MULTIBAND reconfigurable antenna BATCH-5.pptx
- 1. JAWAHARLALNEHRU TECHNOLOGICALUNIVERSITY- GURAJADA-VIZIANAGARAM VIZIANAGARAM ŌĆō 535 003Andhra Pradesh (India) DESIGN AND VALIDATION OF MULTI-BAND RECONFIGURABLE ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS APPLICATIONS UNDER THE ESTEEMED GUIDANCE OF : Prof. K.Chandra Bhushana Rao Professor of ECE JNTU-GV BATCH 5: 19VV1A0401 - A.J.Sridhar 19VV1A0424 - J.Sai Sri 19VV1A0427 - K.Hema Malini 19VV1A0452 - Shaik Mohammeed Abbas 19VV1A0455 ŌĆō S.Lochani Vilehya
- 2. CONTENTS: ’āś OBJECTIVE ’āś DESIGN PARAMETERS ’āś DESIGN EQUATIONS ’āś DESIGN AND VALIDATION PROCEDURE ’āś SIMULATION STEPS IN HFSS ’āś IMPLEMENTATION : 1. ANTENNA DESIGN STEPS 2. ANTENNA DESIGN 3. DESIGN PARAMETERS OF THE PATCH AND GROUND 4. PIN DIODE (BAR50-02V) ’āś PIN DIODE SWITCHING RESULTS ’āś CONCLUSION ’āśSTATUS REPORT
- 3. OBJECTIVE: ’āśTo design a Multi-band frequency reconfigurable antenna. ’āś Obtain results in terms of S parameter, E and H field patterns , 3-D gain plot , and magnitude current distributions. ’āś To validate frequency reconfigurability of antenna with the help of switching of two pin diodes.
- 4. DESIGN PARAMETERS: 1.S parameter : It describes how much the waves are reflected or transmitted from/ through a antenna. The first parameter S11 is known as a reflection coefficient. 2. Resonant frequency : the frequency where maximum power is delivered to the patch of the antenna. 3.Gain : It is the ability of the antenna to radiate power more or less in any direction. 4.Directivity: the ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions. 5.Efficiency : It is the ratio of power radiated by the antenna to the power supplied to the antenna. 6.Front to back ratio: the ratio of power radiated in the front/main radiation lobe and the power radiated in the opposite direction . 7.Impedance bandwidth: the range of frequencies where the antenna has good impedance matching and can be heard by standing wave ratio (VSWR < 2) or module of the reflection coefficient (S11 <= -10 dB).
- 5. DESIGN EQUATIONS: Empirical mathematical equations to design square patch antenna are: W = Co 2ØæōØæ¤ 2 ŌłłØæ¤+1 , co is speed of light ŌłåØÉ┐ ŌäÄ = 0.412 ŌłłØæ¤ØæÆØæōØæō+03 ØæŖ ŌäÄ +0.264 ŌłłØæ¤ØæÆØæōØæōŌłÆ0.258 ØæŖ ŌäÄ +0.8 L = Co 2fr ŌłłØæ¤ØæÆØæōØæō -2ŌłåØÉ┐ ’āś In the typical design procedure of antenna, three essential parameters are: 1. Resonance frequency fr 2. Dielectric constant of the substrate, ╬Ąr 3. Thickness of substrate, h ’āś By increase in the substrate's dielectric constant (╬Ąr) and thickness (h) ,decreases the patch dimensions and small changes in return loss, bandwidth.
- 6. DESIGN AND VALIDATION PROCEDURE: ’āś Step-1: Synthesize the antenna dimensions based on the frequency of resonance, depending on the application. ’āś Step-2: Implement antenna design using simulation tool (HFSS). ’āś Step-3: Make the required changes to the antenna structure to get a multi-band operating response. ’āś Step-4: Include 2-pindiodes at appropriate places in the antenna structure. ’āś Step-5: Obtain the antenna design with 4 switching cases (ON-ON,ON-OFF,OFF-OFF,OFF-ON). ’āś Step-6: Optimize different parameters of the antenna to obtain optimal results. ’āś Step-7: Generate the resultant plots and values (S11,E and H plane Radiation pattern ,Gain , Directivity, Efficiency, Front to Back Ratio , Current distribution ,Radiated power) to verify the performance of designed antenna at multiple resonant frequency bands. ’āś Step-8: Fabricate the antenna and obtain the test results. ’āś Step-9: Compare the simulation results with the tested fabrication results. ’āś Step-10: Verify the antenna performance based on the comparison of simulation results with the tested fabrication results.
