Multi valve technology
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
2 likes•1,053 views
The presentation includes the information about multi valve engine technology. The presentation include the types of multi valve engine with pictures, advantages and disadvantages.
1 of 11
Download to read offline










Recommended
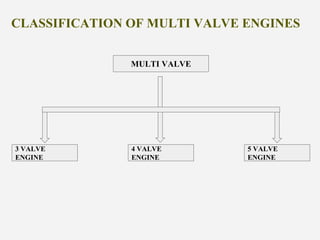
MULTIVALVE ENGINE 



MULTIVALVE ENGINE Nikhilesh Mane
Ěý
This pdf contains the multivalve engine description. the types of multivalve engine are also explain along with suitable pictures. the document gives idea the development in this technology today and market analysisVaccum braking system



Vaccum braking systemyajurvendra tomar
Ěý
The document summarizes the key components and working of a vacuum brake system used in trains. It describes the driver's brake valve, exhauster, dummy couplings, brake cylinders, vacuum reservoirs, brake pipes and other parts. It explains how applying the brakes causes a loss of vacuum in the brake pipe, pushing the piston up and engaging the brake blocks, while releasing the brakes restores vacuum. The vacuum brake allows partial braking and is fail-safe but is less effective than modern air brakes.A Seminar Report On Six Stroke Engine



A Seminar Report On Six Stroke EngineSaurabh Chaudhari
Ěý
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on a six-stroke engine. It describes how a six-stroke engine works, providing six piston movements per cycle through the use of a second piston or by capturing waste heat for an additional power stroke. The document outlines the history of six-stroke engine development and describes several notable six-stroke engine designs, including those that use steam or air from waste heat for a second power stroke and those that use an opposed secondary piston. It also discusses modifications made to convert a four-stroke engine to a six-stroke design. Compressed Air car ppt



Compressed Air car pptPushpendra Rajpoot
Ěý
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on a compressed air car. It describes the key components of the vehicle, including compressed air tanks that store air at 300 bars of pressure, a fiber body, air filters to remove impurities from compressed air, and an aluminum chassis. The presentation explains that the car runs on compressed air stored in the tanks instead of gasoline, with two pistons that compress and expand air to power the engine. It concludes that compressed air cars could help reduce pollution by eliminating the use of non-renewable fuels.CRDI ENGINE 



CRDI ENGINE HOME
Ěý
CRDI stands for common rail direct injection and directly injects fuel into engine cylinders via a single common rail connected to all fuel injectors. It was introduced to remove drawbacks of earlier fuel systems and allows even petrol engines to run with very lean fuel mixtures. The key components are a high pressure fuel pump, common rail, injectors, and engine control unit. CRDI provides benefits like 25% more power and torque, superior pickup, reduced noise and vibrations, and lower fuel consumption. While it has higher initial costs and maintenance than older systems, CRDI lowers emissions and improves engine performance.Six stroke engine ppt



Six stroke engine pptSYNERGY INSTITUTE OF ENGG & TECH,DHENKANALA
Ěý
This document provides an overview of six-stroke engine designs that aim to improve efficiency over traditional four-stroke engines. It describes the working principles of various six-stroke engine types, including single piston designs by Griffin, Bajulaz, Crower, and Velozeta as well as opposed piston designs like the Beare head engine. The document also discusses the modifications needed to convert a conventional engine to a six-stroke design and analyzes the advantages of six-stroke engines like reduced fuel consumption and emissions.Piston less pump



Piston less pumpSatyajeet Das
Ěý
Pistonless pump that makes them different from that of turbopump ,is the absence of piston.
This is a unique technique. In this ,no. of rotating parts is very less as compared to that of turbo pump.Automobile Chassis 



Automobile Chassis PEC University Chandigarh
Ěý
Types of Chassis,Frames type used in Automobiles,Frame and chassis materials,Tubular space frame,Aluminium space frame
Frame and body of Automobile



Frame and body of AutomobileRatnadeepsinh Jadeja
Ěý
Frame and Body of Automobile
Introduction to chassis, Classification of chassis, Conventional chassis,
Semi forward chassis, Full forward chassis, Engine at the front, Engine at the rear, Engine in mid, Frame of the automobile, Function of Frame, types of frame, conventional frame, semi-integral frame, integral frame, defects in chassis, Body of the automobile, types of the body in automobile, Electronic Brake force distribution (EBFD)



Electronic Brake force distribution (EBFD)Felis Goja
Ěý
EBDĚýis anĚýautomobile brakeĚýtechnology that automatically varies the amount ofĚýforceĚýapplied to each of a vehicle's wheels based on road conditions, speed, loading on wheel etc.
Transmission system of HEV



Transmission system of HEVYantralive Parts Technology Pvt. Ltd
Ěý
HEV is perhaps the hottest trend to which the world has adopted. This presentation will focus on different types of transmission systems used in HEVs. Explanation about different car body styles



