Mother board
- 2. PPT Objectives ï Describe the function of the motherboard. ï Identify the different types of motherboards and their characteristics. ï Identify the main components of the motherboard. ï Considerations when purchasing a motherboard. 2 Copyright ÂĐ Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved.
- 3. Introduction ï A motherboard, also known as the primary circuit inside the computer, and where the central processing unit(CPU), Memory slots, drives and other peripherals. ï A motherboard provides the electrical connections by which the other components of the system communicate. it also connects the central processing unit and hosts other subsystems and devices. ï An important component of a motherboard is the microprocessor's supporting chipset, which provides the supporting interfaces between the CPU and the various buses and external components. This chipset determines, to an extent, the features and capabilities of the motherboard.
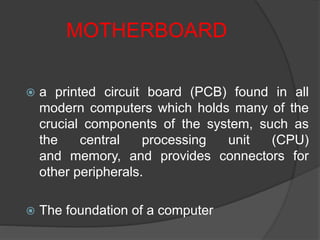
- 5. MOTHERBOARD ï a printed circuit board (PCB) found in all modern computers which holds many of the crucial components of the system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. ï The foundation of a computer
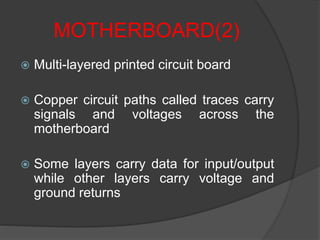
- 6. MOTHERBOARD(2) ï Multi-layered printed circuit board ï Copper circuit paths called traces carry signals and voltages across the motherboard ï Some layers carry data for input/output while other layers carry voltage and ground returns
- 7. FUNCTIONS OF MOTHERBOARD ï§ The motherboard acts as the central backbone of a computer on which other modular parts are installed such as the CPU, RAM and hard disks. ï§ The motherboard also acts as the platform on which various expansion slots are available to install other devices / interfaces. ï§ The motherboard is also responsible to distribute power to the various components of the computer. ï§ They are also used in the coordination of the various devices in the computer and maintain an interface among them.
- 9. TYPES OF MOTHERBOARD ï INTEGRATED MOTHERBOARD ï NON INTEGRATED MOTHERBOARD ï DESKTOP MOTHERBOARD ï LAPTOP MOTHERBOARD ï SERVER MOTHER BORD ï ï AT MOTHERBOARD ï ATX MOTHERBORD
- 10. Types of motherboard based on devices they support ï Integrated motherboard ï Non integrated motherboard
- 11. An integrated system board has multiple components integrated into the board itself. These may include the CPU video card , sound card and various controller cards.
- 12. Non integrated system board uses installable components and expansion cards. For example, non integrated system board may allow you to upgrade the video card by removing the old one and installing a new one. Non integrated motherboard typicaly have several PCI expansion slots as well.
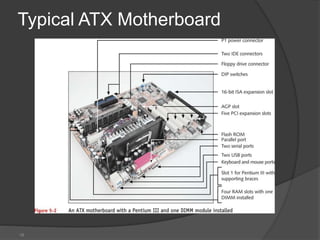
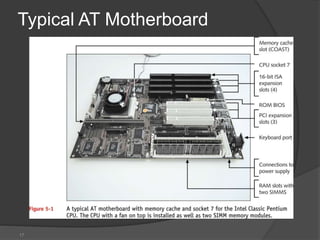
- 13. The form factor determines the general layout, size, and feature placement on a motherboard. Different form factors usually require different style cases. 1. AT 2 . ATX 3. Micro ATX
- 14. AT : AT MOTHERBOARD IS A MOTHERBOARD WHICH HAS DIMENSIONS OF THE ORDER OF SOME HUNDRED MILLIMETERS, BIG ENOUGH TO BE UNABLE TO FIT IN MINI DESKTOP.