- 7. SIMULATION STEPS IN HFSS: 1. Open HFSS ’āĀinsert HFSS design 2. Insert a substrate with required dimensions and assign FR4 epoxy material (Ōłł=4.4) 3. Design the patch and ground structure on the same side of the substrate. 4. Assign the required boundaries to all parts of antenna . 5. Assign a lumped port to the feed line. 6. Insert the required radiation boundary such that it is ╬╗/4 distance away from all outer surfaces of the antenna. 7. Analyse and validate the antenna. 8. Obtain the resultant plots and values.
- 8. MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS OF PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS: 1. Return loss of antenna <= -10dB. 2. VSWR < 2. 3. Gain >= 3dB. 4. Radiation pattern of E and H field should be highly directional. 5. Radiation of antenna predominates in the FresnelŌĆÖs region ,which is the radiating near field of the antenna. 0.62 Øææ^3 ╬╗ < r < 2Øææ^2 ╬╗ d = maximum dimension of antenna ╬╗ = wavelength r = radius of the radiating sphere 6. In radiation pattern ,the major lobes must be predominant than the minor lobes.
- 9. IMPLEMENTATION: ANTENNA DESIGN STEPS STEP:1 STEP:2 STEP:3 STEP:4 STEP:5 STEP:6
- 10. STEP-1: Insert a box of length=35mm , width=40mm and height =1.6mm , which is defined as substrate. STEP-2: Add a rectangle of with required dimensions, which is defined as ground. STEP-3: Add 3 rectangles and unite them , to define a T shaped patch. STEP-4: Add 2 more rectangles at required positions to create a slot. STEP-5: Subtract the slots from the patch. STEP-6: Insert two pin diodes in the slots. STEP-7: Add a port to the T shaped patch. STEP-8: Create a box inculcating antenna of dimensions larger than substate of antenna, which act as a radiation box. STEP-9: Assign the required material, boundaries and excitation: 1. FR4 epoxy(╬Ą =4.4) - substate 2. perfect E boundary - patch and ground 3. lumped port - port 4. lumped RLC - switches 5. Radiation boundary and air medium - Radiation box
- 11. ANTENNA DESIGN TOP VIEW 3D VIEW patch substrate port Ground switch
- 12. Parameter Value(mm) Parameter Value(mm) L1 40 W1 35 L2 36 W2 25 L3 19 W3 2.5 L4 2 W4 3.06 L5 3 g1 1 L6 2 g2 1 L7 2 G1 16 DESIGN PARAMETERS OF THE PATCH AND GROUND :
- 13. PIN-DIODE(BAR50-02V): ’āś In this project we used two PIN diodes. ’āś The design of the PIN diode is based on RLC excitation values. ’āś The diode is operated in OFF state where Lf = 0.6nH , Cp = 0.15pF and parallel resistance Rp = 5Kohm and when operated in ON state , Lf = 0.6nH and series resistance Rs = 3 ohms. ’āś As we used 2 pin diodes , 4 switching cases are possible state Cp Rp Lf Rs ON - - 0.6 nH 3ohms OFF 0.15pF 5Kohms 0.6 nH - D1 D2 ON ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
- 14. PIN-DIODE SWITCHINGRESULTS: CONDITION RESONANT FREQUENCY IMPEDANCE BANDWIDTH ON-ON 1.8 GHz 353 MHz ON-OFF 5.75 GHz 8.62 GHz 1.1133 GHz 390 MHz OFF-OFF 6.21 GHz 1.3186 GHz OFF-ON 2.48 GHz 5.14 GHZ 570 MHz 193.7 MHz