Explanation about different car body stylesCar Leasing Made Simple
Ěý
This document discusses and defines different car body styles including 4x4, city car, coupe, estate, hatchback, MPV, saloon, and sports car. It provides details on each style such as 4x4 having all-wheel drive for rough terrain, city cars being compact for urban use, coupes having two doors and two or four seats, estates having additional cargo space, and hatchbacks having rear doors that open upward. MPVs are designed for multiple purposes like passenger and cargo transport, saloons have separate bonnets and boots, and sports cars prioritize handling and speed over comfort.Fuel energizer



Fuel energizerDhanush Raveendran
Ěý
The document discusses a fuel energizer, which is a device that uses magnets to realign fuel molecules and improve combustion in vehicle engines. It works by subjecting fuel molecules to a strong magnetic field as they pass through the energizer. This causes the molecules to better interlock with oxygen during combustion, resulting in more complete burning of the fuel. Test results showed reductions in harmful emissions like hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide of up to 92% and 85%, respectively. Fuel economy and engine performance also increased with use of the energizer. It provides an affordable alternative to catalytic converters for reducing emissions from vehicle exhaust.FRICTIONLESS COMPRESSION TECHNOLOGY



FRICTIONLESS COMPRESSION TECHNOLOGYANUGRAH MISHRA
Ěý
This document discusses the technology of frictionless compressors which use magnetic bearings and permanent magnet synchronous motors instead of traditional roller or hydrodynamic bearings. Some key advantages of frictionless compressors are that they have no friction, can run at high speeds up to 48,000 RPM with good speed control, are smaller and lighter than conventional compressors due to using permanent magnets instead of windings, and have reduced maintenance needs due to being oil-free. However, their initial price is 50-70% higher than normal compressors. Overall, frictionless compressors provide economic, energy, and environmental benefits after 10 years of development.Six Stroke Engine PPT



Six Stroke Engine PPTSaurabh Chaudhari
Ěý
The document describes a six-stroke engine, which has two additional strokes compared to a four-stroke engine. The additional strokes allow for water injection after the exhaust stroke, which vaporizes and drives the piston for another power stroke. This provides increased efficiency of 40% over a four-stroke engine due to capturing wasted heat. The document outlines the working principle, modifications needed to the engine like materials and cam shaft design, advantages like reduced emissions and fuel consumption, and limitations such as starting problems.Multi point fuel injection



Multi point fuel injectionRAVI KUMAR
Ěý
The document discusses multi-point fuel injection (MPFI) systems. It describes the components of an MPFI system, including the air intake system, pressure regulator system, control system, fuel pump control system, and functional divisions. An MPFI system injects fuel into individual cylinders based on commands from the engine control module. This provides faster throttle response and higher output under varying driving conditions compared to carburetor systems. The MPFI system can be divided into three main components: the electronic control unit, fuel system, and air induction system.Automotive fuel system presentation



Automotive fuel system presentationAbdirahman024
Ěý
The document summarizes an automotive fuel system report created by engineering students at Somali National University. It provides background on fuel systems and their importance, a brief history of their development, classifications of fuels, descriptions of key fuel system components like the fuel tank, lines, filters, pumps, and carburetor or injectors, as well as an overview of fuel additives and common types used.Six stroke engine(presentation)



Six stroke engine(presentation)Prateekvin
Ěý
This document describes the working principles and design of a six-stroke engine that uses water injection to improve efficiency. The six-stroke engine adds two additional strokes to the conventional four-stroke cycle to capture heat from the combustion process. In the secondary power stroke, water is injected into the superheated cylinder where it vaporizes, expanding and producing additional power. Thermodynamic analysis shows the six-stroke engine has higher thermal efficiency and lower fuel consumption compared to a four-stroke. However, modifications are needed to the engine components, camshaft, and valves to accommodate the additional strokes. While more efficient, the six-stroke engine also faces drawbacks such as difficulty starting when cold and requiring a source of neutral water.Automobile chassis,types of automobile



Automobile chassis,types of automobilekgmahesh123
Ěý
There are different types of automobile bodies depending on usage and vehicle type. Bodies are divided into passenger and commercial bodies. Vehicle bodies must meet certain requirements like being light, having sufficient space, withstanding vibrations and providing good visibility. The chassis, frame, and body are the main components of a vehicle. The chassis carries the load and withstands forces from braking, acceleration, and road conditions. Chassis frames can be conventional, integral, or semi-integral depending on their design and construction.Complete guide to Internal Combustion engines (IC engines)



Complete guide to Internal Combustion engines (IC engines)Syed Yaseen
Ěý
The following presentation is a part of an online course called "A brief overview of IC engine". The presentation contains complete information about IC engines and will be helpful for students of Mechanical and Automobile engineering. The presentation is full of graphics to reduce the efforts of students for imagination and help them to understand the concept as soon as possible.BRAKING SYSTEM



BRAKING SYSTEMkumar Sathish
Ěý
The document provides information about braking systems. It discusses the main functions of braking systems which are to stop the vehicle safely and control the vehicle when descending hills. It describes the two main types of braking system layouts - front/rear hydraulic split and diagonal split. It explains the components of braking systems including the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, and discusses different types of braking systems such as mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, and discusses components like brake linings. It provides diagrams to illustrate hydraulic and mechanical braking systems.Six stroke engine 



