MP&AL presentation (8085 microprocessor architecture)
- 2. The Microprocessor : ? An electronic component used by a computer to do its work ? A single integrated circuit chip containing transistors, diodes & resistors
- 3. The 8085 Microprocessor : ? An 8 bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. ? Requires +5 volt power supply ? 8 bit data bus & 16 bit address bus
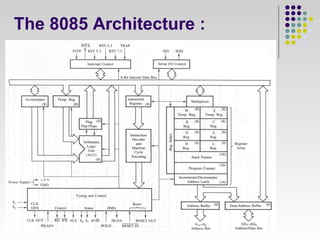
- 5. Functional Units : ? Accumulator ? 8 bit register ? Connected to internal data bus & ALU ? Arithmetic & Logic Unit ? Performs the actual numerical & logical operations ? Uses data from memory and accumulator
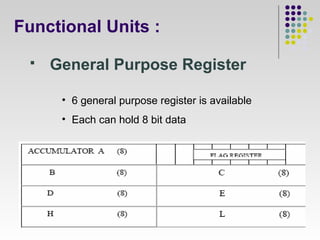
- 6. Functional Units : ? General Purpose Register ? 6 general purpose register is available ? Each can hold 8 bit data
- 7. Functional Units : ? Program Counter ? 16 bit register ? This register is a memory pointer ? Stack Pointer ? 16 bit register ? Functions similar to stack ? Temporary Register ? 8 bit register
- 8. Functional Units : ? Flag Register ? 8 bit register having five flip flops ? The combination of the flag register and accumulator is called Program Status Word and it is the 16 bit unit for stack operation
- 9. Functional Units : ? Instruction Register & Decoder ? 8 bit register ? Temporary store for the current instruction of a program ? Timing and Control Unit ? Control Signals : READY, RD, WR, ALE ? Status Signals : S0, S1, IO/M ? DMA Signals : HOLD, HLDA ? RESET Signals : RESET IN , RESET OUT
- 10. Functional Units : ? Interrupt Control : ? Controls interrupts during process ? Serial Input / Serial Output ? Used to read/write one bit data to and from peripheral devices. They are :- SID (Serial Input Data) line, SOD (Serial Output Data) Line
- 11. Functional Units : ? Address Buffer & Address-Data Buffer ? It stores the copied information from the memory for the execution ? Address Bus & Data Bus ? Address bus is uni-directional ? Data bus is bi-directional
- 12. Pin Diagram :
- 13. Basic Applications Of 8085 In General Life :