Money Matters Class 1: Introduction
- 1. MONEY MATTERS Class 1 Presented by Susan Huff MONEY MATTERS Coordinator
- 2. MONEY MATTERS ’é¦ Series of 6 classes ’é¦ One hour per class ’é¦ Opportunity to earn scholarship money ’é¦ Rate your Financial Behavior ’é¦ Before / After Class
- 3. Benefits of GED ’é¦ Increase earning power ’é¦ More job opportunities ’é¦ Jobs with better benefits ’é¦ Ability to seek additional education ’é¦ Financial Security ’é¦ Other
- 4. Bankruptcy ’é¦ 1.4 million people in 2008 ’é¦ Average age 38 ’é¦ 44% couples ’é¦ 30% women ’é¦ 26% men ’é¦ Every class, race, education, income level
- 5. Reasons ’é¦ 2 of 3 lost job ’é¦ 50% experience serious health problem ’é¦ DEBT ’é¦ Owed more than 1 ┬Į times annual income ’é¦ $24,000 income ŌåÆ $36,000 debt
- 6. States with highest rates ’é¦ Nevada ’é¦ GEORGIA ’é¦ Utah ’é¦ Tennessee
- 7. Financial Literacy ’é¦ Skill for life ’é¦ 68.1% high school seniors failed a basic financial quiz ’é¦ only 10% scored a C or better
- 8. The 1 st Step Understanding: 1. how much money you have 2. where it goes
- 9. What is Income? ’é¦ Income is the flow of cash or cash-equivalents received from work (wage or salary), capital (interest or profit), land (rent), or other sources (gift)
- 10. Monthly Gross Income ’é¦ List each personŌĆÖs fixed income ’é¦ Salary and wages ’é¦ Child support ’é¦ Alimony ’é¦ Social security ’é¦ List variable income ’é¦ Bonus checks ’é¦ income tax refunds ’é¦ tips ’é¦ Add
- 11. RULES: to calculate monthly income ’é¦ Weekly Income ’é¦ Multiply by 4.3 for monthly income ’é¦ Biweekly Income ’é¦ Multiply by 2.2 for monthly income ’é¦ Twice a Month Income ’é¦ Multiply by 2 for monthly income
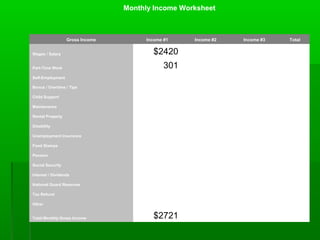
- 12. Monthly Income Worksheet Gross Income Income #1 Income #2 Income #3 Total Wages / Salary Part-Time Work Self-Employment Bonus / Overtime / Tips Child Support Maintenance Rental Property Disability Unemployment Insurance Food Stamps Pension Social Security Interest / Dividends National Guard Reserves Tax Refund Other Total Monthly Gross Income
- 13. Income #1 - Joe $1,100 every two weeks Monthly $1,100 X 2.2 = $2420 Part-time $70 per week Monthly $ 70 X 4.3 = $301 Total Income for Joe $2420 + $301 = 2721
- 14. Monthly Income Worksheet Gross Income Income #1 Income #2 Income #3 Total Wages / Salary $2420 Part-Time Work 301 Self-Employment Bonus / Overtime / Tips Child Support Maintenance Rental Property Disability Unemployment Insurance Food Stamps Pension Social Security Interest / Dividends National Guard Reserves Tax Refund Other Total Monthly Gross Income $2721
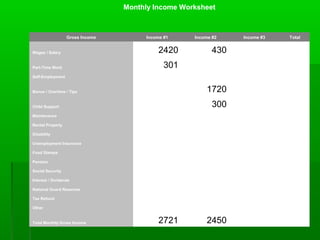
- 15. Income #2 - Maria ’é¦ $ 2.50 per hour plus tips $2.50 X 40 = $100 per week Monthly $100 X 4.3 = $430 ’é¦ Tips average $10 per hour worked or $10 x 40 hours = $400 per week Monthly $400 x 4.3 = $1,720
- 16. Income #2 - Maria ’é¦ Child Support for teenage son $300 per month ’é¦ Total Income ’é¦ $430 + $ 1720 + 300 = $2450
- 17. Monthly Income Worksheet Gross Income Income #1 Income #2 Income #3 Total Wages / Salary 2420 430 Part-Time Work 301 Self-Employment Bonus / Overtime / Tips 1720 Child Support 300 Maintenance Rental Property Disability Unemployment Insurance Food Stamps Pension Social Security Interest / Dividends National Guard Reserves Tax Refund Other Total Monthly Gross Income 2721 2450
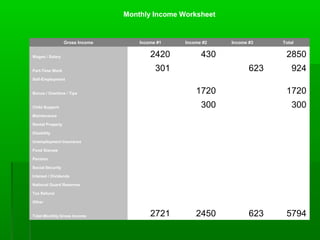
- 18. Income # 3 - Matt ’é¦ Works 20 hours per week at $7.25 $7.25 X 20 = $145 Monthly $145 X 4.3 = 623.50
- 19. Monthly Income Worksheet Gross Income Income #1 Income #2 Income #3 Total Wages / Salary 2420 430 2850 Part-Time Work 301 623 924 Self-Employment Bonus / Overtime / Tips 1720 1720 Child Support 300 300 Maintenance Rental Property Disability Unemployment Insurance Food Stamps Pension Social Security Interest / Dividends National Guard Reserves Tax Refund Other Total Monthly Gross Income 2721 2450 623 5794
- 20. Determine Your Deductions ’é¦ Money taken from your paycheck to cover things like taxes and health insurance ’é¦ Required Deductions ’é¦ Federal Tax ’é¦ State Tax ’é¦ FICA ŌĆō social security tax (6.2%) ’é¦ Medicare (1.45%)
- 21. Determine Your Deductions ’é¦ Voluntary Deductions: ’é¦ Health Insurance ’é¦ Life Insurance ’é¦ Retirement ŌĆō 401 K ’é¦ FSA ŌĆō Flexible Spending Account ’é¦ Others
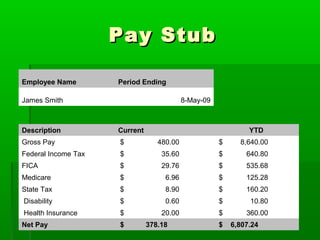
- 22. Pay Stub Employee Name Period Ending James Smith 8-May-09 Description Current YTD Gross Pay $ 480.00 $ 8,640.00 Federal Income Tax $ 35.60 $ 640.80 FICA $ 29.76 $ 535.68 Medicare $ 6.96 $ 125.28 State Tax $ 8.90 $ 160.20 Disability $ 0.60 $ 10.80 Health Insurance $ 20.00 $ 360.00 Net Pay $ 378.18 $ 6,807.24