Six stroke engine Sivanjaneya Reddy
Ěý
The six-stroke engine was developed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions compared to conventional four-stroke engines. It operates with two additional strokes: in one, water is injected into the hot cylinder and turns to steam, forcing the piston down. In the other, the steam is exhausted up. This captures wasted heat to improve efficiency. Issues include potential engine damage from thermal expansion and needing separate water tanks. However, benefits are 40-60% reduced fuel use and lower emissions than four-stroke engines.Turbocharging



TurbochargingShubham Patel
Ěý
A turbocharger increases an engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber using a turbine powered by the engine's exhaust gases. It was invented in 1905 but took 20 years to be implemented. Turbochargers are used widely in vehicles to allow smaller engines to have improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and higher power/torque. A turbocharger works by using the exhaust flow to spin a turbine, which spins an air pump to compress more air into the engine.Dual Fuel Engine 



Dual Fuel Engine Hassan Raza
Ěý
This was presentation prepared by Mechanical Engineering students during their course of Internal Combustion Engines. EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION 



EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION nithishreddy1999
Ěý
IN OUR COUNTRY EVERY YEAR 10LAKH OF PEOPLE WERE SEVERELY AAFFECTED BY AIR POLLUTION IN WHICH AUTOMOBILES ARE THE MAJOR CONTRIBUTOR TO POLLUTION THEREFORE BY IMPLEMENTING RECIRCULATION TECHNOLOGY WE CAN REDUCE POLLUTION GENERATED FROM AUTOMOBILES. Hybrid Vehicle



Hybrid VehicleKaran Prajapati
Ěý
This slide is about the type of hybrid vehicle available in the market along with the case study of some hybrid cars. It is prepared from the study paper - presented at the SAE Research Paper competition, School of Technology, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University. The Research Paper on the above topic which is renamed as "Hybrid Vehicle: A Study on Technology" is published at http://www.ijert.org/view.php?id=12126&title=hybrid-vehicle-a-study-on-technology.Cryocar(1)



Cryocar(1)New Horizon Collage of Engineering
Ěý
This document summarizes a proposed vehicle called the Cryocar that is powered by liquid nitrogen. The Cryocar works similarly to a steam engine by pressurizing and vaporizing liquid nitrogen using ambient heat, which expands to drive the vehicle. It has zero emissions and refueling takes only a few minutes. However, issues around safety from nitrogen leaks and the energy required to liquefy nitrogen have prevented commercialization. The document outlines the components, working principle, advantages over electric vehicles, drawbacks, and potential solutions of the Cryocar concept.Common rail direct injection



Common rail direct injectionYashwadhan Sahi
Ěý
This document provides an overview of common rail direct injection (CRDI) technology for diesel engines. It discusses the history and development of CRDI, the operating principle, key components like the high-pressure pump and fuel rail, and how it works. CRDI allows for more precise fuel injection compared to older direct injection systems, improving power, efficiency and reducing emissions. It sees widespread use in modern passenger vehicles from many automakers. The document also covers the differences between direct and indirect injection, advantages and disadvantages of CRDI, and common applications.My six stroke engine



My six stroke enginepruthvi K
Ěý
This document discusses six-stroke engines as a more efficient alternative to four-stroke engines. It describes two main types of six-stroke engine designs: single piston and opposed piston. Several single piston engine examples are provided, including the Griffin engine which uses a heated vaporizer to improve fuel efficiency. The Bajulaz engine is also described, which uses two additional chambers above each cylinder for combustion and air preheating. Benefits over four-stroke engines include increased power and torque, lower emissions, and simpler design. However, six-stroke engines also have increased complexity and cost compared to four-stroke engines. The document suggests they may be best suited for applications like racing vehicles, heavy machinery, and stationary engines.Six stroke Engine by Harish Kushwaha



Six stroke Engine by Harish KushwahaHARISH KUSHWAHA
Ěý
The document discusses the six-stroke engine, which adds an additional power stroke compared to traditional four-stroke engines. It provides a brief history, describing how the concept was introduced in 1883 but the design did not fit automobiles until more recent inventions like the Bajulaz engine in 1989. The key features of six-stroke engines are described as increased efficiency, torque, and reduction in fuel consumption and pollution compared to four-stroke engines. Examples of different six-stroke engine types and designs are provided, along with their advantages and potential applications, particularly for automobiles where it could significantly reduce fuel use and emissions.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Frame and body of Automobile



Frame and body of AutomobileRatnadeepsinh Jadeja
Ěý
Frame and Body of Automobile
Introduction to chassis, Classification of chassis, Conventional chassis,
Semi forward chassis, Full forward chassis, Engine at the front, Engine at the rear, Engine in mid, Frame of the automobile, Function of Frame, types of frame, conventional frame, semi-integral frame, integral frame, defects in chassis, Body of the automobile, types of the body in automobile, Electronic Brake force distribution (EBFD)



