical Rain Sensor (ERS) Procedure for preparing Rain Sensor v Use a container of suitable size with a seperation to seperate the electrolytes v Construct a salt bridge from an accordion joint plastic straw v Use a container typically usedfor giving medicines to adults or babies as a container for collecting rainwater v Use a spring from a normal ball point pen to complete the straw-spring-container assembly v Allow a spacing of 50 microns (thickness of paper) between the salt bridge and the electrolytes v Place the rain sensor in the hood of the vehicle just below the area where there is collection of rain water from the windshield.
- 5. Performance of the Electrochemical Rain Sensor (ERS) Impulse response of rain sensor v A single droplet of rain produces a 3.2 micron deflection of the salt bridge v Assuming the damping of air to be 0.01, the response dies down after oscillating as shown in the Figure v Sensitivity of the sensor is 227 micron/ml of rainwater v Test were conducted to find the life of the accordion salt bridge using a plastic straw v Cell life was found using the following formula v Cell life in days = (No of cells x Molarity x Volume (liters) x No of electrons/mole x 96485)/(60 x 60 x 24 x (Final current + Initial current)/2) ) v The life was found to be 18 days in practice while it was found to be 22.9 days thoeretically.
- 6. Comparison of different rain sensors DIFFERENT TYPES OF RAIN SENSORS Plate based sensor Piezo- electric sensor Probe based sensor Optical based rain sensor Electro-chemical rain sensor Operating principle Micro controller based Micro controller based External circuits connected to micro controller Micro- controller based Independent of micro controller Working Small drops of water change the resistance Water between plates decrease resistance Contact of water with probe completes rain circuit Change in reflection due to rain water Rainwater energy is converted into displacement of electrochemical switch False rain detection rate Very high Less than 5% Less than 2% Less than 2 % Less than 2% Voltage required 12 ŌĆō 5 V DC 12 ŌĆō 5 V DC 2 ŌĆō 6 V DC 12 ŌĆō 5 V DC 1 ŌĆō 3 V per single cell System response time Not mentioned 500 ms after rain contact On collection of 10 cu.cm Very low 550 ms after rain contact Sensor surface size Very large <= 4 cm x 4 cm >=2.58 cm x2.58 cm Not applicable 1 cm x 1 cm Placement of sensor On the windshield On the windshield Inside the font hood Inside the car cabin Inside the front hood Cost of replacement Quite high Quite high Around Rs 1000 Around Rs 7000 Around Rs 200 (sensor ONLY) Adaptivity Changes the aesthetics of the vehicle Embedded on windshield Volume of rain collected is high Seamless integration with vehicles Adaptable to all vehicles
- 7. Comparison of Conventional Lucas Wiper System and Electrochemical Rain Sensing (ERS) system 28/11/19 Parameters Conventional Lucas Wiper Motor DC Geared Motor with rack-pinion Weight of wiper arm 330 gms 330 gms Length of wiper arm 450 mm 450 mm Crank rod length NA 25 mm Connecting rod length NA 50 mm Diameter of pinion NA 79 mm (Module 1.41,Teeth ŌĆō 56, Pitch - 18) Length of rack NA 100 mm Weight of motor 800 gms 180 gms Stall torque of motor 180 kg-cm 80 kg-cm Stall Current 14 A 7.5 A
- 8. Details of the Electrochemical Rain Sensing Wiper System v Water collected in the container displaces the salt bridge and connects the electrolytes v The base current to the transistor makes it forward biased v Transistors are connected in Darlington pair to amplify the current and run the motor at the desired speed v Rack and pinion with slider-crank mechanism is used to actuate the wiper v The motor needs to be run only in a single direction without reversal v Li-ion batteries connected to a solar panel can act as a power source
- 9. Performance comparison between the two wiper systems Motor Configuration 45 RPM 65 RPM 100 RPM Cost Of System Per Vehicle Tavg N-m Iavg (A) Imax (A) Tavg N-m Iavg (A) Imax (A) Tavg N-m Iavg A Imax (A) Conventional Lucas Wiper motor arrangement 2.44 1.71 2.18 2.44 1.71 3.29 2.44 1.71 6.2 4400/- (MIN) (TVS SINGLE WIPER SYSTEM) DC Geared Wiper motor with Rack- pinion mechanism 2 1.68 2.13 2 1.68 3.2 2 1.68 6 1500/- 1000 (DC GEARED MOTOR) + 200 (RACK AND PINION) + 100 (SLIDER CRANK) + 200 (ERS) % Change in parameter from conventional arrangement -18 -1.75 -2.75 -18 -1.75 -2.75 -18 -1.75 -3.23 66% reduction