- 23. Calculate Your Net Income Take home pay, the money you have left after deductions are made Monthly Net Income Income #1 Income #2 Income #3 Total Total Monthly Gross Income (-) Total Monthly Deductions (=) Monthly Net Income
- 24. BUDGET ’é¦ A budget is simply a plan showing how you plan to spend your money to meet you financial goals. ’é¦ What do I need to prepare a budget? ’é¦ List of income ’é¦ List of expenses, including debt payments
- 25. Financial Problems and Work ’é¦ Pre-employment screening ’é¦ Call from Creditors ’é¦ Wage Garnishment
- 26. Put Yourself In Charge ’é¦ Have a plan for your money and stick to it ’é¦ Prepare a budget for yourself and keep it up to date ’é¦ Establish a savings habit ŌĆō save as much as you can and do it regularly!!
Editor's Notes
- #4: Increase earning power ŌĆō GED graduates makes $12,000 more a year on average than those without a high school diploma, this amount is often greater for women. More job opportunities ŌĆō The GED shows employers that you have important life skills Jobs with better benefits ŌĆō many minimum wages jobs do not offer employee benefits such as medical and dental insurance, retirement plans, vacations, etc. In addition, some employers require a diploma to be eligible for benefits. Ability to seek additional education - The GED is accepted by 97% of colleges and universities Financial security
- #5: We all know that making and having more money is a good thing, however more money is only useful when we know how to manage it. In 2008, 1.4 million people filed for bankruptcy. Bankruptcies come from every class, race, education and income level. they tended to be slightly better educated than the general population
- #6: JOB LOSS ŌĆō If you are living paycheck to paycheck, as many Americans are and have no savings for emergencies a job loss can quickly devastate you. Another reason for bankruptcies are serious health problems. If you have a serious health problem and have no health insurance or disability and are out of work for a time it doesnŌĆÖt take long to cause financial problems. This is why a job with benefits is important. Lastly, DEBT. Those filing for bankruptcy on average owed more than 1 ┬Į time their annual income.
- #7: In a recent survey, 7 out of 10 people said they felt very stressed about money. As the economy weakens, that number is going up. Financial stress like all stress can cause health problems like depression and sleep problems. To reduce stress and move toward a more secure future, we will learn the secrets to being good with money. There are a few basic habits that can really make a difference. We will talk about how to make your money work for you. How to avoid mistakes that can cost you money. What to do if you lose your job, how to save more and get out of debt. You will learn information that you can use to be more financially secure regardless of how much you make.
- #8: Financial literacy is a skill for life. In a 2012 Consumer Financial Literacy Survey, 42% of Americans gave themselves a grade of C or worse when it comes knowledge of personal finance. Only 43% of Americans have a budget. Spending has increased for the second year in a row and yet 39% of Americans have $0 savings. No matter what your age or income, understanding money can help you and your family meet your goals and get the most out of life. Taking a few simple steps to manage your money better can make a real difference to the control you have over your life and the choices available to you.
- #9: The First Step Understanding how much money you have and where it goes. Most of us have a good idea of how much money comes in, but are less aware of how our money is spent. We just know that at the end of the month or week the money is gone and we donŌĆÖt have much to show for it.
- #11: Figure your Monthly Gross Income ( what you make before taxes and other expenses are taken out ) List each household memberŌĆÖs ŌĆ£regularŌĆØ earned income. Include full, part-time and self-employment income as well as tips and overtime. Be sure to list income before deductions are taken. List ŌĆ£otherŌĆØ monthly income that comes from sources other than employment, such as child support, alimony, social security, disability, etc. List ŌĆ£sporadicŌĆØ income from bonus checks, income-tax refunds, etc. *list only if you are sure that you will receive these items. CAUTION: Calculate variable income conservatively