Electronic Brake force distribution (EBFD)Felis Goja
Ěý
EBDĚýis anĚýautomobile brakeĚýtechnology that automatically varies the amount ofĚýforceĚýapplied to each of a vehicle's wheels based on road conditions, speed, loading on wheel etc.
Transmission system of HEV



Transmission system of HEVYantralive Parts Technology Pvt. Ltd
Ěý
HEV is perhaps the hottest trend to which the world has adopted. This presentation will focus on different types of transmission systems used in HEVs. Explanation about different car body styles



Explanation about different car body stylesCar Leasing Made Simple
Ěý
This document discusses and defines different car body styles including 4x4, city car, coupe, estate, hatchback, MPV, saloon, and sports car. It provides details on each style such as 4x4 having all-wheel drive for rough terrain, city cars being compact for urban use, coupes having two doors and two or four seats, estates having additional cargo space, and hatchbacks having rear doors that open upward. MPVs are designed for multiple purposes like passenger and cargo transport, saloons have separate bonnets and boots, and sports cars prioritize handling and speed over comfort.Fuel energizer



Fuel energizerDhanush Raveendran
Ěý
The document discusses a fuel energizer, which is a device that uses magnets to realign fuel molecules and improve combustion in vehicle engines. It works by subjecting fuel molecules to a strong magnetic field as they pass through the energizer. This causes the molecules to better interlock with oxygen during combustion, resulting in more complete burning of the fuel. Test results showed reductions in harmful emissions like hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide of up to 92% and 85%, respectively. Fuel economy and engine performance also increased with use of the energizer. It provides an affordable alternative to catalytic converters for reducing emissions from vehicle exhaust.FRICTIONLESS COMPRESSION TECHNOLOGY



FRICTIONLESS COMPRESSION TECHNOLOGYANUGRAH MISHRA
Ěý
This document discusses the technology of frictionless compressors which use magnetic bearings and permanent magnet synchronous motors instead of traditional roller or hydrodynamic bearings. Some key advantages of frictionless compressors are that they have no friction, can run at high speeds up to 48,000 RPM with good speed control, are smaller and lighter than conventional compressors due to using permanent magnets instead of windings, and have reduced maintenance needs due to being oil-free. However, their initial price is 50-70% higher than normal compressors. Overall, frictionless compressors provide economic, energy, and environmental benefits after 10 years of development.Six Stroke Engine PPT



Six Stroke Engine PPTSaurabh Chaudhari
Ěý
The document describes a six-stroke engine, which has two additional strokes compared to a four-stroke engine. The additional strokes allow for water injection after the exhaust stroke, which vaporizes and drives the piston for another power stroke. This provides increased efficiency of 40% over a four-stroke engine due to capturing wasted heat. The document outlines the working principle, modifications needed to the engine like materials and cam shaft design, advantages like reduced emissions and fuel consumption, and limitations such as starting problems.Multi point fuel injection



Multi point fuel injectionRAVI KUMAR
Ěý
The document discusses multi-point fuel injection (MPFI) systems. It describes the components of an MPFI system, including the air intake system, pressure regulator system, control system, fuel pump control system, and functional divisions. An MPFI system injects fuel into individual cylinders based on commands from the engine control module. This provides faster throttle response and higher output under varying driving conditions compared to carburetor systems. The MPFI system can be divided into three main components: the electronic control unit, fuel system, and air induction system.Automotive fuel system presentation



Automotive fuel system presentationAbdirahman024
Ěý
The document summarizes an automotive fuel system report created by engineering students at Somali National University. It provides background on fuel systems and their importance, a brief history of their development, classifications of fuels, descriptions of key fuel system components like the fuel tank, lines, filters, pumps, and carburetor or injectors, as well as an overview of fuel additives and common types used.Six stroke engine(presentation)



Six stroke engine(presentation)Prateekvin
Ěý
This document describes the working principles and design of a six-stroke engine that uses water injection to improve efficiency. The six-stroke engine adds two additional strokes to the conventional four-stroke cycle to capture heat from the combustion process. In the secondary power stroke, water is injected into the superheated cylinder where it vaporizes, expanding and producing additional power. Thermodynamic analysis shows the six-stroke engine has higher thermal efficiency and lower fuel consumption compared to a four-stroke. However, modifications are needed to the engine components, camshaft, and valves to accommodate the additional strokes. While more efficient, the six-stroke engine also faces drawbacks such as difficulty starting when cold and requiring a source of neutral water.Automobile chassis,types of automobile



Automobile chassis,types of automobilekgmahesh123
Ěý
There are different types of automobile bodies depending on usage and vehicle type. Bodies are divided into passenger and commercial bodies. Vehicle bodies must meet certain requirements like being light, having sufficient space, withstanding vibrations and providing good visibility. The chassis, frame, and body are the main components of a vehicle. The chassis carries the load and withstands forces from braking, acceleration, and road conditions. Chassis frames can be conventional, integral, or semi-integral depending on their design and construction.Complete guide to Internal Combustion engines (IC engines)



