Morale and motivation
Download as pptx, pdf20 likes11,096 views
This document discusses morale and motivation in the workplace. It defines morale as the mental attitude and satisfaction that determines an individual's willingness to work. High morale is characterized by enthusiasm, satisfaction, team spirit and pride. Motivation refers to factors that encourage employees to achieve goals and objectives. It discusses theories of motivation from McGregor, Maslow, Herzberg, Adams and Locke. The document also covers factors that influence morale like management practices, and signs of low employee morale such as absenteeism and turnover.
1 of 20
Downloaded 228 times















Ad
Recommended
Chapter 11 morale and motivation
Chapter 11 morale and motivationInternational Islamic University Chittagong, Batch 28 A9
╠²
This document discusses various tips and strategies for boosting employee morale and motivation in the workplace. It outlines approaches like supervisors greeting employees, writing personal notes, inviting part-time staff to social events, and allowing flexible work hours. The document also summarizes several major motivation theories including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McClelland's motivational drives of achievement, affiliation, competence and power.-Morale.ppt
-Morale.pptNishabagad
╠²
The document discusses employee morale in an organization. It defines morale as the enthusiasm and confidence of individuals or groups to complete tasks. High morale is important because it leads to greater productivity, teamwork, and employee commitment. Morale can be measured through surveys and analyses of factors like absenteeism and turnover. Signs of low morale include unrest, absenteeism, and grievances. Management can improve morale by enriching jobs, modifying the work environment, offering profit-sharing, and recognizing employee achievements.Organisational Morale
Organisational MoraleVaishu Raji
╠²
This document discusses employee morale, including its definition, factors that influence it, symptoms of low and high morale, and ways to boost it. Morale is defined as the capacity of a group to work consistently towards a common purpose and resides in people's minds and emotions. Key factors that influence morale include job security, satisfaction, culture, management style, and perceptions of work and rewards. Symptoms of low morale include tardiness, absenteeism, and poor relationships, while high morale is indicated by feelings of belongingness, team spirit, and commitment. To boost morale, managers should motivate employees through communication, job enrichment, recognition, consultation, and empowerment while creating a healthy work environment. Morale is also related to productivityMotivation & Productivity in the Workplace
Motivation & Productivity in the WorkplaceSunny Mervyne Baa
╠²
Motivation in the workplace can come from intrinsic or extrinsic factors. Intrinsically, employees seek autonomy, responsibility, and to have their higher order needs for esteem and self-actualization fulfilled through their work. Extrinsically, employees can be motivated by incentives and rewards, though natural theories of motivation argue humans are not solely driven by economic factors. Effective managers understand both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and strive to create an environment where employees feel autonomous and can achieve their highest potential.Chapter 14: Stress and Counseling
Chapter 14: Stress and CounselingNaj Umpa
╠²
The document discusses the concept of stress within organizations, identifying various organizational, job-related, and external factors that contribute to employee stress. Symptoms of stress include absenteeism, performance deterioration, and health issues, which can arise from factors like ineffective communication and excessive control. Employee counseling is highlighted as a method to address stress, involving a collaborative approach between supervisors and employees to identify and solve performance-related problems.Importance of Motivation
Importance of MotivationPrantika Ghosh
╠²
This document discusses the importance of motivation and identifies four key factors that motivate employees: the reward system, leadership style, organizational climate, and the nature of the work. It explains that employees are motivated by incentives and rewards that allow them to acquire things. Leadership style and organizational climate also impact motivation by influencing how employees feel about the company and their bonds with coworkers. Matching job roles to employees' interests can make work more motivating.Hrm discipline
Hrm disciplinePratik Agarwal
╠²
The document discusses the concept of discipline within organizations, highlighting meanings, types, and approaches, emphasizing the distinction between self-controlled and enforced discipline. It outlines the causes and symptoms of indiscipline, principles for maintaining discipline, differences between constructive and destructive discipline, and the roles of personnel management. Additionally, it covers disciplinary procedures, types of problem employees, and a research study exploring classroom management challenges and solutions.Leadership and Motivation
Leadership and MotivationISAAC Jayant
╠²
The document discusses the concept of leadership, explaining its role in influencing group behavior and achieving organizational goals through various styles and theories. It details different leadership styles, including autocratic, participative, and free-rein, as well as motivation theories, particularly Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory. Key aspects include the importance of understanding individual needs and how they impact work behavior to enhance organizational performance.Organizing in management
Organizing in managementAMALDASKH
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of organizing and organization. It defines organizing as identifying and grouping work to be performed, delegating responsibility and authority, and establishing relationships to enable efficient work. An organization differentiates tasks among specialized units and integrates their work. Key aspects of an organization include a group working toward common objectives, division of labor, cooperative efforts, communication, central authority, rules, and a dynamic element. A sound organizational structure facilitates administration, encourages growth and innovation, ensures optimal resource use, and continuity of the enterprise. The organizing process involves identifying activities, grouping them, assigning duties, and delegating appropriate authority.7. motivation, theories of motivation
7. motivation, theories of motivationDr. Parveen Kaur Nagpal
╠²
The document discusses motivation as a critical factor influencing behavior at work, distinguishing between intrinsic and extrinsic motivations. It reviews various motivation theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's dual-factor theory, and McGregor's theory X and theory Y, highlighting how different managerial styles can impact employee motivation. Additionally, it presents the carrot and stick approach as a method for motivating employees through rewards and consequences.Management by objectives
Management by objectivesshangrillajagtap18
╠²
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a process where employees and supervisors jointly set goals, employees define their own goals and plans, and performance is evaluated based on achieving objectives. MBO aims to improve management by clarifying responsibilities, setting individual and organizational goals aligned with the overall strategy, and providing feedback. Key aspects of MBO include participative goal setting, explicit time periods for goals, and linking performance reviews to achieving objectives.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsDivya Prabhu
╠²
Group dynamics is the study of groups and group processes. Key aspects of group dynamics include:
- Groups form through regular interaction over time where members see themselves as a distinct entity working towards common goals.
