Monte Carlo Simulation lecture.pdf
- 1. ŌĆó Monte Carlo simulation is a computerized mathematical technique to generate random sample data based on some known distribution for numerical experiments. ŌĆó The Law of large numbers ensures that the relative frequency of occurrence of a possible result of a random variable converges to the theoretical or expected outcome as the number of experiments increases. ŌĆó The essence of Monte Carlo simulation is to sample random variables significant number of times so that the relative frequency converges to the theoretical probability with greatest reliability. MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
- 2. ŌĆó Step 1: Identify the factors and formulate a model ŌĆó Step 2: carry out a preliminary sensitivity analysis to establish the factors (variables) for which probability distribution should be assessed. ( random variables). ŌĆó Step 3: Establish the shape of the probability distribution for each random variables. MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
- 3. ŌĆó Step 4: sampling of random variables (random variables sample generation). Use random numbers from a standard uniform distribuition on the interval [0,1]. Each number in the range [0,1] is given an equal chance of being generated at any one time. These numbers are used as inputs in the cumulative distribution functions in order to obtain the values of the random variables. The logic for the procedure is that the cumulative distribution, F (x), has value between 0 and 1, that is, it is in the same range as a random number. Therefore, the formula converts the values of the random numbers into quantities of the variables ŌĆó Step 5: description of output variables ŌĆó Step 6 : Performing statistical analysis on output results MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
- 4. An important step of Monte Carlo Simulation is to determine de probability distribution for the random variables. There are two ways of categorizing distributions: by whether it is discrete or continuous, and by whether it is a probability density function (PDF) or a cumulative distribution function(CDF). The probability density function specifies the probability that the random variable will take on a specific value. The cumulative distribution function gives the probability that the random variable is less than or equal to a specific value. The CDF plays an important role in Monte Carlo Simulation. The probability distribution might be determined by: ŌĆó time series data; ŌĆó estimates from experts; ŌĆó Previous knowledge MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
- 5. Common Probability distributions in Monte Carlo Simulation Uniform distribution Triangular distribution Normal distribution Lognormal distribution Beta distribution MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
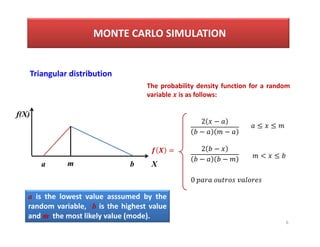
- 6. MONTE CARLO SIMULATION 6 Triangular distribution a m b a is the lowest value asssumed by the random variable, b is the highest value and m the most likely value (mode). f(X) X The probability density function for a random variable is as follows: = 2 ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ 2 ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ Ōēż Ōēż < Ōēż 0
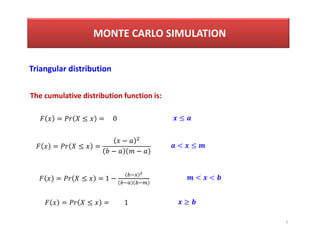
- 7. 7 Triangular distribution The cumulative distribution function is: = Ōēż = ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ = Ōēż = 1 ŌłÆ < Ōēż < < MONTE CARLO SIMULATION = Ōēż = 0 Ōēż = Ōēż = 1 Ōēź
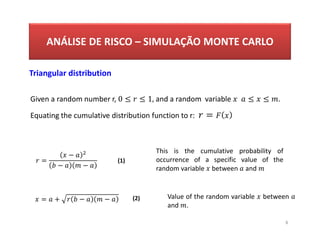
- 8. AN├üLISE DE RISCO ŌĆō SIMULA├ć├āO MONTE CARLO 8 Triangular distribution Given a random number r, 0 Ōēż Ōēż 1, and a random variable Ōēż Ōēż . Equating the cumulative distribution function to r: = = ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ = + ŌłÆ ŌłÆ This is the cumulative probability of occurrence of a specific value of the random variable between and Value of the random variable between and . (1) (2)
- 9. 9 Triangular Distribution Given a random number r [0,1] and a random variable < Ōēż . Assuming = : = 1 ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ = ŌłÆ 1 ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ This is the cumulative probability of occurrence of a specific value of the random variable between and b Value of the random variable between and b. (3) 4) MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