Complete guide to Internal Combustion engines (IC engines)Syed Yaseen
Ěý
The following presentation is a part of an online course called "A brief overview of IC engine". The presentation contains complete information about IC engines and will be helpful for students of Mechanical and Automobile engineering. The presentation is full of graphics to reduce the efforts of students for imagination and help them to understand the concept as soon as possible.BRAKING SYSTEM



BRAKING SYSTEMkumar Sathish
Ěý
The document provides information about braking systems. It discusses the main functions of braking systems which are to stop the vehicle safely and control the vehicle when descending hills. It describes the two main types of braking system layouts - front/rear hydraulic split and diagonal split. It explains the components of braking systems including the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, and discusses different types of braking systems such as mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, and discusses components like brake linings. It provides diagrams to illustrate hydraulic and mechanical braking systems.Six stroke engine 



Six stroke engine Sivanjaneya Reddy
Ěý
The six-stroke engine was developed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions compared to conventional four-stroke engines. It operates with two additional strokes: in one, water is injected into the hot cylinder and turns to steam, forcing the piston down. In the other, the steam is exhausted up. This captures wasted heat to improve efficiency. Issues include potential engine damage from thermal expansion and needing separate water tanks. However, benefits are 40-60% reduced fuel use and lower emissions than four-stroke engines.Turbocharging



TurbochargingShubham Patel
Ěý
A turbocharger increases an engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber using a turbine powered by the engine's exhaust gases. It was invented in 1905 but took 20 years to be implemented. Turbochargers are used widely in vehicles to allow smaller engines to have improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and higher power/torque. A turbocharger works by using the exhaust flow to spin a turbine, which spins an air pump to compress more air into the engine.Dual Fuel Engine 



Dual Fuel Engine Hassan Raza
Ěý
This was presentation prepared by Mechanical Engineering students during their course of Internal Combustion Engines. EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION 



EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION nithishreddy1999
Ěý
IN OUR COUNTRY EVERY YEAR 10LAKH OF PEOPLE WERE SEVERELY AAFFECTED BY AIR POLLUTION IN WHICH AUTOMOBILES ARE THE MAJOR CONTRIBUTOR TO POLLUTION THEREFORE BY IMPLEMENTING RECIRCULATION TECHNOLOGY WE CAN REDUCE POLLUTION GENERATED FROM AUTOMOBILES. Hybrid Vehicle



Hybrid VehicleKaran Prajapati
Ěý
This slide is about the type of hybrid vehicle available in the market along with the case study of some hybrid cars. It is prepared from the study paper - presented at the SAE Research Paper competition, School of Technology, Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University. The Research Paper on the above topic which is renamed as "Hybrid Vehicle: A Study on Technology" is published at http://www.ijert.org/view.php?id=12126&title=hybrid-vehicle-a-study-on-technology.Cryocar(1)



Cryocar(1)New Horizon Collage of Engineering
Ěý
This document summarizes a proposed vehicle called the Cryocar that is powered by liquid nitrogen. The Cryocar works similarly to a steam engine by pressurizing and vaporizing liquid nitrogen using ambient heat, which expands to drive the vehicle. It has zero emissions and refueling takes only a few minutes. However, issues around safety from nitrogen leaks and the energy required to liquefy nitrogen have prevented commercialization. The document outlines the components, working principle, advantages over electric vehicles, drawbacks, and potential solutions of the Cryocar concept.Common rail direct injection



Common rail direct injectionYashwadhan Sahi
Ěý
This document provides an overview of common rail direct injection (CRDI) technology for diesel engines. It discusses the history and development of CRDI, the operating principle, key components like the high-pressure pump and fuel rail, and how it works. CRDI allows for more precise fuel injection compared to older direct injection systems, improving power, efficiency and reducing emissions. It sees widespread use in modern passenger vehicles from many automakers. The document also covers the differences between direct and indirect injection, advantages and disadvantages of CRDI, and common applications.Similar to Multi valve technology (20)
My six stroke engine



My six stroke enginepruthvi K
Ěý
This document discusses six-stroke engines as a more efficient alternative to four-stroke engines. It describes two main types of six-stroke engine designs: single piston and opposed piston. Several single piston engine examples are provided, including the Griffin engine which uses a heated vaporizer to improve fuel efficiency. The Bajulaz engine is also described, which uses two additional chambers above each cylinder for combustion and air preheating. Benefits over four-stroke engines include increased power and torque, lower emissions, and simpler design. However, six-stroke engines also have increased complexity and cost compared to four-stroke engines. The document suggests they may be best suited for applications like racing vehicles, heavy machinery, and stationary engines.Six stroke Engine by Harish Kushwaha



Six stroke Engine by Harish KushwahaHARISH KUSHWAHA
Ěý
The document discusses the six-stroke engine, which adds an additional power stroke compared to traditional four-stroke engines. It provides a brief history, describing how the concept was introduced in 1883 but the design did not fit automobiles until more recent inventions like the Bajulaz engine in 1989. The key features of six-stroke engines are described as increased efficiency, torque, and reduction in fuel consumption and pollution compared to four-stroke engines. Examples of different six-stroke engine types and designs are provided, along with their advantages and potential applications, particularly for automobiles where it could significantly reduce fuel use and emissions.SIx stroke engine