- Group processes involve understanding how groups function to solve problems or make decisions. An expert can help groups improve their functioning.
- Cohesiveness occurs when members strongly agree on common values, beliefs, and objectives and how to achieve group aims.
- Groups progress through forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning stages as defined by Tuckman's model of group development.
- Important group processes include roles and expectations, norms, conformity, and status within the groupOrganization development
Organization developmentKrishna Kanth
╠²
This document provides an overview of organizational development and interventions. It defines organizational development as a deliberately planned effort to increase an organization's relevance and viability. The key aspects covered include:
- The meaning, definitions, objectives, assumptions, values and process of organizational development.
- Common organizational development interventions like team building, coaching, large group interventions and leadership development.
- The assumptions underlying organizational interventions, which include viewing groups as the basic building blocks and aiming to reduce inappropriate competition between parts of an organization.
- The effectiveness of organizational development in providing opportunities for employees and organizations to reach their full potential and treating people with dignity and respect.Morale
MoraleCurtin University, Perth, Australia
╠²
The document discusses employee morale, defined as the willingness to work, and its crucial impact on productivity and organizational success. It highlights various determinants of morale, including individual confidence in leadership and organizational efficiency, as well as administrative measures to enhance morale. Additionally, it outlines methods for measuring morale indirectly and addresses specific causes of low morale among industrial workers in Bangladesh.Human relation theory_l5
Human relation theory_l5Jack Ong
╠²
This document provides an overview of human relations theory in organizational analysis. Some key points:
- Human relations theory emerged in the 1930s as an alternative to classical management theories that treated workers as cogs in a machine. It focused on social and emotional aspects of work.
- Theories discussed include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, findings from the Hawthorne studies that social factors impact productivity, McGregor's Theory X and Y about management assumptions of workers, and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory distinguishing job factors and environmental factors.
- Human relations theory sought to increase efficiency and productivity by addressing issues like specialization, hierarchies, and dehumanization through practices like counseling, incentives, andEMPLOYEE DISCIPLINE
EMPLOYEE DISCIPLINEJithin Omanakuttan
╠²
The document discusses employee discipline within human resource management, emphasizing the need for corrective action when performance is unsatisfactory and outlining the concept of discipline as a means of promoting self-control and adherence to organizational rules. It addresses components of discipline such as self-discipline, orderly behavior, and punishment, while differentiating between positive and punitive approaches to discipline. Effective workplace discipline is crucial for curbing problem behaviors, improving performance, and fostering a productive organizational environment.Mbo ppt
Mbo pptReshma Susan
╠²
MBO (Management by Objectives) is a process introduced by Peter Drucker in 1954 where managers and subordinates jointly define goals, responsibilities, and measures for evaluating performance. The key aspects of MBO include participative goal setting, regular performance reviews, and rewarding employees based on goal achievement. MBO aims to align individual and organizational objectives to improve communication, motivation, and results. The process involves defining organizational goals, setting objectives for employees, monitoring performance, providing feedback, and conducting performance appraisals on a recurring basis.Human Resource Management
Human Resource ManagementRahul Mahida
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), including its definition, objectives, scope, functions, and importance across various types of organizations. It discusses the managerial and operative functions, recruitment processes, selection techniques, and placement strategies that are essential for achieving organizational goals effectively. Furthermore, it addresses the significance of maintaining ethical relationships between management and employees, as well as the necessity of treating human resources as valuable assets within any organization.Organisational Climate
Organisational ClimateShilpi Panchal
╠²
The document discusses organizational climate, defining it as the interpretation of the work environment by employees and identifying factors that influence it such as supervisor support and employee involvement. It outlines how HR practices affect this climate through areas like employee relations, performance management, and corporate branding. The document also presents theories of organizational climate, key success factors for organizations, and provides suggestions for improvement.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsJyothi Chinnasamy
╠²
The document defines groups and group dynamics, discussing types of groups, roles within groups, stages of group development, and processes like communication, problem solving, and leadership. It notes that a group requires a minimum of two people, common goals, interdependence, and self-identification as members. Group dynamics examines how groups form and develop over multiple stages, focusing on elements like roles, communication, decision-making, influence, and relationships between task completion and social bonds.Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic Leadershipnabaz4u
╠²
This document discusses autocratic leadership. It defines autocratic leadership as a leadership style where power is centralized in one individual who makes all decisions without input from group members. The document outlines some key characteristics of autocratic leadership, such as leaders having full control over decision-making and not entertaining suggestions. It also notes some potential negative effects, like low employee morale and high turnover. However, the document acknowledges that autocratic leadership can allow for fast decision-making and may be useful in dangerous situations where strict rules are needed. In conclusion, it states that autocratic leadership is best for short-term stability but can negatively impact organizations over the long run.STAFFING
STAFFINGabhinandnandakumar
╠²
The document outlines the staffing process, emphasizing the importance of acquiring, developing, and maintaining human resources effectively. It details the steps involved in staffing, including manpower planning, recruitment, selection, orientation, training, compensation, and performance evaluation. Additionally, it highlights the significance of matching the right individuals to jobs to enhance organizational productivity and employee satisfaction.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsRohit Kumar
╠²
