Mv perivalvular leak
Download as PPT, PDF1 like190 views
Perivalvular leak. Structural heart disease. Vascular plug. Interventional cardiology. Mechanical prosthesis. Mitral regurgitation.
1 of 14
Download to read offline












Recommended
Transesophageal ECHO in anesthesia lecture usama Elsayed 



Transesophageal ECHO in anesthesia lecture usama Elsayed usama elsayed
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) in anesthesia. It discusses the equipment used for TEE including ultrasound transducers and probes. Indications for TEE include cardiac and noncardiac surgeries, while contraindications include esophageal and gastric pathology. Complications of TEE can include esophageal injury, bleeding, and dental damage. Several standard TEE views are described including the 4-chamber, 2-chamber, aortic valve, and bicaval views which provide assessment of cardiac structures and function.Perception and coordination



Perception and coordinationArt Bryan Arcinas
Ėý
1. Full consciousness is an alert state where one is oriented to person, place, time and can comprehend language and think clearly.
2. A confused state involves disorientation and inability to think clearly or use sound judgment.
3. Lethargy is characterized by slowed speech, mental processing and motor activity while still maintaining some orientation.CNS Ppt



CNS Pptprecyrose
Ėý
The document provides information on neuroanatomy and physiology, including the structure and function of the central and peripheral nervous systems, brain anatomy and lobes, spinal cord anatomy, and various diagnostic assessments for the neurologic system such as lumbar puncture, CT scan, EEG, and evoked responses. Key areas covered include the brainstem, cerebellum, meninges, cranial nerves, increased intracranial pressure manifestations and treatment, and aphasia.Perception And Coordination



Perception And Coordinationshenell delfin
Ėý
The document discusses perception, coordination, brain anatomy, cranial nerves, levels of consciousness, neurological assessment of older adults, the Glasgow Coma Scale, and common neurological diagnostic tests. It provides nursing implications for several diagnostic tests including MRI, CT scan, EEG, and lumbar puncture. Critical thinking questions assess ability to apply knowledge of the Glasgow Coma Scale.2nd lect mri safety7 very-short_form



2nd lect mri safety7 very-short_formhutham
Ėý
MRI uses powerful magnets that can be dangerous if metal objects are brought into the scan room, as they can become projectiles that pose risks to patients and staff. Strict safety precautions must be followed when in an MRI suite to avoid injury, including removing all metal, respecting the magnetic field, and not entering the magnet room alone. Pregnancy is generally not considered a risk for MRI, but the first trimester should be avoided out of an abundance of caution due to potential effects on rapidly developing cells.Neurological examination



Neurological examinationRam Prasad
Ėý
The document outlines the steps and components of a neurological examination. It includes obtaining a comprehensive health history, performing a physical exam testing vital signs, cranial nerves, motor skills, coordination, and reflexes. Neurological exams also involve assessing the patient's mental status and administering tests of sensation. The goal is to gather clinical information about any neurological abnormalities through a standardized exam process.Neurologic nursing



Neurologic nursingClarissa Sabado
Ėý
Perception involves awareness of sensory stimuli through mental processes like memory and interpretation. Coordination requires perception of necessary movements and completion of actions via muscles working together. The central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, autonomic nervous system, and neuroendocrine system control coordination and perception. [Neurons, neuroglia, neurotransmitters, and nerves are the basic structures involved. The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system includes cranial and spinal nerves. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions and has sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.]Lumbar puncture



Lumbar punctureCristi Francis
Ėý
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure where cerebrospinal fluid is collected from the lower back for diagnostic purposes. It is indicated for conditions like meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and certain CNS diseases. Contraindications include infected skin at the needle site, brain abnormalities, or increased intracranial pressure. The procedure involves locating the interspace between vertebrae, inserting a needle at a slight upward angle, and checking for fluid return. Potential complications are local pain, infection, bleeding, spinal fluid leak, or spinal headache.Perception And Coordination Revised



Perception And Coordination RevisedTosca Torres
Ėý
The document discusses sensory perception and coordination. It defines key terms like sensory reception, kinesthetics, stereognosis, and visceral sensation. It describes the four aspects of the sensory process - stimulus, receptor, impulse conduction, and perception. It discusses factors that can affect sensory perception like environment, previous experience, and illness. It also outlines nursing interventions to promote normal sensory perception like stimulation, sensory aids, positioning, joint mobility exercises, ambulation assistance, and assistive devices.Ct carotid and cerebral