SIx stroke engineNrj Nagarkoti
Ěý
A six stroke engine is a combination of 4+2 stroke engine.
in this type of engine all four stroke are same as like four stroke engine and two additional stroke is added the stroke are air intake and air exhaust.Wankle rotary engine by mrityunjaya chauhan



Wankle rotary engine by mrityunjaya chauhanMrityunjaya Chauhan
Ěý
The document discusses the Wankel rotary engine, including its history, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It was designed by Felix Wankel in the 1920s and primarily manufactured by Mazda. Key advantages include high power-to-weight ratio, small size, and ability to reach high RPMs with little vibration. Main disadvantages are lower fuel efficiency than piston engines and difficult emissions control. Applications include automobiles, motorcycles, aircraft, range extenders, and personal watercraft.Ic engines



Ic enginesSaleem Malik Chilakala
Ěý
This document provides an overview of internal combustion engines. It begins with an introduction that defines engines and heat engines. It then covers the history and classification of IC engines. The main parts of an IC engine are described along with advancements like direct fuel injection. Performance parameters and the operation of 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines are explained. Emerging technologies like digital triple spark ignition and nano engines are also discussed.126734966 study-case-engine



126734966 study-case-enginehomeworkping8
Ěý
The document discusses 3 vehicle engines - the Ford Fiesta 1.6L Ti-VCT I engine, the Volkswagen Polo 1.6L DOHC engine, and the Mini Cooper S 1.6L SOHC supercharged engine. It analyzes key specifications of each like compression ratio, materials, valves, and horsepower. Calculations were performed to determine the thermal efficiency of each, with the Ford engine found to be the most efficient at 62%, followed by the Volkswagen at 61%, and the Mini Cooper at 57% due to its supercharger.6-strokeengine



6-strokeengineRavi Kumar
Ěý
This document summarizes and compares a 4-stroke and 6-stroke internal combustion engine. It explains that a 6-stroke engine adds two additional strokes - an air intake stroke and air exhaust stroke - to the standard 4-stroke cycle. This captures normally wasted heat to power an additional piston stroke, thereby increasing fuel efficiency by up to 50%. The 6-stroke engine also generates less pollution and heat compared to a 4-stroke while maintaining similar power levels. In conclusion, 6-stroke engine technology promises more efficient use of fossil fuels and could help transition to an era with limited oil reserves.evolution of honda vtec engine



evolution of honda vtec engineyashonandanp
Ěý
This ppt is on evolution of vtec engines, also explains about the working of an engine along with explanation of an vtec engine.
This ppt on evolution of vtec engine published by HECTIC also briefs about the versions of vtec engines.Ice d-1 to 15 fundamentals



Ice d-1 to 15 fundamentalsjahanzaibkhawja
Ěý
The document compares the characteristics of four-stroke and two-stroke engines. Four-stroke engines have more moving parts, run cooler, are heavier, use separate fuel and oil, produce less power per revolution, and require less maintenance than two-stroke engines. However, two-stroke engines are smaller, lighter, more powerful per revolution, and more fuel efficient.R&D Project



R&D ProjectSood Sahil
Ěý
The document discusses a student project on the development of a diesel motorcycle. It provides details on the motorcycle's engine specifications, technical specifications, and parts. The engine is a 325cc 4-stroke air-cooled diesel engine that produces 6.5 bhp at 3600 rpm. The document also explains how diesel engines work through compression ignition and discusses advantages like fuel efficiency and reliability as well as emissions challenges.Trala



TralaSood Sahil
Ěý
The document discusses a student project on the development of a diesel motorcycle. It provides details on the motorcycle's engine specifications, technical specifications, and parts. The engine is a 325cc 4-stroke air-cooled diesel engine that produces 6.5 bhp at 3600 rpm. The document also explains how diesel engines work through compression ignition and discusses advantages like fuel efficiency and reliability as well as emissions challenges.R&D Project



R&D Projectsahil sood
Ěý
The document discusses a student project on the development of a diesel motorcycle. It provides details on the motorcycle's engine specifications, technical specifications, and parts. The engine is a 325cc 4-stroke air-cooled diesel engine that produces 6.5 bhp at 3600 rpm. The document also explains how diesel engines work through compression ignition and discusses advantages like fuel efficiency and reliability as well as emissions challenges.Hemi engine



Hemi enginesalamony1992
Ěý
The document discusses the design objectives and history of the hemispherical or "HEMI" engine. Key points include:
- HEMI engines aim to maximize power extraction from each combustion stroke by burning all fuel, having maximum cylinder pressure occur at the optimal crankshaft angle, and minimizing losses.
- Chrysler introduced the HEMI design in the 1950s to increase power without higher compression ratios. It provided better airflow and efficiency than flathead designs.
- Advantages of HEMI engines include smaller combustion chamber surface area, more room for larger intake/exhaust valves, and centrally-located spark plugs. However, disadvantages include sensitivity to fuel octane and inability to use moreFour stroke petrol engine