Group dynamics refers to the attitudinal and behavioral characteristics of a group. A group is defined as two or more individuals interacting and interdependent, who have come together to achieve particular objectives. Groups form through various stages of development including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. There are both formal and informal groups. Formal groups are designated work groups within an organization while informal groups form in response to social needs. When making decisions as a group, individuals may shift their positions towards a more extreme risk level than their original individual decision due to factors like diffused responsibility and social status within the group.Organizational Behavior : Learning
Organizational Behavior : Learning Shruti Pendharkar
╠²
This document discusses various theories of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive processes, and social learning. It provides examples of Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments with dogs. It also explains B.F. Skinner's operant conditioning theory and the use of reinforcement and punishment. The document then discusses Edward Tolman's cognitive theory involving relationships between cues and expectations. Finally, it covers social learning theory and the processes of attention, retention, motor reproduction, and reinforcement through observation.Job satisfaction.ppt
Job satisfaction.pptsadia saeed
╠²
The document discusses job satisfaction, including its definition, theories, measurement, determinants, and impact. It defines job satisfaction as positive feelings about one's job based on an evaluation of its characteristics. Content theories suggest job satisfaction occurs when needs are met, while process theories examine expectancies and values. The document also discusses how satisfied employees generally perform better and are less likely to engage in counterproductive behaviors.Theories of management
Theories of managementFidy Zegge
╠²
The document discusses several theories of management including:
1) Scientific Management Theory proposed by Frederick Taylor which emphasized time-motion studies, piece-rate wages, division of labor, and functional foremanship.
2) Bureaucratic Theory proposed by Max Weber which advocated for hierarchies, rules, impersonality, and career advancement based on qualifications.
3) Administrative Management principles proposed by Henri Fayol including planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling.
4) Human Relations Approach advocated by Mary Parker Follett and Elton Mayo which emphasized cooperation between employers and employees, job satisfaction, and team spirit.Recruitment Process
Recruitment Process Centurion University of Technology and Management
╠²
The document outlines the 9 key steps to an effective recruitment process: 1) Identify hiring needs, 2) Prepare job descriptions, 3) Create a recruitment plan, 4) Start searching for candidates, 5) Recruit top candidates, 6) Conduct phone screenings, 7) Interview candidates in person, 8) Make a job offer, 9) Onboard the new employee. The process involves identifying job vacancies, defining requirements, reviewing applications, screening candidates, conducting interviews, and ultimately hiring the best candidate for the role.5 stages of group development, norms (tuckman)
5 stages of group development, norms (tuckman)perspectum
╠²
This document summarizes Tuckman's five stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. It provides details about each stage, including characteristics such as uncertainty in forming, inner conflict in storming, establishment of norms in norming, productivity in performing, and separation feelings in adjourning. The stages describe the typical progression of how groups develop and work together over time.Motivation
MotivationGeetha Priya
╠²
The document discusses various theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Adams' equity theory, McClelland's acquired-needs theory, and Skinner's reinforcement theory. It also defines motivation, job satisfaction, and morale, and discusses ways to measure and improve motivation, job satisfaction, and morale in an organization.Motivation,early theories of motivation and job satisfaction
Motivation,early theories of motivation and job satisfactionanwaar alam
╠²
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs like physical survival and safety before moving on to more advanced needs for love, esteem, and self-actualization. McGregor's Theory X sees workers as largely unmotivated while Theory Y sees workers as generally self-motivated. Herzberg's two-factor theory distinguishes between motivators like achievement that improve job satisfaction and hygiene factors like pay that prevent dissatisfaction. Job satisfaction depends on intrinsic motivation from the work itself as well as extrinsic factors like compensation, supervision, and coworkers. Satisfied workers tend to be more productive, less absent, and less likely to quit their jobs.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Organizing in management
Organizing in managementAMALDASKH
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of organizing and organization. It defines organizing as identifying and grouping work to be performed, delegating responsibility and authority, and establishing relationships to enable efficient work. An organization differentiates tasks among specialized units and integrates their work. Key aspects of an organization include a group working toward common objectives, division of labor, cooperative efforts, communication, central authority, rules, and a dynamic element. A sound organizational structure facilitates administration, encourages growth and innovation, ensures optimal resource use, and continuity of the enterprise. The organizing process involves identifying activities, grouping them, assigning duties, and delegating appropriate authority.7. motivation, theories of motivation
7. motivation, theories of motivationDr. Parveen Kaur Nagpal
╠²
The document discusses motivation as a critical factor influencing behavior at work, distinguishing between intrinsic and extrinsic motivations. It reviews various motivation theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's dual-factor theory, and McGregor's theory X and theory Y, highlighting how different managerial styles can impact employee motivation. Additionally, it presents the carrot and stick approach as a method for motivating employees through rewards and consequences.Management by objectives
Management by objectivesshangrillajagtap18
╠²
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a process where employees and supervisors jointly set goals, employees define their own goals and plans, and performance is evaluated based on achieving objectives. MBO aims to improve management by clarifying responsibilities, setting individual and organizational goals aligned with the overall strategy, and providing feedback. Key aspects of MBO include participative goal setting, explicit time periods for goals, and linking performance reviews to achieving objectives.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsDivya Prabhu
╠²
Group dynamics is the study of groups and group processes. Key aspects of group dynamics include:
- Groups form through regular interaction over time where members see themselves as a distinct entity working towards common goals.