- 15. ATX : ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY EXTENDED,OR POPULARLY KNOWN AS THE ATX, ARE THE MOTHERBOARD WHICH WERE PRODUCED BY THE INTEL IN MID 90`S AS AN IMPROVEMENT FROM THE PREVIOUSLY WORKING MOTHERBOARD SUCH AS AT.
- 18. microATX motherboard âĒ Laptop computers generally use highly integrated, miniaturized and customized motherboards. This is one of the reasons that laptop computers are difficult to upgrade and expensive to repair. âĒ Often the failure of one laptop component requires the replacement of the entire motherboard, which is usually more expensive than a desktop motherboard due to the large number of integrated components.
- 19. 1. Desktop motherboard 2. laptop Motherboard 3. server motherboard
- 20. Desktop motherboard ï Desktop motherboard are used in personal or desktop computer. As it is used for application at home and in office, this type of motherboard is the most basic type
- 21. Laptop motherboard ï Laptop motherboard is used to connect different parts of a laptop system. These motherboard generally have very advanced features as compared to the desktop motherboard and most of the functions have been integrated into the laptop motherboard
- 23. Server motherboard ï Server motherboard are more advanced then desktop motherboard and are designed to offer high -end service which are more reliable and ready to operate in 24*7 environments.
- 25. Manufacturers of motherboard Motherboard are available in various sizes and configurations. Some motherboard support 32 and 64 bit processor as well operating system. It is manufacturers by many companies such as. 1. Asus 3. Intel 3. MSI 4. Gigabyte.
- 26. COMPONENTS OF MOTHERBOARD Back Panel Connectors & Ports : Connectors and ports for connecting the computer to external devices such as display ports, audio ports, USB ports, Ethernet ports, PS/2 ports etc.
- 28. Expansion Slot ( PCI ) ï Expansion slot or Expansion bus is the slot that enable the user to add the adapter card for additional function to the system Example. ï Sound card or Multimedia ï LAN card. ï SCSI controller card. ï Internal Modem card. ï TV tuner card. ï Additional hard disc controller card.
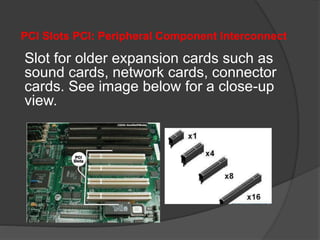
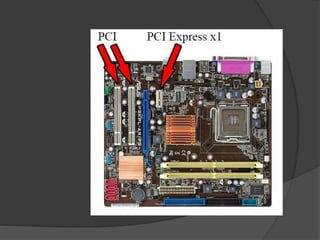
- 29. PCI Slots PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect Slot for older expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards, connector cards. See image below for a close-up view.
- 30. PCI Express x1 Slots Slot for modern expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth), connector cards (USB, FireWire, eSATA) and certain low-end graphics cards. See image below for a close-up view
- 32. PCI Express x16 Slot Slot for discrete graphic cards and high bandwidth devices such as top-end solid state drives. See image below for a close-up view
- 33. AGP SLOT ï AGP slots are used to insert or install AGP Cards. ï AGP full form is Accelerated Graphics Port. This slot is for graphics and 3d gaming purpose. it is always beside the PCI slots
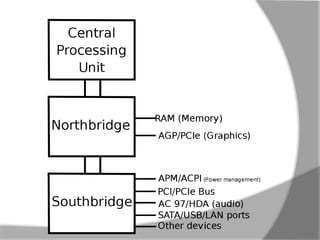
- 34. CHIPSET A chipset is a group of small circuits that coordinate the flow of data to and from key components of a PC. This includes the CPU itself, the main memory, the secondary cache and any devices situated on the buses. The chipset also controls data flow to and from hard disks, and other devices connected to the IDE channels. A computer has got two main chipsets: ï Northbridge ï Southbridge
- 35. Northbridge Also known as Memory Controller Hub (MCH). Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate with the RAM and graphics card. Beginning from Intel Sandy Bridge in 2011, this motherboard component is no longer present as it has been integrated within the CPU itself.
