MongoDB - Getting Started
- 1. AHMED HELMY (@HELMY204) SOFTWARE ENGINEER | CSD | CSM AHMEDHELMY204@HOTMAIL.COM mongoDB Getting Started
- 2. Agenda • Intro • Power of RDBMS • Problems with RDBMS • Solutions from NoSQL • MongoDB Document Model • Demo | MongoDB basic CRUD Operations
- 3. Power of RDBMS • Default choice for serious data storage • Specific Vendor • Concurrency (ACID) • Almost Standard • Model • Query Language
- 4. Share your thoughts Are there problems with RDBMS!
- 5. Big Data • Websites tracking activities in a very detailed way • Links, social networks, activity logs, etc… • Require more computing resources • Scaling up • Scaling out (Clusters)
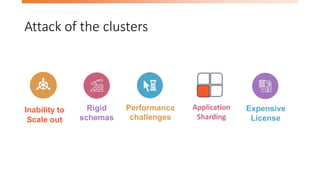
- 6. Attack of the clusters Rigid schemas Inability to Scale out Performance challenges •Expensive License Application Sharding
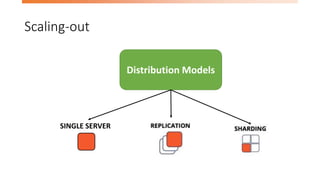
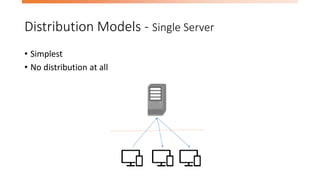
- 8. Distribution Models - Single Server • Simplest • No distribution at all
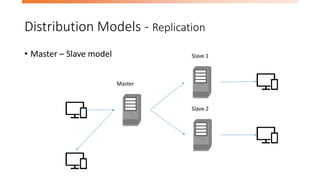
- 9. Distribution Models - Replication • Master – Slave model Master Slave 1 Slave 2
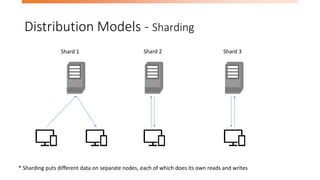
- 10. Distribution Models - Sharding Shard 1 Shard 2 Shard 3 * Sharding puts different data on separate nodes, each of which does its own reads and writes
- 11. Impedance Mismatch • Relational Model • Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations • We are developers • OOP, Polymorphism, Inheritance • Objects are not uniform • Work around • Mapping layer, ORMs Id Name 1 Comp A 2 Comp B Id Name 02 Cairo 03 Alexandria CompanyId CityId 1 02 2 03 1 03 // application code class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; }
- 12. Solution is NoSQL Google and Amazon • Scale out (distributed ,clusters) • BigTable, DynamoDB
- 13. What is NoSQL • No Relational Model • No SQL (some use others i.e. CQL) • Schemaless • BASE (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) instead of ACID • Distributed (Run on Clusters) • Open-source • Classified into four types • Key-Value pair (Redis) • Document (MongoDB) • Column Family (Cassandra) • Graph (neo4j)
- 14. Impedance Mismatch - Solution • No Relational Model • Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations // application code class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; } // mongo document for Company { id: 1, name: “Comp A”, cities: [ “Cairo”, ”Alexandria” ] }
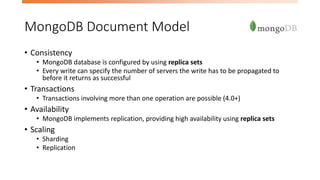
- 15. MongoDB Document Model • Consistency • MongoDB database is configured by using replica sets • Every write can specify the number of servers the write has to be propagated to before it returns as successful • Transactions • Transactions involving more than one operation are possible (4.0+) • Availability • MongoDB implements replication, providing high availability using replica sets • Scaling • Sharding • Replication
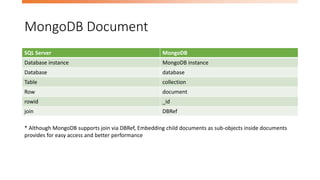
- 16. MongoDB Document SQL Server MongoDB Database instance MongoDB instance Database database Table collection Row document rowid _id join DBRef * Although MongoDB supports join via DBRef, Embedding child documents as sub-objects inside documents provides for easy access and better performance
- 17. Use cases • Event Logging • CMS, Blogs • Web analytics • E-commerce
- 18. Using compass for CRUD operations Demo
- 19. Questions
- 20. Summary • RDBMS pros and cons • Solutions from NoSQL • MongoDB Document Model • Demo
- 21. References • NoSQL Distilled • https://martinfowler.com/books/nosql.html • Understanding NoSQL • https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/understanding-nosql
- 22. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- #6: Attack of the clusters Big data Websites tracking activities in a very detailed way Links, social networks, activity logs, etc… Require more computing resources Scaling up Scaling out (Clusters) Relational databases are not designed to be run on clusters Relational sharding has to be controlled by the application Relational on clusters has high license prices
- #7: Attack of the clusters Big data Websites tracking activities in a very detailed way Links, social networks, activity logs, etc… Require more computing resources Scaling up Scaling out (Clusters) Relational databases are not designed to be run on clusters Relational sharding has to be controlled by the application Relational on clusters has high license prices
- #10: One node is the master or primary Master used to update data Slave nodes used for scaling read requests horizontally If Master fails, the slaves can still handle read request Slave can act as a hot backup
- #11: Horizontal Scalability Putting different parts of the data onto different servers Each node does its own reads and writes Improve performance Can place the data close to where it’s being accessed Many NoSQL databases offers auto-sharding
- #14: NoSQL databases known by it’s characteristics Not using Relational Model Not using SQL (some use others i.e. CQL) Schemaless BASE (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) instead of ACID Distributed (Run on Clusters) Open-source Classified into four types Key-Value pair Document Column Family Graph
- #15: NoSQL databases known by it’s characteristics Not using Relational Model Not using SQL (some use others i.e. CQL) Schemaless BASE (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) instead of ACID Distributed (Run on Clusters) Open-source Classified into four types Key-Value pair Document Column Family Graph
- #16: Consistency MongoDB database is configured by using replica sets Every write can specify the number of servers the write has to be propagated to before it returns as successful You can increase the w value for stronger consistency but will suffer on write performance Transactions Transactions involving more than one operation are possible (4.0+) Availability MongoDB implements replication, providing high availability using replica sets Scaling Sharding Replication






![Impedance Mismatch
• Relational Model
• Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations
• We are developers
• OOP, Polymorphism, Inheritance
• Objects are not uniform
• Work around
• Mapping layer, ORMs
Id Name
1 Comp A
2 Comp B
Id Name
02 Cairo
03 Alexandria
CompanyId CityId
1 02
2 03
1 03
// application code
class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-gettingstarted-200406132530/85/MongoDB-Getting-Started-11-320.jpg)


![Impedance Mismatch - Solution
• No Relational Model
• Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations
// application code
class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; }
// mongo document for Company
{
id: 1,
name: “Comp A”,
cities: [ “Cairo”, ”Alexandria” ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-gettingstarted-200406132530/85/MongoDB-Getting-Started-14-320.jpg)