- Group processes involve understanding how groups function to solve problems or make decisions. An expert can help groups improve their functioning.
- Cohesiveness occurs when members strongly agree on common values, beliefs, and objectives and how to achieve group aims.
- Groups progress through forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning stages as defined by Tuckman's model of group development.
- Important group processes include roles and expectations, norms, conformity, and status within the groupOrganization development
Organization developmentKrishna Kanth
╠²
This document provides an overview of organizational development and interventions. It defines organizational development as a deliberately planned effort to increase an organization's relevance and viability. The key aspects covered include:
- The meaning, definitions, objectives, assumptions, values and process of organizational development.
- Common organizational development interventions like team building, coaching, large group interventions and leadership development.
- The assumptions underlying organizational interventions, which include viewing groups as the basic building blocks and aiming to reduce inappropriate competition between parts of an organization.
- The effectiveness of organizational development in providing opportunities for employees and organizations to reach their full potential and treating people with dignity and respect.Morale
MoraleCurtin University, Perth, Australia
╠²
The document discusses employee morale, defined as the willingness to work, and its crucial impact on productivity and organizational success. It highlights various determinants of morale, including individual confidence in leadership and organizational efficiency, as well as administrative measures to enhance morale. Additionally, it outlines methods for measuring morale indirectly and addresses specific causes of low morale among industrial workers in Bangladesh.Human relation theory_l5
Human relation theory_l5Jack Ong
╠²
This document provides an overview of human relations theory in organizational analysis. Some key points:
- Human relations theory emerged in the 1930s as an alternative to classical management theories that treated workers as cogs in a machine. It focused on social and emotional aspects of work.
- Theories discussed include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, findings from the Hawthorne studies that social factors impact productivity, McGregor's Theory X and Y about management assumptions of workers, and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory distinguishing job factors and environmental factors.
- Human relations theory sought to increase efficiency and productivity by addressing issues like specialization, hierarchies, and dehumanization through practices like counseling, incentives, andEMPLOYEE DISCIPLINE
EMPLOYEE DISCIPLINEJithin Omanakuttan
╠²
The document discusses employee discipline within human resource management, emphasizing the need for corrective action when performance is unsatisfactory and outlining the concept of discipline as a means of promoting self-control and adherence to organizational rules. It addresses components of discipline such as self-discipline, orderly behavior, and punishment, while differentiating between positive and punitive approaches to discipline. Effective workplace discipline is crucial for curbing problem behaviors, improving performance, and fostering a productive organizational environment.Mbo ppt
Mbo pptReshma Susan
╠²
MBO (Management by Objectives) is a process introduced by Peter Drucker in 1954 where managers and subordinates jointly define goals, responsibilities, and measures for evaluating performance. The key aspects of MBO include participative goal setting, regular performance reviews, and rewarding employees based on goal achievement. MBO aims to align individual and organizational objectives to improve communication, motivation, and results. The process involves defining organizational goals, setting objectives for employees, monitoring performance, providing feedback, and conducting performance appraisals on a recurring basis.Human Resource Management
Human Resource ManagementRahul Mahida
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), including its definition, objectives, scope, functions, and importance across various types of organizations. It discusses the managerial and operative functions, recruitment processes, selection techniques, and placement strategies that are essential for achieving organizational goals effectively. Furthermore, it addresses the significance of maintaining ethical relationships between management and employees, as well as the necessity of treating human resources as valuable assets within any organization.Organisational Climate
Organisational ClimateShilpi Panchal
╠²
The document discusses organizational climate, defining it as the interpretation of the work environment by employees and identifying factors that influence it such as supervisor support and employee involvement. It outlines how HR practices affect this climate through areas like employee relations, performance management, and corporate branding. The document also presents theories of organizational climate, key success factors for organizations, and provides suggestions for improvement.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsJyothi Chinnasamy
╠²
The document defines groups and group dynamics, discussing types of groups, roles within groups, stages of group development, and processes like communication, problem solving, and leadership. It notes that a group requires a minimum of two people, common goals, interdependence, and self-identification as members. Group dynamics examines how groups form and develop over multiple stages, focusing on elements like roles, communication, decision-making, influence, and relationships between task completion and social bonds.Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic Leadershipnabaz4u
╠²
This document discusses autocratic leadership. It defines autocratic leadership as a leadership style where power is centralized in one individual who makes all decisions without input from group members. The document outlines some key characteristics of autocratic leadership, such as leaders having full control over decision-making and not entertaining suggestions. It also notes some potential negative effects, like low employee morale and high turnover. However, the document acknowledges that autocratic leadership can allow for fast decision-making and may be useful in dangerous situations where strict rules are needed. In conclusion, it states that autocratic leadership is best for short-term stability but can negatively impact organizations over the long run.STAFFING