Four stroke petrol engineMuhammad Ali Bhalli Zada
Ěý
This document discusses the four-stroke petrol engine. It provides an introduction to four-stroke engines and their basic components. It then describes the four strokes of the engine's cycle: the intake stroke, compression stroke, power stroke, and exhaust stroke. The document also discusses the thermodynamic process, advantages and disadvantages, applications, and lubrication of the four-stroke petrol engine. It was authored by four students - Muhammad Ali, Muhammad Akhtar, Muhammad Waseem, and Usman Sajid.car and technology



car and technologyAnil Kumar
Ěý
The document summarizes the key systems and components of a typical car, including:
1) The major systems are the power plant (engine), power train (transmission), running gear (suspension, wheels), and control system (steering, brakes).
2) The power plant includes subsystems like the engine, fuel system, electrical system, exhaust, lubrication, and cooling.
3) Most cars use a four-stroke engine cycle to power the vehicle.Gagan.Ppt



Gagan.PptGaganpreet Singh
Ěý
New technologies in engines can provide economic, environmental, and efficiency benefits. These technologies include alternative fuels that are less polluting than conventional fuels, advanced ignition and fuel injection systems, new piston and valve designs, and lighter aluminum engine components. Variable valve timing, compression ratios, and turbocharging optimize engine performance for different operating conditions. Overall, the new technologies enhance engine efficiency and reduce emissions.Wankel engine



Wankel engineAbdul Rehman Basit
Ěý
The document summarizes the Wankel rotary engine. It describes the main parts of the engine including the rotor, housing, eccentric shaft, and apex seal. It explains the four-stroke working principle of intake, compression, power, and exhaust. The Wankel engine offers benefits like simplicity and high power but has disadvantages such as oil leakage and high fuel consumption. Applications include use in automotive racing, motorcycles, and aircraft.Different types of automotive engines



Different types of automotive enginesMyAssignmenthelp.com
Ěý
Types of Automotive Engines. Different types of engines.Know about the different types of car engines and the cars in which they were used.5 stroke ic engine



5 stroke ic engineFAHAD KHAN
Ěý
The 5-stroke internal combustion engine developed by Ilmor utilizes two firing cylinders that exhaust alternately into a central expansion cylinder, extracting extra work. This allows the engine to run with an expansion ratio of 14.5:1 like a diesel while achieving fuel consumption of only 226 g/kWh. The expansion and compression processes are decoupled, enabling independent optimization. Initial running of the prototype produced impressive fuel efficiency over a wide operating range due to greater work extraction in the low pressure cylinder upon knock onset, providing self-compensation.More from Nikhilesh Mane (11)
Be project - PRDS (Pressure Reducing And Desuperheater Station)



Be project - PRDS (Pressure Reducing And Desuperheater Station)Nikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The document describes the design of a pressure reducing and desuperheater station (PRDS) by a group of mechanical engineering students. It includes the objectives, methodology, design calculations, layout, and components of the PRDS. The group analyzed steam properties, selected valves and layout, designed an inline multi-nozzle desuperheater, and installed and analyzed the PRDS. Calculations were shown for sizing the steam and water pipes, nozzle dimensions, and validating the design was safe. The layout included valves, strainers, gauges and the desuperheater. References were provided for standards and related research.BE-Project Pressure Reducing And Desuperheater Station



BE-Project Pressure Reducing And Desuperheater StationNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
This document presents the design project of a Pressure Reducing and Desuperheating Station (PRDS) carried out by 4 mechanical engineering students to fulfill their bachelor's degree requirements. It includes an introduction to desuperheating and the need for a PRDS, a literature review on desuperheater design, the methodology adopted for the project, design calculations and layout, and plans for testing the final assembly.SCR VI Characteristics 



SCR VI Characteristics Nikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The report depicts the information about the SCR (Silicon Control Rectifier) circuit i.e. components, procedure.Be project final_project_first_stage_presentation



Be project final_project_first_stage_presentationNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The document describes the design of an inline desuperheater for Bajaj Power Equipment Pvt. LTD. It includes an introduction to desuperheaters and their purpose in reducing steam temperature for process applications. The objectives are to design an effective compact desuperheater and analyze its operation. The methodology involves analyzing steam properties, calculating desuperheater parameters, manufacturing it, and analyzing performance. Key calculations like mass flow rates and nozzle sizing are shown. The proposed design includes a steam pipe, spray nozzles, control valves, and sensors. References on desuperheater design and applications are also provided.Fy project black book



Fy project black bookNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
Final Year project Black Book. Gives description about each and every element used in project. Detail procedure of design and assembly of project model with images. Modern trends in automobile



Modern trends in automobileNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The presentation consists of the 5 modern trends in automobile sector. The history, working, and recent development of these trends are discussed in the presentation along with the images which help in understanding.GENEVA CONVEYOR



GENEVA CONVEYORNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The document give a brief idea of geneva mechanism and how it operates. this document also gives procedure to make geneva mechanism, methodology, components, design and calculationsEXAMPLE OF NOTICE (MEETING)