- 10. Location of sensors in vehicle A suitable ŌĆ£ERS KIT ŌĆō ELECTROCHEMICAL RAIN SENSING KITŌĆØ will be designed using the following components as shown in the Table 5. Table 5 : ERS Kit Components Components Manufacturing Cost Rain Sensitive Cell 200 Accordion Joint Salt bridge (12 QTY) 70 Rack and Pinion 180 ║▌║▌▀Żr crank 50 DC geared motor 1000 TOTAL 1500
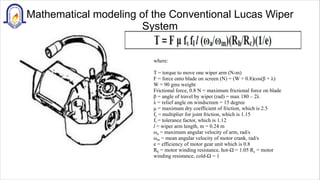
- 11. Mathematical modeling of the Conventional Lucas Wiper System where: T = torque to move one wiper arm (N-m) F = force onto blade on screen (N) = (W + 0.8)cos(╬▓ + ╬╗) W = 90 gms weight Frictional force, 0.8 N = maximum frictional force on blade ╬▓ = angle of travel by wiper (rad) = max 180 ŌĆō 2╬╗ ╬╗ = relief angle on windscreen = 15 degree ╬╝ = maximum dry coefficient of friction, which is 2.5 fs = multiplier for joint friction, which is 1.15 fl = tolerance factor, which is 1.12 l = wiper arm length, m = 0.24 m Žēa = maximum angular velocity of arm, rad/s Žēm = mean angular velocity of motor crank, rad/s e = efficiency of motor gear unit which is 0.8 Rh = motor winding resistance, hot-╬® = 1.05 Rc = motor winding resistance, cold-╬® = 1
- 12. Mathematical modeling of the Electrochemical Rain Sensing (ERS) Wiper System Taking downward direction as positive W + mg = N.................(1) Taking right side positive -Ft + ┬ĄN = -mddot(x)....................(2) Moment about O taking clockwise positive -T - WLcos(╬▓ + ╬╗0)/2 + FtR - ┬ĄNR = Iddot(╬▓) = (WL2/3g)ddot(╬▓).........................(3) Also, for the pinion and rack arrangement, ╬▓ = -x/R dot(╬▓) = + dot(x)/R ddot(╬▓) = -ddot(x)/R Substituting in the equation (3), we get
- 13. Torque requirement and Current drawn by the two wiper motor arrangements
- 14. Salient features of the ERS wiper system v Since, the electrochemical reaction is spontaneous, the actuation by this kind of a cell will result in very less response time. (approx 700 ms ŌĆō 550 ms by rack and pinion + 150 ms by the ERS v The DC geared motor consumes almost 18% less torque than the conventional Lucas motor and runs with very minimal parts. v Also, 80% weight reduction by replacement of Lucas motor with geared DC motor and the easy off the shelf availability of the rack and pinion setup are a lucrative point to choose this alternative. v Compactness of this arrangement as seen in Figure 6 which has a dimension of 36 inches to a reduction of 6 inches which is 1/6th the original size is a great advantage for the auto industry. v The cost reduction estimated with the alternative wiper system is around 66% per vehicle. v Experimental verification of the same is a part of ongoing work. Following enhancements will be done in due course of time which will lead to value addition of the above rain sensing wiper: v Automatic speed control of wiper based on rate of rainfall v Automatic mist and fog removal v Design of parking mechanism for wiper v Design of vibration isolation system for cell and effect of temperature on the performance. v The introduction of this new type of system in current cars needs to also be checked in terms of its effect on the fuel economy especially the effect on reduction in usage of air-conditioning and the gains/losses that it has as compared to an existing rain wiper system.
- 15. Future Open Research Areas 1. Design of a linear variable electrochemical transducer 2. Stabilisation of agar agar gel with plastic 3. Embedment of ERS and other sensors for SHM of civil infrastructure 4. Development of miniaturised rain sensor for Indian conditions Acknowledgements The presenters are grateful to Mina Bairagi for helping in the fabrication of the ERS We thank Ramkumar Maurya for providing us guidance in electronics We thank Husain Jasdanwala and Dr Sujata Rout (ex-HOD Mechanical Department) and our principal Dr Varsha Shah for motivating us in doing the project
- 16. THANK YOU Dr Amol M Khatkhate amolmk@eng.rizvi.edu.in/amol.khatkhate@gmai l.com Look up our other projects from Mechatronics and Robotics Lab at ResearchGate 28/11/19