STAFFINGabhinandnandakumar
╠²
The document outlines the staffing process, emphasizing the importance of acquiring, developing, and maintaining human resources effectively. It details the steps involved in staffing, including manpower planning, recruitment, selection, orientation, training, compensation, and performance evaluation. Additionally, it highlights the significance of matching the right individuals to jobs to enhance organizational productivity and employee satisfaction.Group dynamics
Group dynamicsRohit Kumar
╠²
Group dynamics refers to the attitudinal and behavioral characteristics of a group. A group is defined as two or more individuals interacting and interdependent, who have come together to achieve particular objectives. Groups form through various stages of development including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. There are both formal and informal groups. Formal groups are designated work groups within an organization while informal groups form in response to social needs. When making decisions as a group, individuals may shift their positions towards a more extreme risk level than their original individual decision due to factors like diffused responsibility and social status within the group.Organizational Behavior : Learning
Organizational Behavior : Learning Shruti Pendharkar
╠²
This document discusses various theories of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive processes, and social learning. It provides examples of Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning experiments with dogs. It also explains B.F. Skinner's operant conditioning theory and the use of reinforcement and punishment. The document then discusses Edward Tolman's cognitive theory involving relationships between cues and expectations. Finally, it covers social learning theory and the processes of attention, retention, motor reproduction, and reinforcement through observation.Job satisfaction.ppt
Job satisfaction.pptsadia saeed
╠²
The document discusses job satisfaction, including its definition, theories, measurement, determinants, and impact. It defines job satisfaction as positive feelings about one's job based on an evaluation of its characteristics. Content theories suggest job satisfaction occurs when needs are met, while process theories examine expectancies and values. The document also discusses how satisfied employees generally perform better and are less likely to engage in counterproductive behaviors.Theories of management
Theories of managementFidy Zegge
╠²
The document discusses several theories of management including:
1) Scientific Management Theory proposed by Frederick Taylor which emphasized time-motion studies, piece-rate wages, division of labor, and functional foremanship.
2) Bureaucratic Theory proposed by Max Weber which advocated for hierarchies, rules, impersonality, and career advancement based on qualifications.
3) Administrative Management principles proposed by Henri Fayol including planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling.
4) Human Relations Approach advocated by Mary Parker Follett and Elton Mayo which emphasized cooperation between employers and employees, job satisfaction, and team spirit.Recruitment Process
Recruitment Process Centurion University of Technology and Management
╠²
The document outlines the 9 key steps to an effective recruitment process: 1) Identify hiring needs, 2) Prepare job descriptions, 3) Create a recruitment plan, 4) Start searching for candidates, 5) Recruit top candidates, 6) Conduct phone screenings, 7) Interview candidates in person, 8) Make a job offer, 9) Onboard the new employee. The process involves identifying job vacancies, defining requirements, reviewing applications, screening candidates, conducting interviews, and ultimately hiring the best candidate for the role.5 stages of group development, norms (tuckman)
5 stages of group development, norms (tuckman)perspectum
╠²
This document summarizes Tuckman's five stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. It provides details about each stage, including characteristics such as uncertainty in forming, inner conflict in storming, establishment of norms in norming, productivity in performing, and separation feelings in adjourning. The stages describe the typical progression of how groups develop and work together over time.Similar to Morale and motivation (20)
Motivation
MotivationGeetha Priya
╠²
The document discusses various theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Adams' equity theory, McClelland's acquired-needs theory, and Skinner's reinforcement theory. It also defines motivation, job satisfaction, and morale, and discusses ways to measure and improve motivation, job satisfaction, and morale in an organization.Motivation,early theories of motivation and job satisfaction
Motivation,early theories of motivation and job satisfactionanwaar alam
╠²
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs like physical survival and safety before moving on to more advanced needs for love, esteem, and self-actualization. McGregor's Theory X sees workers as largely unmotivated while Theory Y sees workers as generally self-motivated. Herzberg's two-factor theory distinguishes between motivators like achievement that improve job satisfaction and hygiene factors like pay that prevent dissatisfaction. Job satisfaction depends on intrinsic motivation from the work itself as well as extrinsic factors like compensation, supervision, and coworkers. Satisfied workers tend to be more productive, less absent, and less likely to quit their jobs.7. Motivation.ppt
7. Motivation.pptlekhakuriakose1
╠²
The document discusses various theories and concepts related to motivation and direction in management. It covers topics like the need for motivation in organizations, intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and various techniques that can be used to motivate employees such as management by objectives and job rotation. Effective direction involves giving clear orders to employees and leading and motivating them to achieve goals.MHRM: Principles of Management- unit-iii.pptx
MHRM: Principles of Management- unit-iii.pptxSatyaM733268
╠²
The document discusses principles and practices of management, specifically focusing on the directing function. It defines directing as influencing, guiding, supervising, and motivating subordinates to achieve organizational goals. The key elements of directing are motivation, leadership, supervision, and communication. Motivation theories discussed include Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Leadership is defined as influencing others to willingly work towards objectives. Leadership styles covered are democratic and autocratic.Motivational