EXAMPLE OF NOTICE (MEETING)Nikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The document gives idea how the notice for any meeting should be, and it also gives format, and presentation of the noticeModern trends in automobile



Modern trends in automobileNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
The document is a project report on modern trends in the automobile sector. It discusses four key trends: continuous variable transmission (CVT), amphibious vehicles, flying cars, and fuel cell drives. The report provides details on the history, working principles, advantages and disadvantages of each trend. It aims to analyze how these trends can boost the automobile sector and their potential effects on the global market. Survey results from industry professionals on these trends are also included.Hydraulic turbines



Hydraulic turbinesNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
contains pelton turbine , kaplan turbine , and francis turbine with their working. contains GIF and videos of working Water pollution



Water pollutionNikhilesh Mane
Ěý
This document discusses water pollution, defining it as the contamination of water bodies by human activities. It outlines different types of water pollution like surface and groundwater pollution. It discusses facts about water and lists major causes of pollution like industrial waste, marine dumping, accidental oil spills, and urban/animal waste. The effects of pollution are described as harm to aquatic animals, diseases, and destroyed ecosystems. The document concludes with preventive measures like sewage treatment, river cleaning, self hygiene, and actions by governing bodies.Recently uploaded (20)
Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
Ěý
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACAI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharma



AI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharmaShivamSharma588604
Ěý
this ppt is made on the topic of water jug problem.Designing Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs to Prevent Failure



Designing Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs to Prevent FailureEpec Engineered Technologies
Ěý
Flex and rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be considered at the basic level some of the most complex PCBs in the industry. With that in mind, it’s incredibly easy to make a mistake, to leave something out, or to create a design that was doomed from the start.
Such design failures can end up leading to an eventual failure by delamination, short circuits, damage to the flex portions, and many other things. The easiest way to circumvent these is to start at the beginning, to design with preventing failure in mind rather than trying to fix existing designs to accommodate for problems.
In this webinar, we cover how to design flex and rigid-flex PCBs with failure prevention in mind to save time, money, and headaches, and what failure can look like.
For more information on our flex and rigid-flex PCB solutions, visit https://www.epectec.com/flex.GE 6B GT Ratcheting Animation- Hemananda Chinara.ppsx



GE 6B GT Ratcheting Animation- Hemananda Chinara.ppsxHemananda Chinara
Ěý
GE 6B Gas Turbine Ratcheting Mechanism Animation made by Hemananda Chinara, SIC, CPP, HPL.Failover System in Cloud Computing System



Failover System in Cloud Computing SystemHitesh Mohapatra
Ěý
Uses established clustering technologies for redundancy
Boosts availability and reliability of IT resources
Automatically transitions to standby instances when active resources become unavailable
Protects mission-critical software and reusable services from single points of failure
Can cover multiple geographical areas
Hosts redundant implementations of the same IT resource at each location
Relies on resource replication for monitoring defects and unavailability conditionsDefining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS
Ěý
Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
Machine Vision lecture notes for Unit 3.ppt



Machine Vision lecture notes for Unit 3.pptSATHISHKUMARSD1
Ěý
This is the document related to machine vision subject for final year mechatronics students.Von karman Equation full derivation .pdf



Von karman Equation full derivation .pdfEr. Gurmeet Singh
Ěý
Von karman Equation full derivation
By Er. GURMEET SINGH
G.C.E.T JAMMU
Contact: gurmeet.b.tech@gmail.com
M.tech Transportation Engineering TASK-DECOMPOSITION BASED ANOMALY DETECTION OF MASSIVE AND HIGH-VOLATILITY SES...



TASK-DECOMPOSITION BASED ANOMALY DETECTION OF MASSIVE AND HIGH-VOLATILITY SES...samueljackson3773
Ěý
The Science Information Network (SINET) is a Japanese academic backbone network for more than 800
universities and research institutions. The characteristic of SINET traffic is that it is enormous and highly
variableESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3prasadmutkule1
Ěý
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3 AI-Powered Power Converter Design Workflow.pdf



AI-Powered Power Converter Design Workflow.pdfAleksandr Terlo
Ěý
Blending human expertise with AI-driven optimization for efficient power converter design.Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
Ěý
Wireless technology used in chargerUnit 1- Review of Basic Concepts-part 1.pptx



Unit 1- Review of Basic Concepts-part 1.pptxSujataSonawane11
Ěý
DS, ADT, Algorithms, Asymptotic Notations are summarized. How to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?



How to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?CircuitDigest
Ěý
Learn how to measure speed using IR sensors in this simple DIY project. This tutorial cover circuit diagram, Sensor calibration and speed calculations and optimized Arduino code for real time speed measurements.Biases, our brain and software development



Biases, our brain and software developmentMatias Iacono
Ěý
Quick presentation about cognitive biases, classic psychological researches and quite new papers that displays how those biases might be impacting software developers.IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptx



IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptxatharvapardeshi03
Ěý
IoT-based-Electrical-Motor-Fault-Detection-System.pptx



