Moving To IP Backhaul
- 1. Moving to IP Backhaul August 22nd, 2012 Matt Reath, Director of Sales Engineering
- 2. CCI • Presales, System Integration, Engineer/Design, Outside Plant Construction, and Wireless • Start-to-Finish Solutions/Whole Product Solutions • Optical, Routing/Switching, CMTS, Video, and WiFi • A leader in the telecommunications industry for over 50 years (since 1955) • Cisco Partner (focused on SP)
- 3. Agenda • Introduction • What is backhaul? • Current/Legacy backhaul solutions • Challenges • Future backhaul solutions • Q & A
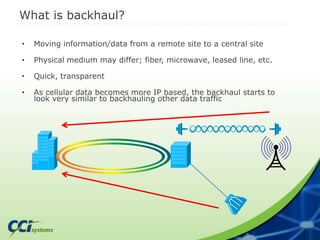
- 4. What is backhaul? • Moving information/data from a remote site to a central site • Physical medium may differ; fiber, microwave, leased line, etc. • Quick, transparent • As cellular data becomes more IP based, the backhaul starts to look very similar to backhauling other data traffic
- 5. Backhaul Drivers • Increased number of mobile devices • Increased mobile data usage (3G, 4G/LTE, WiFi) • Increased overall data usage for wireline and wireless • Large wireless companies contracting out IP/TDM backhaul portion of 3G/4G. • Providers usually only have a small number of “Internet” connected POPs. All Internet traffic needs to be backhauled to those POPs.
- 6. Growth in Mobile Data Usage
- 7. Growth in Internet Bandwidth Usage
- 8. Current/Legacy Backhaul Solutions Separate Networks SONET/TDM • Voice services • Legacy data (DS1,DS3) ATM • Data services (DSL) • Leased line • Video IP • Data services • Internet routing (BGP) • IPv4 + IPv6 • MetroEthernet
- 9. Challenges • Increased TCO of owning multiple networks – Maintenance & Support – Operation (Employee costs) – Training – Initial cost of purchase • TDM/ATM hardware tends to be more expensive • Leasing TDM lines for backhaul purposes can be expensive – Average T1 costs around $400/mo, only providing 1.5Mbps • Less deployment flexibility – different device/network to accomplish tasks – not enough bandwidth
- 10. Future • Consolidated Network – Single network, various services – TDM emulation over IP (DS1,DS3,Oc-n) – Cost/TCO savings versus separate networks • Intelligence throughout network • Common transport and core • Varying edge services
- 11. Consolidated Network • TDM traffic transported using circuit emulation over MPLS • Ethernet transported using L3VPN, VPLS, Pseudowires, or standard routing • Flexible interface and transport support over a common MPLS infrastructure
- 12. Example Edge Device Example Edge Device • 1 port 10GbE • 8 port Copper GbE • 8 port SFP GbE • 16 port T1 **TDM** • 4 port OC-3/1 port OC-12 **TDM** Interfaces Protocols • Ethernet OAM (802.1ag, 802.3ah, Y.1731) • SyncE / BITS • IPv4 + IPv6 • MPLS (LDP, VPN, OAM, TE, FRR, TP) • EoMPLS, CESoPSN, SAToP **The TDM interface modules support the Any Service Any Port (ASAP) concept, including Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and circuit emulation functionality.
- 13. Converged Network What needs to be supported? TDM Services • RFC1588/SyncE Timing • Y.1731 Ethernet OAM • Circuit Emulation Services over MPLS Data Services • Routing protocols • L3VPN • BGP • IPv4+IPv6 • Data prioritization • MEF (E-LINE,E-LAN,E-tree) Video Services • Multicast • Video monitoring (QoE) • Quality of service Voice Services • Priority Queue (QoS) • HQOS • VRF support
- 14. Conclusion • Industry moving to network consolidation • IPv4 and IPv6 need to be supported • Network intelligence provides advanced routing, QoS, and network management • Multipurpose devices provide ATM, TDM, and IP over a common backbone • Cost savings through management of a common network • Increased revenue through additional service offerings