Motivationalhardeekacharya
╠²
This document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as the drive within an individual that pushes them towards goal-oriented action. Motivation can be positive, through incentives like rewards, or negative, through fear-based pushes. The document outlines several theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y. It also discusses characteristics, importance, types, and problems related to motivation.Motivational
Motivationalhardeekacharya
╠²
The document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as the drive within an individual that pushes them towards goal-oriented action. Motivation can be positive, through incentives like rewards, or negative, through fear-based pushes. Several theories of motivation are described, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y. Motivation is explained as important for job satisfaction, performance, and goal achievement, but can face problems in implementation and maintaining moderate levels. Cooperation between managers and employees is emphasized for effective motivation.Motivation.pptx
Motivation.pptxRobbia Rana
╠²
Motivation is the process of encouraging people to accomplish goals. It comes from internal desires (intrinsic) or external rewards/punishments (extrinsic). Motivation is important because it leads to improved employee efficiency and productivity, helps achieve organizational goals, builds relationships, and reduces turnover. Managers are responsible for motivating subordinates through both financial and non-financial means like appreciation, incentives, and fulfilling employee needs. Motivation is an ongoing process that can be positive or negative depending on the actions of management.Motivation
MotivationKarpagam Alagappan
╠²
Motivation is the process of encouraging people to accomplish goals. It comes from both internal desires (intrinsic) and external rewards/incentives (extrinsic). Motivation is important because it leads to improved employee performance and productivity, helps achieve organizational goals, builds relationships, and reduces turnover. Managers are responsible for motivating subordinates through both financial and non-financial means like recognition, opportunities for growth, and engaging meaningful work. Proper motivation results in maximum utilization of human resources.leadership Skills in social work and motivation
leadership Skills in social work and motivationsangeethan69
╠²
The document discusses various leadership theories and styles, emphasizing the importance of influencing people towards common goals. It explores motivation as a key component in leadership, detailing intrinsic and extrinsic motivation types, and outlines early theories of motivation such as Maslow's hierarchy and McGregor's Theory X and Y. Additionally, it addresses practical aspects of enhancing motivation through team dynamics, time management, and conflict resolution.directing, communication, motivation, supervision.pptx
directing, communication, motivation, supervision.pptxGokulDev16
╠²
This document discusses the concept of directing, which is the third function of management aimed at achieving organizational goals. Directing involves activities like issuing orders, training subordinates, motivating staff, maintaining discipline, and rewarding good performance. It is a complex process that encourages effective and efficient work. Key elements of directing include supervision, motivation, leadership, communication, and order giving. The document also discusses theories of motivation like Maslow's hierarchy of needs and McClelland's need theory, which aim to explain what motivates employees.motivation nursing administration pptx,
motivation nursing administration pptx,AlanSudhan
╠²
The document discusses motivation as a psychological process that drives employees to achieve their best performance, highlighting various definitions and types such as intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. It outlines the motivation process, factors influencing motivation, and several motivation theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Additionally, it emphasizes the crucial role of nurse managers in motivating their staff through supportive leadership and recognition of individual needs.motivation
motivationsimran wadhwani
╠²
This document discusses various aspects of motivation in management. It defines motivation as the process through which managers build desire in employees to be productive. It outlines the significance of motivation, including increased efficiency, lower turnover, and better relationships. It also discusses the nature of motivation as internal, continuous, and complex. Different motivation theories are presented, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and Vroom's expectancy theory. Types of financial and non-financial incentives are listed. The concepts of job enrichment, job enlargement, and morale are also explained in relation to motivation.Motivation and Performance Appraisal
Motivation and Performance AppraisalNima
╠²
The document discusses various theories and concepts related to motivation. It begins by defining motivation as the process of influencing employees' behavior. It then outlines several theories of motivation including: Maslow's hierarchy of needs which proposes that lower level needs must be met before higher level needs motivate; Herzberg's two-factor theory distinguishing between hygiene and motivational factors; McGregor's Theory X and Y about employee assumptions; and Vroom's expectancy theory examining valence, expectancy and instrumentality. The document also discusses techniques for motivating employees including monetary incentives, job enrichment, and leadership styles.Val finnell on Leadership and Motivation
Val finnell on Leadership and MotivationVal Finnell
╠²
The document discusses various leadership theories, defining leadership as a process of guiding and influencing individuals towards achieving goals. It covers different leadership styles, including autocratic, democratic, and situational, alongside motivational theories such as Maslow's hierarchy and Herzberg's two-factor model. Additionally, it addresses the importance of perceptions, values, and attitudes in motivation, as well as generational considerations that impact workplace dynamics.Motivation
MotivationPayal Deep
╠²
This document discusses motivation and morale in the workplace. It defines motivation as the willingness to work hard towards organizational goals to satisfy individual needs. Morale refers to employee satisfaction and optimism about working towards shared goals with confidence. High morale is associated with high productivity when both individual and group goals are satisfied, leading to high motivation. Morale can be indicated by factors like the nature of work, satisfaction levels, supervision quality, and perceptions of fairness. Maintaining high motivation and morale is important for managers to succeed.Motivational Skills_NASC_December 5, 2014.ppt
