Mrp 1
- 1. Material Requirement Planning (MRP1)
- 2. What is MRP? Computerized Inventory Control Production Planning System Management Information System Manufacturing Control System
- 3. What is MRP ? (contd) This is the most comprehensive approach to manufacturing inventory and other dependents which demand an efficient inventory management system.
- 4. The MRP system determines item-by-item, what is to be processed and when, as well as what is to be manufactured when. This is based on order priorities and available capacities.
- 5. When to use MRP Job Shop Production Complex Products Assemble-to-Order Environments Discrete and Dependent Demand Items
- 6. What can MRP do? Reduce Inventory Levels Reduce Component Shortages Improve Shipping Performance Improve Customer Service Improve Productivity Simplified and Accurate Scheduling Reduce Purchasing Cost Improve Production Schedules Reduce Manufacturing Cost Reduce Lead Times Less Scrap and Rework Higher Production Quality
- 7. What can MRP do?(contd) Improve Communication Improve Plant Efficiency Reduce Freight Cost Reduction in Excess Inventory Reduce Overtime Improve Supply Schedules Improve Calculation of Material Requirements Improve Competitive Position
- 8. Three Basic Steps of MRP Identifying Requirements Running MRP ŌĆō Creating the Suggestions Firming the Suggestions
- 9. Step 1: Identifying the Requirements Quantity on Hand Quantity on Open Purchase Order Quantity in/or Planned for Manufacturing Quantity Committed to Existing Orders Quantity Forecasted
- 10. Step 1: Important Information MRP isŌĆ”.. Company Sensitive Location Sensitive Date Sensitive
- 11. Step 2: Running MRP ŌĆō Creating the Suggestions Critical Items Expedite Items Delay Items
- 12. Step 3: Firming the Suggestions Manufacturing Orders Purchasing Orders Various Reports
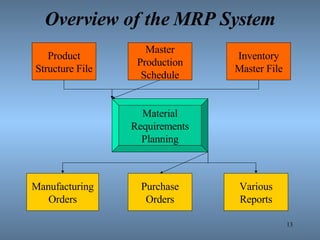
- 13. Overview of the MRP System Product Structure File Master Production Schedule Inventory Master File Material Requirements Planning Manufacturing Orders Purchase Orders Various Reports
- 14. MRP Inputs Product Structure File Master Production Schedule Inventory Master File
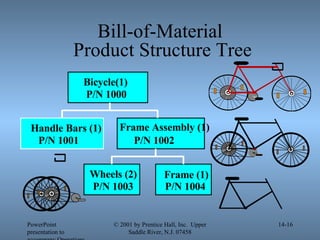
- 15. Product Structure File Bill of Materials: It is a materials list that provides information useful to reconstruct the manufacturing process. It is the master product definition that contains ŌĆ£as designedŌĆØ information.
- 16. Bill-of-Material Product Structure Tree PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) ┬® 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 14- Bicycle(1) P/N 1000 Handle Bars (1) P/N 1001 Frame Assembly (1) P/N 1002 Wheels (2) P/N 1003 Frame (1) P/N 1004
- 17. Master Production Schedule Schedule of Finished Products Represents Production, not Demand Combination of Customer Orders and Demand Forecasts What Needs to be Produced
- 18. Inventory Master File On-Hand Quantities On-Order Quantities Lot Sizes Safety Stock Lead Time Past-Usage Figures
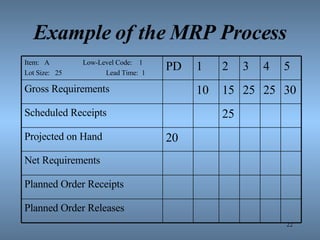
- 19. MRP Process Schedules the Production of all items using an MRP Matrix MRP Matrix Item: Low-Level Code: Lot Size: Lead Time: PD 1 2 3 4 5 Gross Requirements Scheduled Receipts Projected on Hand Net Requirements Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases
- 20. Terms Defined Item ŌĆō name or number for the item being scheduled Low-Level Code ŌĆō the lowest level of the item on the product structure file Lot Size ŌĆō order multiples of quantity Lead Time ŌĆō the time from when an order is placed to when it is received PD ŌĆō Past Due Time Bucket, orders behind schedule
- 21. Terms Defined Gross Requirements ŌĆō demand for an item by time period Scheduled Receipts ŌĆō material already ordered Projected on Hand ŌĆō expected ending inventory Net Requirements ŌĆō number of items to be provided and when Planned Order Receipts ŌĆō net requirements adjusted for lot size Planned Order Releases ŌĆō planned order receipts offset for lead times
- 22. Example of the MRP Process Item: A Low-Level Code: 1 Lot Size: 25 Lead Time: 1 PD 1 2 3 4 5 Gross Requirements 10 15 25 25 30 Scheduled Receipts 25 Projected on Hand 20 Net Requirements Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases
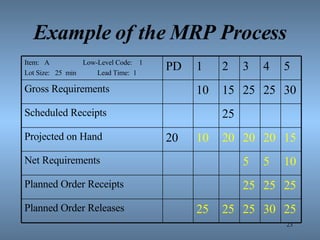
- 23. Example of the MRP Process Item: A Low-Level Code: 1 Lot Size: 25 min Lead Time: 1 PD 1 2 3 4 5 Gross Requirements 10 15 25 25 30 Scheduled Receipts 25 Projected on Hand 20 10 20 20 20 15 Net Requirements 5 5 10 Planned Order Receipts 25 25 25 Planned Order Releases 25 25 25 30 25
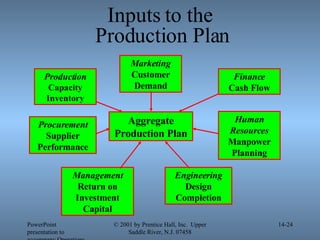
- 24. Inputs to the Production Plan PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) ┬® 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 14- Aggregate Production Plan Marketing Customer Demand Engineering Design Completion Management Return on Investment Capital Human Resources Manpower Planning Procurement Supplier Performance Finance Cash Flow Production Capacity Inventory
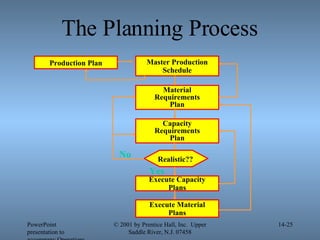
- 25. The Planning Process PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) ┬® 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 14- Production Plan Execute Material Plans Master Production Schedule Material Requirements Plan Capacity Requirements Plan Execute Capacity Plans Realistic?? No Yes
- 26. MRP Outputs Manufacturing Orders Purchasing Orders Various Reports
- 27. Hubbell Lighting Case Manufactures Industrial Lighting Products Good-Quality Products Poor at Meeting Due Dates Work is Specialized for Each Customer Job Shop Environment Complex Products
- 28. Hubbell Lighting Case Before MRP Implementation Less than 75% of orders completed on time After MRP Implementation 97% of orders completed on time 2% of orders completed with 1 to 2 days after due date
- 29. Summary of MRP MRP is aŌĆ”.. Computerized Inventory Control Production Planning System thatŌĆ”.. Schedules Component Items as Needed which willŌĆ”.. Track Inventory andŌĆ”.. Help you in many other aspects of business
Editor's Notes
- #2: Today we will discuss what Material Requirements Planning is and how we can use it in our organization.