- 15. DIODE STATE RESONANT FREQUENCY(GHz) FREQUENCY BAND FH (GHz) FL (GHz) BANDWIDTH(FH-FL) ON-ON 1.8 L 2.0119 1.6186 353 MHz ON-OFF 5.75 8.62 C X 6.51 8.86 5.3967 8.47 1.1133 GHz 390 MHz OFF-ON 2.48 5.14 S C 2.784 5.2337 2.212 5.04 570 MHz 193.7 MHz OFF-OFF 6.21 C 7.21 5.8914 1.3186 GHz BANDWIDTH CALCULATION: ’āś Draw a horizontal line on to S11 curve at -10dB, it cuts the deep of the resonant frequency curve at 2 points called FH(high frequency) and FL(low frequency) ’āś BANDWIDTH = High frequency ŌĆō Low frequency (FH-FL)
- 16. E-Plane Radiation Pattern D1,D2=ON,ON: AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 1.8GHz H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained two major lobes in both E and H field radiation patterns E-field: 22.15V/m at 0deg and 23.32V/m at 180deg H-field: 21.13A/m at 270deg and 21.07A/m at 90deg
- 17. Vector Current Distribution 3D-gain plot of antenna E-field Distribution Obtained a maximum gain of 5.6dB
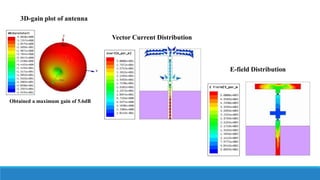
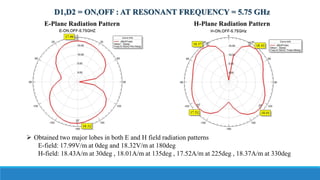
- 18. D1,D2 = ON,OFF : AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 5.75 GHz E-Plane Radiation Pattern H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained two major lobes in both E and H field radiation patterns E-field: 17.99V/m at 0deg and 18.32V/m at 180deg H-field: 18.43A/m at 30deg , 18.01A/m at 135deg , 17.52A/m at 225deg , 18.37A/m at 330deg
- 19. Vector Current Distribution 3D-gain plot of antenna E-field Distribution Obtained a maximum gain of 1.98dB
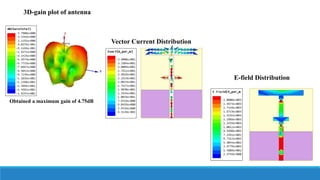
- 20. D1,D2 = ON,OFF : AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 8.62 GHz E-Plane Radiation Pattern H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained major and minor lobes in both E and H field radiation patterns E-field: 16.5V/m at 330deg , 14.73V/m at 10deg , 12.85V/m at 60deg , 13.08V/m at 120deg ,14.54V/m at 160deg, 14.46V/m at 240deg H-field: 17.36A/m at 20deg , 17.82A/m at 90deg , 18.74A/m at 150deg , 17.33A/m at 225deg, 15.27A/m at 225deg
- 21. 3D-gain plot of antenna Vector Current Distribution E-field Distribution Obtained a maximum gain of 4.75dB
- 22. D1,D2 = OFF,ON : AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 2.48 GHz E-Plane Radiation Pattern H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained two major lobes in both E and H field radiation patterns E-field: 20.3V/m at 0deg and 21.75V/m at 180deg H-field: 19.02A/m at 90deg , 18.88A/m at 270deg
- 23. 3D-gain plot of antenna Vector Current Distribution E-field Distribution Obtained a maximum gain of 4.04dB
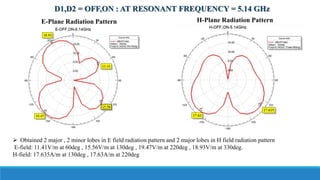
- 24. D1,D2 = OFF,ON : AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 5.14 GHz E-Plane Radiation Pattern H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained 2 major , 2 minor lobes in E field radiation pattern and 2 major lobes in H field radiation pattern E-field: 11.41V/m at 60deg , 15.56V/m at 130deg , 19.47V/m at 220deg , 18.93V/m at 330deg. H-field: 17.635A/m at 130deg , 17.63A/m at 220deg
- 25. 3D-gain plot of antenna Vector Current Distribution E-field Distribution Obtained a maximum gain of 2.014dB
- 26. D1,D2 = OFF,OFF : AT RESONANT FREQUENCY = 6.21 GHz E-Plane Radiation Pattern H-Plane Radiation Pattern ’āś Obtained two major lobes in both E and H field radiation patterns E-field: 13.01V/m at 60deg and 13.85V/m at 120deg,16.7V/m at 210deg , 18.75V/m at 340deg H-field: 19.01A/m at 30deg , 19.09A/m at 130deg , 18.63A/m at 230deg , 18.99A/m at 330deg