Motivational Skills_NASC_December 5, 2014.pptAvinashKShrivastava
╠²
The document discusses the importance of motivation in management and leadership, covering various motivation theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory. It emphasizes that effective management requires understanding both self-motivation and the motivation of others, particularly in challenging environments like the military. Key motivational techniques involve creating a supportive environment, recognizing achievements, and addressing individual needs to enhance job satisfaction and performance.MOtivation
MOtivationRajeevKumarGangwar
╠²
The document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation and discusses types of motivation like external and internal motivation. It also summarizes several theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory. The document emphasizes that motivation comes from within and that both intrinsic and extrinsic factors play a role in motivating employees. It also stresses the importance of recognizing individual differences when motivating people.motivation-new-ppt.ppt
motivation-new-ppt.pptresearchanimalsciences
╠²
This document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation and discusses several theories of motivation, including: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McGregor's Theory X and Y, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and McClelland's manifest needs theory. It also covers Mayo's theory of human relations and discusses what motivates employees, including maintainers who value job security and benefits, and motivators who seek growth opportunities. The document emphasizes that a motivating work climate fosters feelings of belonging, competence, and autonomy.How to Motivate Your Self By Ravinder Tulsiani
How to Motivate Your Self By Ravinder Tulsianiravindertulsiani1
╠²
This document discusses motivating, satisfying, and leading employees. It describes psychological contracts between employees and employers, the importance of job satisfaction and morale, and major theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's hygiene factors. The document also discusses strategies to improve motivation such as job enrichment, flexible work schedules, and performance-based rewards. Finally, it covers different leadership styles and the importance of adapting one's style to the situation.Motivation
Motivation AshwiniKumbar1
╠²
Here are a few key points on the role of money in motivating Indian employees:
- For most Indian employees, basic financial security and needs are important motivating factors given the country's developing economy. Meeting basic needs like paying bills, supporting a family, saving for the future etc. are priorities. So money does play an important role in motivation.
- However, money alone may not be a long-term sustaining motivator. While pay is important, Indian employees also want meaningful work, growth opportunities, recognition from managers/leaders, an engaging workplace culture etc. Non-monetary factors become increasingly important over time.
- In jobs that are more mundane or repetitive, money could be a stronger motivatorAd
Recently uploaded (9)
ORGANIZATION Development and human ressoucre development .pdf
ORGANIZATION Development and human ressoucre development .pdfAyaSenhaji2
╠²
This is an introduction to what is organizational development and its impact on HRDHRMS_Software skill_Presentation_Sample.pptx
HRMS_Software skill_Presentation_Sample.pptxbalavig06
╠²
HRMS stands for human resource management system ŌĆō often referred to as human capital management (HCM) software. Companies use an HRMS to digitalise, automate, and centralise core HR processes, such as employee data storage, benefits administration, time and attendance, and payroll. In addition, an HRMS provides talent management capabilities, such as recruiting, onboarding, performance management, goal planning, learning and training, compensation, and succession planning.Webinar - Crafting a Clear Compensation Strategy for 2025
Webinar - Crafting a Clear Compensation Strategy for 2025PayScale, Inc.
╠²
Join compensation experts as they unpack the latest data, insights, and best practices to help you build or refine a compensation strategy that drives performance, retention, and equity.What Are the Hiring Process Steps_ A Complete Breakdown for Employers.pdf
What Are the Hiring Process Steps_ A Complete Breakdown for Employers.pdfKlay Hr Consultants
╠²
Hiring the right people isnŌĆÖt just about posting a job adŌĆöitŌĆÖs about following a structured process that ensures you find, evaluate, and onboard top talent effectively. In this informative guide, we break down the key hiring process steps every employer should followŌĆöfrom identifying a hiring need and crafting the perfect job description to screening candidates, conducting interviews, and onboarding new hires. Whether you're a growing business or an HR manager refining your recruitment approach, this step-by-step breakdown offers practical insights to streamline your efforts. We also highlight how partnering with the best HR consultancy in Dubai can help speed up and strengthen your hiring strategy. If you want to build a reliable, scalable hiring system that brings the right people into your team, this blog is a must-read. Discover how each stage of recruitment connects and how you can make smarter hiring decisions with confidence.Webinar - Unlock the Power of Data in Your Compensation Strategy
Webinar - Unlock the Power of Data in Your Compensation StrategyPayScale, Inc.
╠²
Join compensation leaders from Mercer and Payscale as we explore how organizations can harness salary data to drive smarter compensation strategies.Module-IV- Culture and Global Management.pptx
Module-IV- Culture and Global Management.pptxpujamishrarnc
╠²
Module ŌĆō IV ŌĆō Culture and Organization
Culture and corporate structures, Culture and Leadership, Culture and Strategy, Cultural
change in Organizations, Culture and marketing, Cultural Diversity in OrganizationAd
Morale and motivation
- 2. MORALE ’é¢It is the mental attitude which makes the individual perform his work either willingly and enthusiastically or poorly and reluctantly. ’é¢It is used to describe the level or quality of the attitude or reaction displayed by an individual or by a group as being high or low, good or poor, positive or negative. ’é¢The qualities indicating high morale are known by such terms as enthusiasm, personal satisfaction, team spirit, pride of achievement, and willingness to work.