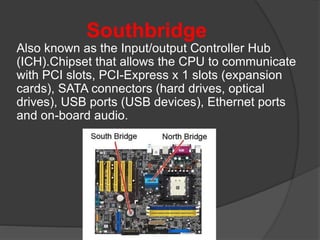
- 36. Southbridge Also known as the Input/output Controller Hub (ICH).Chipset that allows the CPU to communicate with PCI slots, PCI-Express x 1 slots (expansion cards), SATA connectors (hard drives, optical drives), USB ports (USB devices), Ethernet ports and on-board audio.
- 38. CPU SOCKET ï§ Another vital motherboard component is the CPU socket usually being located near the centre of the motherboard. which is used to install the processor on the motherboard. This allows CPU to be replaced and placed without soldering. ï§CPU is a part that controls the activities of a computer. It is the brain of the computer, and it is responsible for fetching, decoding and executing program instructions as well as performing mathematical and logical calculations.
- 39. CPU SOCKET(2) The type of sockets used are: ï LGA (Land Grid Array) â In this, the pins are present on the socket. ï PGA (Pin Grid Array) â In this, the pins are present on the CPU chip. ï ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) â In this, while inserting the CPU chip the contacts on the socket are made loose by lifting a lever. Thus, the CPU gets fitted easily. The LGA type sockets are mainly used by Intel whereas, AMD uses the PGA-ZIF type sockets.
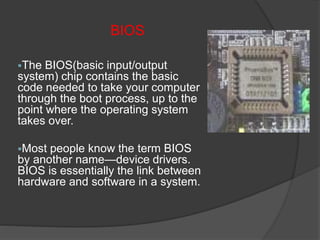
- 40. BIOS ï§The BIOS(basic input/output system) chip contains the basic code needed to take your computer through the boot process, up to the point where the operating system takes over. ï§Most people know the term BIOS by another nameâdevice drivers. BIOS is essentially the link between hardware and software in a system.
- 41. BIOS(2) ï§ The system BIOS is a ROM chip on the motherboard used by the computer during the start up routine (boot process) to check out the system and prepare to run the hardware. The BIOS is stored on a ROM chip because ROM retains information even when no power is being supplied to the computer. ï§ the BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions.
- 42. CMOS BATTERY ï§The battery or a cell is a 3.0 Volts lithium type cell. The cell is responsible for storing the information in BIOS and the full form is Complementary Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor. ï§Supplies power to bios settings and keep the real time clock running.
- 43. CMOS RAM ï Motherboards also include a small separate block of memory made from CMOS RAM chips which is kept alive by a battery (known as a CMOS battery) even when the PCâs power is off. This prevents reconfiguration when the PC is powered on. ï CMOS devices require very little power to operate. ï The CMOS RAM is used to store basic Information about the PCâs configuration for instance:- ï Floppy disk and hard disk drive types ï Information about CPU ï RAM size ï Date and time ï Serial and parallel port information ï Plug and Play information ï Power Saving settings ï Other Important data kept in CMOS memory is the time and date, which is updated by a Real Time Clock (RTC).
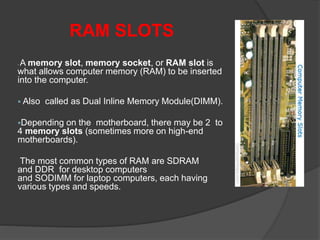
- 44. RAM SLOTS ï§ A memory slot, memory socket, or RAM slot is what allows computer memory (RAM) to be inserted into the computer. ï§ Also called as Dual Inline Memory Module(DIMM). ï§Depending on the motherboard, there may be 2 to 4 memory slots (sometimes more on high-end motherboards). The most common types of RAM are SDRAM and DDR for desktop computers and SODIMM for laptop computers, each having various types and speeds.
- 45. RAM SLOTS(2) ï Random access memory or RAM most commonly refers to computer chips that temporarily store dynamic data when you are working with your computer to enhance the computer performance. ï§ Random access memory is volatile memory, meaning it loses its contents once power is turned off ï§ When a computer shuts down properly, all data located in random access memory is returned back to permanent storage on the hard drive or flash drive. At the next boot- up, RAM begins to fill with programs automatically loaded at start up, and with files opened by the user a process called booting.