- 10. 10 To establish a routine to generate the random variable, equating = and calculating ŌłŚ through the equation 1: Triangular distribution ŌłŚ = ŌłÆ ŌłÆ Then, create random numbers r 0 Ōēż Ōēż 1 and calculate as follows: ’é¦ if < ŌłŚ, calculate using equation 2 ’é¦ if > ŌłŚ , calculate using equation 4 ’é¦ if = ŌłŚ , ent├Żo = MONTE CARLO SIMULATION
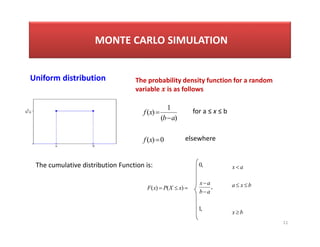
- 11. 11 Uniform distribution MONTE CARLO SIMULATION 0 ) ( ) ( 1 ) ( ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ x f a b x f for a Ōēż x Ōēż b elsewhere The cumulative distribution Function is: ’ĆĮ ’éŻ ’ĆĮ ) ( ) ( x X P x F , 1 , , 0 a b a x ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ b x b x a a x ’é│ ’éŻ ’éŻ ’Ć╝ The probability density function for a random variable is as follows
- 12. 12 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION Example 1 (Goodwin and Wright, 2009) Cash inflows ($) Probability (%) CDF Cash outflows ($) Probability (%) CDF 50000 30 30 50000 45 45 60000 40 70 70000 55 100 70000 30 100 Cash inflows ($) CDF Random number Cash outflows ($) CDF Random number 50000 30 00-29 50000 45 00-44 60000 70 30-69 70000 100 45-99 70000 100 70-99
- 13. 13 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION Example 1 Net cash flow($) Calculated probability Simulated Probability 1570 -20000 0.165 0.166 -10000 0.220 0.206 0 0.300 0.300 10000 0.180 0.193 20000 0.135 0.135
- 14. 14 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION Example 2: The Elite Pottery Company (Goodwin and Wright, 2009) The Elite Pottery Company is planing to market a special product (commemorative plate) to comemorate a major sporting event that is due to take place in a few monthŌĆÖs time. The company needs to estimate the profit that would be earned by the plate. There is some uncertainty about the costs of manufacturing the product and the level of sales. The company is willing to use Monte Carlo Simulation to assess the risk involved in the project. Stage 1: Identify the factors we think will affect the profit. costs and level of sales can be treated as random variables Stage 2: Formulate the model Profit = (price ŌĆō variable cost) x sales ŌĆō fixed costs
- 15. 15 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION Example 2: The Elite Pottery Company Stage 3: Assess probability distribution Estimates of values of the Elite Pottery Problem Random variables Most Likely value Lowest possible value Highest possible value Variable Costs ($) 13 8 18 Sales (units) 22000 10000 30000 Fixed Costs ($) 175000 100000 300000 Stage 4: Perform the simulation Monte Carlo Simulation examples.xlsx The price of the plate will be fixed at $ 25 per unit.
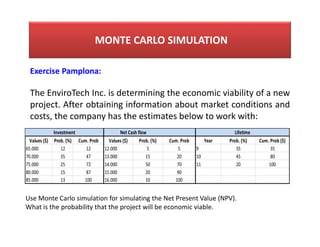
- 16. MONTE CARLO SIMULATION Exercise Pamplona: The EnviroTech Inc. is determining the economic viability of a new project. After obtaining information about market conditions and costs, the company has the estimates below to work with: Values ($) Prob. (%) Cum. Prob Values ($) Prob. (%) Cum. Prob Year Prob. (%) Cum. Prob ($) 65.000 12 12 12.000 5 5 9 35 35 70.000 35 47 13.000 15 20 10 45 80 75.000 25 72 14.000 50 70 11 20 100 80.000 15 87 15.000 20 90 85.000 13 100 16.000 10 100 Investment Net Cash flow Lifetime Use Monte Carlo simulation for simulating the Net Present Value (NPV). What is the probability that the project will be economic viable.


![ŌĆó Step 4: sampling of random variables (random variables sample
generation). Use random numbers from a standard uniform
distribuition on the interval [0,1]. Each number in the range [0,1] is
given an equal chance of being generated at any one time. These
numbers are used as inputs in the cumulative distribution functions in
order to obtain the values of the random variables. The logic for the
procedure is that the cumulative distribution, F (x), has value between
0 and 1, that is, it is in the same range as a random number. Therefore,
the formula converts the values of the random numbers into
quantities of the variables
ŌĆó Step 5: description of output variables
ŌĆó Step 6 : Performing statistical analysis on output results
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/montecarlosimulationlecture-220724204742-9dcac495/85/Monte-Carlo-Simulation-lecture-pdf-3-320.jpg)


![9
Triangular Distribution
Given a random number r [0,1] and a random variable < Ōēż .
Assuming = :
= 1 ŌłÆ
ŌłÆ
ŌłÆ ŌłÆ
= ŌłÆ 1 ŌłÆ ŌłÆ ŌłÆ
This is the cumulative probability of
occurrence of a specific value of the
random variable between and b
Value of the random variable
between and b.
(3)
4)
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/montecarlosimulationlecture-220724204742-9dcac495/85/Monte-Carlo-Simulation-lecture-pdf-9-320.jpg)