- 3. MORALE Professor Michael J. Jucius defines morale ŌĆ£as a state of mind and emotions, affecting willingness to work, which in turn affects individual and organizational objectives.ŌĆØ ’é¢What it is ’é¢What it does ’é¢Where it resides ’é¢Whom it affects ’é¢What it affects
- 4. MORALE Professor Dale S. Beach defined morale as the ŌĆ£total satisfaction a person derives from his job, his work group, his boss, the organization, and his environment. It is also affected by his personality structure. Morale pertains to the general feeling of well-being, satisfaction, and happiness of people.ŌĆØ Professor Flippo describes morale as a ŌĆ£mental condition or attitude of individuals and group which determines their willingness to cooperate.ŌĆØ
- 5. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORALE 1. The employees themselves 2. Management practices 3. Outside factors 4. State of communication in the firm
- 6. INDICATIONS OF LOW EMPLOYEE MORALE 1. Customer complaints 2. Frequent absenteeism and tardiness 3. Frequent sick leave 4. Low production, spoilage of materials due to inattention 5. Unjustified overtime 6. Careless handling of machines causing breakdowns 7. Spoilage and waste of supplies and materials
- 7. INDICATIONS OF LOW EMPLOYEE MORALE 8. Grievance and complaints 9. High labor turnover 10.Rumors, quarrels or fights 11.Frequent violations of rules and regulations 12.Lost man-hours because of long breaks and frequent trips to comfort rooms 13.Unsatisfactory ratings in performance appraisal
- 8. METHODS USED IN DETERMINING MORALE 1. Counseling and exit interview 2. Grievance procedure 3. Spy system or ŌĆ£management informersŌĆØ 4. Interview 5. Studying or reviewing the employeesŌĆÖ records 6. Observation 7. Attitude or Morale survey
- 9. MOTIVATION ’é¢The word motivation is derived from the word ŌĆ£motivateŌĆØ which means to move, impel or induce to act to satisfy a need or want. ’é¢Any consideration, idea or object prompting or exciting an individual to act or move him to do what his leader wants to be accomplished is motivation. ’é¢It is the willingness to exert effort to achieve a goal or objective for reward. ’é¢It is the need, want, or motive within the individual that will urge him to accomplish his objectives.
- 10. TYPESOF MOTIVATION 1. POSITIVE MOTIVATION ŌĆō human relations or leadership approach whereby subordinates enthusiastically follow the leaderŌĆÖs will because of some possible gain, reward or satisfaction they expect to get such as feeling of achievement, sense of responsibility, appreciation, promotion etc. 2. NEGATIVE MOTIVATION ŌĆō influences others to follow the leaderŌĆÖs will, but not because of any expected advantage but of fear of punishment or the application of certain sanctions such as losing some money or status, recognition, or even oneŌĆÖs job.
- 11. POSITIVE FACTORS IN MOTIVATING PEOPLE 1. Money 2. Job security 3. Praise and recognition 4. Sense of belonging 5. Competition 6. Delegation of responsibility and authority 7. Employee participation 8. Sincere interest in subordinate
- 12. EFFECTSOF MOTIVATION 1. Move and act to follow the direction desired by management 2. Achieve high output and produce good quality products and services 3. More careful in the use and care of machines and equipment, avoid or prevent accidents, and minimize or prevent losses or waste
- 13. EFFECTSOF MOTIVATION 4. Accept willingly the changes made by the management provided that the changes to be made have been previously explained and understood by them and proper training is provided to adjust them to the change 5. Willingly respond in times of emergencies or during rush periods or occasions requiring special effort, overtime, and the like 6. Problems of disciplines are minimized
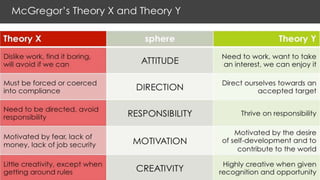
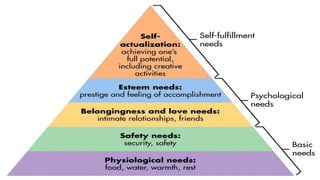
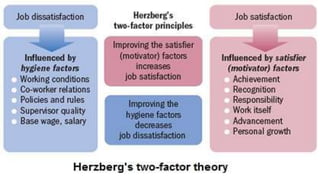
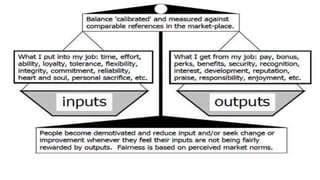
- 14. THEORIESOF MOTIVATION 1. McGregorŌĆÖsTheory X andTheoryY 2. MaslowŌĆÖs Hierarchy of Needs 3. HerzbergŌĆÖsTwo-FactorTheory 4. AdamsŌĆÖ EquityTheory 5. LockeŌĆÖs GoalTheory