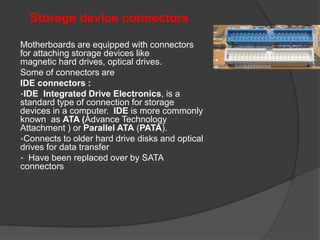
- 46. Storage device connectors Motherboards are equipped with connectors for attaching storage devices like magnetic hard drives, optical drives. Some of connectors are IDE connectors : ï§IDE Integrated Drive Electronics, is a standard type of connection for storage devices in a computer. IDE is more commonly known as ATA (Advance Technology Attachment ) or Parallel ATA (PATA). ï§Connects to older hard drive disks and optical drives for data transfer ï§ Have been replaced over by SATA connectors
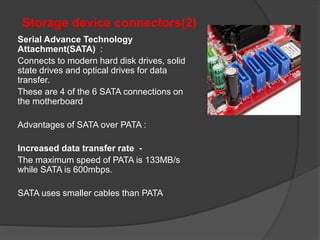
- 47. Storage device connectors(2) Serial Advance Technology Attachment(SATA) : Connects to modern hard disk drives, solid state drives and optical drives for data transfer. These are 4 of the 6 SATA connections on the motherboard Advantages of SATA over PATA : Increased data transfer rate - The maximum speed of PATA is 133MB/s while SATA is 600mbps. SATA uses smaller cables than PATA
- 48. POWER CONNECTORS Computers have a main power supply unit but it is not possible to deliver power to all the components directly from it. Hence, power connectors are used to distribute the power from the main supply to various components like RAM, CPU, chipset, and expansion cards. ATX connector. (Advanced Technologies Extended)The latest in the series of power connectors ATX Power Connector - Connects to the 24-pin ATX power cable of a power supply unit which supplies power to the motherboard. ATX 12v power connector - Connects to the 4-pin power cable of a power supply unit which supplies power to the CPU
- 49. FAN HEADER Supplies power to the CPU heat sink fan and computer case fans. The heat sink is attached securely to the CPU, and is used to draw the heat out of and away from the CPU. In turn, a fan is then attached to the heat sink to draw the heat from the CPU via the heat sink. Without these, the CPU would most certainly burn out. For the purpose of monitoring capabilities, the CPU fan is connected directly to special motherboard pins,
- 50. Floppy Drive Connector Floppy Drive Connector is used to connect floppy drives. It supports two floppy drives. so that A and B drives are reserved for two floppy drives in My computer. it has 32 pins.
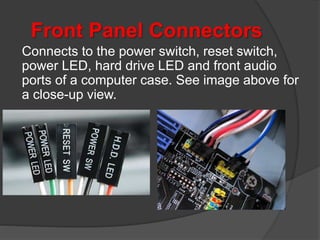
- 51. Front Panel Connectors Connects to the power switch, reset switch, power LED, hard drive LED and front audio ports of a computer case. See image above for a close-up view.
- 52. Power & Reset Button The reset button would typically kick off a soft boot, instructing the computer to go through the process of shutting down, which would clear memory and reset devices to their initialized state. Contrary to the 'Power Button', which would simply remove power immediately.
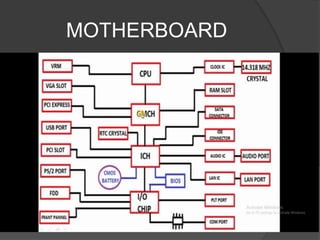
- 53. MOTHERBOARD
- 54. Considerations When Selecting a MOTHER BOARD ï Processor support ï FORM FACTOR/SIZE ï RAM support. ï SATA support ï Expansion Slots and Port ï BRAND 54 Copyright ÂĐ Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved.
- 56. ANY QUERIES?
Editor's Notes
- #55: 54