- 27. 3D-gain plot of antenna Obtained a maximum gain of 2.89dB Vector Current Distribution E-field Distribution
- 28. REASONS FOR VARIATION OF THE RADIATION PATTERN IN 4 DIODE SWITCHING CASES ’āś In general, the radiation pattern of an antenna is affected by a range of factors, including 1. the physical characteristics of the antenna 2. the frequency of the signal 3. By switching different elements using diodes ’āś In an antenna, diodes are often used as switches to switch different elements of the antenna on and off, which can help to direct the radiation in a specific direction. ’āś When a diode is switched on or off, it can affect the current flowing through the antenna, and this can affect the radiation pattern. Specifically, the diode switching can affect the phase and amplitude of the electromagnetic waves radiated by the antenna. ’āś In a switchable beam antenna, when a diode is switched from a forward-biased state to a reverse-biased state, the electric field within the diode can cause the charge carriers to be accelerated in the opposite direction. This can result in the emission of radiation in a different direction than when the diode was in the forward-biased state.
- 29. DIODE SWITCHING S11(REFLECTION COEFFICIENT) (dB) IMPEDANCE BANDWIDTH RESONANT FREQUENCY (GHz) FREQUENCY BAND GAIN (dB) DIRECTIVITY FRONT BACK RATIO EFFICIEN CY RADIATED POWER(W) BAND APPLICATIONS ON ON -18.4457 353 MHz 1.8 GHz L 3.6324 2.24 1.3096 1.6216 1.5985 Bluetooth ON OFF -38.2287 -13.3273 1.1133 GHz 390 MHz 5.75 GHz 8.62 GHz C X 1.5806 2.9854 1.8307 3.6549 1.9979 7.6014 0.8634 0.8168 0.8633 0.7788 WLAN OFF OFF -29.0031 1.3186 GHz 6.21 GHz C 1.9467 2.1526 1.2347 0.9044 0.9941 WLAN OFF ON -18.2855 -11.769 570 MHz 193.7 MHz 2.48 GHz 5.14 GHZ S C 2.5359 1.5903 2.5132 2.7222 1.394 6.0136 1.009 0.5842 0.5453 0.9032 Wi-Fi WiMAX ANTENNA WITH PIN DIODES RESULTS: D1 D2
- 30. CONCLUSION: ’āś Measured results shows that the antenna exhibits frequency reconfigurability at four switching modes (ON- ON,ON-OFF,OFF-ON,OFF-OFF) at six resonant frequencies 1.8GHz ,5.75GHz, 8.62GHz , 2.48GHz , 5.14GHz and 6.21GHz. ’āś The antenna is operated at L,C,S and X band , exhibits almost omnidirectional radiation patterns both in E- and H- planes. ’āś Due to the switching mechanism of the diode we obtained different radiation patterns in the 4 switching cases. ’āś The reflection coefficient (S11) is less than -10dB for all above frequencies which is a sign of better result. ’āś The gain obtained in the above frequencies are positive , it specifies the maximum input power is fed in a particular direction. ’āś The resonant frequency range of antenna is used for the wireless applications like Bluetooth , WLAN, Wi-Fi and WiMAX.
- 31. STATUS REPORT WORK DONE: ’āś Antenna designing ’āś Analysed and verified antenna parameters ’āś Obtained frequency reconfigurability ’āś Obtained required plots and values through simulation in HFSS WORK TO BE DONE: ’āś Antenna fabrication Fabrication status : antenna structure is verified and will be fabricated within 10-15 days ’āś To obtain hardware results ’āś Comparison of hardware and simulation results