Mt s12 test_execution
- 2. 2 Test Execution Objectives: 1. Definition: â The processing of a test case by the software under test, producing an outcome. 2. Purpose : â To execute the appropriate collections of tests required to evaluate product quality. â To capture test results that facilitate ongoing assessment of the product . Test Execution
- 3. 3 Execution Considerations: â Execute tests which are deemed highest risks first. â Tests on which there are many dependent tests will be executed first. â Test cases central to the architecture. â Test execution on number of Operating system, browsers, servers etc. â Execution Manual or Automated? Test Execution
- 4. 4 Execution Activities: 1. Set up Test platforms. 2. Identify Test cycle strategy. 3. Execute ïž Executing the Unit Test ïž Executing the Integration Test ïž Executing the System Test Test Execution
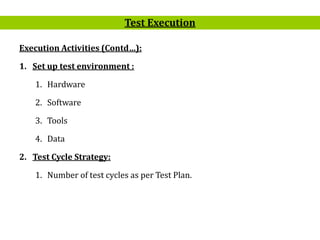
- 5. 5 Execution Activities (ContdâĶ): 1. Set up test environment : 1. Hardware 2. Software 3. Tools 4. Data 2. Test Cycle Strategy: 1. Number of test cycles as per Test Plan. Test Execution
- 6. 6 Execute Unit Tests: 1. Execute using tools or manually: 1. Execute tests individually 2. Execute a suite 2. Executed by Developer. 3. Defects are not reported in Defect Tracking tool. 4. Entrance Criteria: 1. The unit is compiled successfully. 2. Code has gone through Code inspection process. 3. Unit Test Environment is ready. Test Execution
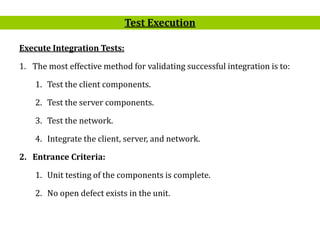
- 7. 7 Execute Integration Tests: 1. The most effective method for validating successful integration is to: 1. Test the client components. 2. Test the server components. 3. Test the network. 4. Integrate the client, server, and network. 2. Entrance Criteria: 1. Unit testing of the components is complete. 2. No open defect exists in the unit. Test Execution
- 8. 8 Execute System Tests: Entrance Criteria: âĒ Unit & Integration Testing must be successful. âĒ Set up system test environment, mirroring the planned production environment as closely as possible. âĒ Test Cases must be Reviewed & Approved Successfully. âĒ Build must be deployed in the Test Environment. âĒ Identify test cycles needed to replicate production where batch processing is involved. âĒ Assign test cases to test cycles. âĒ Execute the tests. Test Execution
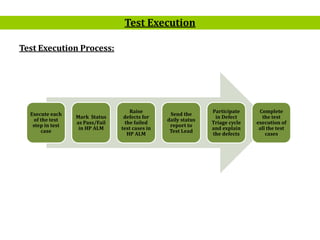
- 9. 9 Test Execution Process: Test Execution Execute each of the test step in test case Mark Status as Pass/Fail in HP ALM Raise defects for the failed test cases in HP ALM Send the daily status report to Test Lead Participate in Defect Triage cycle and explain the defects Complete the test execution of all the test cases
- 10. 10 Test Execution Process ContdâĶ: âĒ Once all Test cases are approved and the test environment is ready for testing, tester conduct smoke/sanity testing to confirm whether the build is testable or not. âĒ Each Tester is assigned Test cases directly in HP ALM. âĒ Testers to ensure necessary access to the testing environment, HP ALM for updating test status and raise defects. âĒ If any issues, will be escalated to the Test Lead and in turn to the Project Manager as escalation. âĒ If any showstopper during Smoke/Sanity testing will be escalated to the respective development team for fixes. Test Execution
- 11. 11 Test Execution Process ContdâĶ: âĒ Tester will prepare a Run chart with day-wise execution details. âĒ If any failures, defect will be raised as per severity guidelines in HP ALM tool detailing steps to simulate along with screenshots if appropriate. âĒ Daily Test execution status as well as Defect status will be reported to all stakeholders. âĒ Testing team will participate in defect triage meetings in order to ensure all test cases are executed with either pass/fail category. âĒ If there are any defects that are not part of steps but could be outside the test steps, such defects need to be captured in HP ALM and map it against the test case level or at the specific step that issue was encountered after confirming with Test Lead. Test Execution
- 12. 12 Test Execution Process ContdâĶ: âĒ This process is repeated until all test cases are executed fully with Pass/Fail status. âĒ During the subsequent cycle, any defects fixed applied will be tested and results will be updated in HP ALM during the cycle. Note: âĒ The defects identified will be documented in a defects report template or in a bug reporting tool, and then we report the same to developers. âĒ Once we receive a modified build from development team, we conduct smoke test, re-test and regression testing. âĒ If any new-defects identified again we document and report the same to developers. This process will continue until all test cases are passed and all reported defects are fixed and closed. Test Execution
- 13. 13 Review - When to Stop Testing: Test Manager will consider the following factors: â Deadlines, e.g. release deadlines, testing deadlines; â Test cases completed with certain percentage passed; â Test budget has been depleted; â Coverage of code, functionality or requirements reaches a specified point; â Bug rate falls below a certain level; or â Beta or alpha testing period ends Test Execution
- 14. 14 Concerns in Test Execution: 1. Software is not in a testable mode for this test level. 2. There is inadequate time and resources. 3. Significant problems will not be uncovered during testing. Test Execution
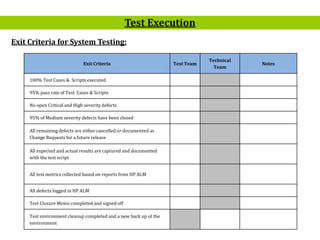
- 15. 15 Exit Criteria Test Team Technical Team Notes 100% Test Cases & Scripts executed 95% pass rate of Test Cases & Scripts No open Critical and High severity defects 95% of Medium severity defects have been closed All remaining defects are either cancelled or documented as Change Requests for a future release All expected and actual results are captured and documented with the test script All test metrics collected based on reports from HP ALM All defects logged in HP ALM Test Closure Memo completed and signed off Test environment cleanup completed and a new back up of the environment Test Execution Exit Criteria for System Testing:
- 16. 16 1. Exit criteria of Unit Testing is the Entry criteria for the Integration testing. 1. TRUE 2. FALSE 2. All the functionalities are implemented and all the âopenâ defects are addressed in the Unit Testing, will indicate ___________. 1. Exit criteria of Integration Testing 2. Exit criteria of System Testing 3. Exit criteria of UAT 4. Exit Criteria of Unit Testing Test Execution-Review Questions