Money and banking
- 1. BY NITESH RAJ MURARIKAR Money and Banking
- 2. Trading without money ’é¦ Mohan has come with ragi to shyamala to buy mangoes. ’é¦ Shyamala made two equal heaps of the ragi. ’é¦ She gave Mohan a few mangoes that together weighed as much as one of the ragi heaps. ’é¦ This system of exchanging goods directly against other goods without the use of money is called the Barter system.
- 3. Exchange with Money ’é¦ If we use money, for the exchange of goods, there will be no problem in exchanging commodities. ’é¦ Then, a person who has something in excess will not have to necessarily find another person who needs it and has something also to give in return. ’é¦ Money acts as an intermediary ’é¦ One can also borrow and pay back in the form of money.
- 4. Evolution of Money ’é¦ People all over the world practised barter system and also encountered the problems with this system. ’é¦ Over time, people preferred scarce and attractive metals as a medium of exchange. ’é¦ Copper, bronze, silver and gold are durable, can be divided into parts and be carried around. ’é¦ Since they were scarce, they became acceptable by all.
- 5. ’é¦ In the Roman period, ŌĆ£BesantŌĆØ ŌĆō a gold coin, was the standard currency and in the Mauryan period, ŌĆ£PanaŌĆØ a silver coin, was the standard currency. ’é¦ Coins became the acceptable form of money by traders and people.
- 6. Paper Money and Emergence of Banks ’é¦ People who had to buy and sell in large quantities had to carry large amounts of gold or silver coins for their transactions. ’é¦ So, they started looking for safe places to keep them. ’é¦ They went to goldsmiths, where their money would be protected. ’é¦ These goldsmiths would also give loans and had branches in many cities, leading to a new system of paper money or hundis.
- 7. ’é¦ The early bankers in India such as Jagatseths of Bengal, Shahs of Patna, Arunji Nathji of Surat, Chettiars of Madras enjoyed such wealth and reputation their receipts ŌĆō paper money called hundis were accepted throughout the country and outside too. ’é¦ The bank operated honestly and it was trusted by all the traders. ’é¦ They would ask for receipts of the bank or a transfer to their account, instead of the coins. ’é¦ The operation of bank deposits as money had evolved.
- 8. Commercial Banks ’é¦ Banking is a business activity where money deposits are collected from the public, and these deposits can be transferred from one person to another. ’é¦ Banks also give loans to businessmen, industrialists, farmers and individuals. ’é¦ Such banks called Commercial banks.
- 9. Few Banking terms ’é¦ Cash Deposits Deposits refer to the money that people keep in the banks. Types of Cash deposits: 1. Savings Deposits: Geeta has saved Rs. 5000 from her salary and wants to keep is safely. She goes to a branch of SBH which is close to her home and opens a Savings Account. She gets some interest on this money and her money is also safe. Most importantly, she can withdraw this money any time she wants.The bank promises to pay on demand.
- 10. Basic Saving Bank Deposit Account (BSBDA): ŌĆó It can have ŌĆ£zeroŌĆØ or very low minimum balance. ŌĆó There are no restrictions like age, income, amount etc. criteria for opening for individuals. ŌĆó Maximum of four withdrawals in a month is allowed including ATM withdrawals. ŌĆó The services available include deposit and withdrawal of cash; receipt/credit of money through electronic payment channels or cheques. ŌĆó PMJDY: PM JAN DHANYOJANA ŌĆó Under the scheme the Govt is giving rupay debit card along with Rs: 1 Lakh accident insurance coverage and overdrafting facility.
- 11. Small Account ’é¦ If ŌĆśBasic Savings Bank Deposit AccountŌĆÖ is opened on the basis of simplified KYC norms, the account would additionally be treated as a ŌĆśSmall AccountŌĆÖ and would be subject to conditions stipulated for such accounts. ’é¦ Total=not exceed one lakh rupees in a year. ’é¦ Maximum balance=not exceed 50,000. ’é¦ Cash withdrawals and transfers will not exceed 10,000 in a month. ’é¦ Small accounts are valid of a period of 12 months and can extend for another 12 months if valid Documents provided Officially.
- 12. Current Account Deposits ’é¦ Many businessmen, shopkeepers companies and traders have a larger number of daily transactions, earnings and payments. ’é¦ They have to withdraw money multiple times to buy goods, pay labourers etc., ’é¦ Similarly, large business offices get money from customers who purchase their goods and services every day and they pay to those who have supplied them various things or done some work for them daily. ’é¦ For many requirements of these kind, banks have a separate type of account called Current Account.
- 13. Fixed Deposit ’é¦ ManaswiniŌĆÖs grandfather wanted to give her a gift. So he gave her a Fixed Deposit certificate for Rs. 10,000. ŌĆ£It will grow enough in the next five years to pay for your college admission,ŌĆØ grandfather said. How can it grow? ’é¦ The money in a Fixed Deposit or aTerm Deposit cannot be withdrawn from the bank for a fixed period of time. ’é¦ It could be one year, two, five or seven years. ’é¦ The rate of interest is higher on a fixed deposit.
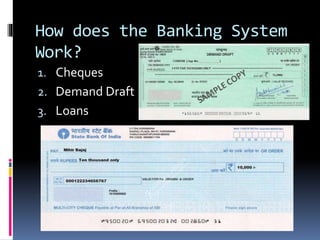
- 14. How does the Banking System Work? 1. Cheques 2. Demand Draft 3. Loans
- 15. Types of Loans ’é¦ Banks give loans to people. People will pay these loans back with interest. ’é¦ Banks also give loans to the government and earn some interest. ’é¦ The interest earned on loans given by the bank is the source of revenue.
- 16. Internet Banking ’é¦ Now a days, computers and internet are used everywhere. ’é¦ In most banks, human and manual teller counters are being replaced by the Automated Teller Maching(ATM). ’é¦ Banking activity is being done with computers, internet and other electronic means of communication which is known as electronic banking or internet banking. ’é¦ Internet banking helps buying and selling goods, investments, repaying loans, payments of electricity, phone and other utility bills.