Ct carotid and cerebralMithlesh shah
Ėý
CT carotid and cerebral angiography is used to study the neck arteries (carotid arteries) and brain arteries (cerebral arteries) using a CT scanner. It can detect aneurysms, narrowing of arteries in the brain, abnormal blood vessels, stenosis, and narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. The procedure involves inserting a cannula if needed, obtaining plain CT images of the neck and brain, injecting contrast dye using a pressure injector, and obtaining images of the arteries. It can help determine the risk of future strokes and identify issues like strictures of the carotid arteries.Roentgenology of skull



Roentgenology of skullakshay_gursale
Ėý
The document discusses the anatomy and radiographic evaluation of the skull, describing the bones that make up the cranial vault and facial skeleton, landmarks and sutures, skull projections including PA, lateral, Towne's view and submentovertical views, and anatomical structures visible on each view such as sinuses, foramina and cervical spine. Standard exposure factors are provided for the various skull radiographic projections.Basic anatomy Views -importance and positioning Interpretation Skull radiography



Basic anatomy Views -importance and positioning Interpretation Skull radiographyairwave12
Ėý
The document provides instructions for various skull and sinus x-ray views including positioning, collimation, and interpretation guidelines. Key views covered include PA, Caldwell, Chamberlain-Townes, lateral, base, Schuller's, Water's, sinus lateral, and basilar views. Proper positioning is emphasized to ensure quality images and evaluation of important anatomical structures like the sinuses, orbits, and temporomandibular joints.Lumbar puncture 



Lumbar puncture Aravind Ravi
Ėý
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is performed to obtain cerebrospinal fluid for diagnostic purposes. It carries risks such as post-lumbar puncture headache, infection, and nerve injury. The procedure involves positioning the patient, prepping and draping the skin, administering local anesthesia, and inserting a spinal needle between lumbar vertebrae to collect CSF samples for analysis. Complications are usually minor but can include headache, back pain, bleeding, or neurological issues and may require treatment.Understanding ultrasound



Understanding ultrasoundMohammad Amir
Ėý
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures. It has several medical applications such as visualizing soft tissues, assessing blood vessels, and guiding procedures. The document discusses how ultrasound works, including how sound waves are produced and reflected to form images, and factors that affect image quality such as frequency, attenuation, and gain. Ultrasound is a valuable medical imaging tool when used by an operator with the proper knowledge and skills to acquire and interpret the images.Basics of CT Scan



Basics of CT ScanDr. Sreedhar Rao
Ėý
CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body by combining x-rays with computer technology. CT scans are useful for diagnosing many medical conditions by allowing physicians to examine tissues and organs. While CT scans provide valuable medical information with minimal risks, they do involve exposure to radiation, so the benefits must be weighed against the risks for each individual patient's circumstance.Basics of Ultrasound



Basics of UltrasoundDr. Sreedhar Rao
Ėý
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body in real-time without using radiation. It is widely used due to its availability, low cost, speed, and ability to show internal structures and blood flow. Common uses include examining organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys, as well as guiding procedures, imaging breasts and blood vessels, and assessing fetal development in pregnancies. The procedure works by a transducer sending sound waves into the body and receiving echoes to create images based on the return signal.Computer Tomography (CT Scan)



Computer Tomography (CT Scan)Likan Patra
Ėý
Computed tomography (CT scan) is a medical imaging procedure that uses computer-processed X-rays to produce tomographic images or 'slices' of specific areas of the body. These cross-sectional images are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical disciplines.X ray



X rayWaliullah Wali
Ėý
This document provides an overview of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques. It discusses the principles, methods, applications, advantages, and limitations of both XRD and XRF. XRD is described as a technique that uses X-ray scattering from crystalline materials to determine their atomic structure, while XRF involves bombarding a material with X-rays and analyzing the characteristic secondary X-rays emitted to determine its elemental composition. A variety of applications are outlined for each technique in fields such as materials science, geology, and chemistry.Basic principles of CT scanning



Basic principles of CT scanningHareesha N Gowda, Dayananda Sagar College of Engg, Bangalore
Ėý
This presentation gives an information about Basic principles of CT scanning covering the syllabus of Non Destructive testing Mri ppt



Mri pptshonimaindiaultrasound
Ėý
MRI uses magnetism and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues in the body. It was developed based on principles of nuclear magnetic resonance and the first MRI exam took 5 hours to produce one image. Key components of an MRI scanner include powerful magnets to align hydrogen nuclei in tissues, gradient coils to localize images, and radiofrequency coils to transmit signals and receive returning signals used to construct images. MRI provides advantages over other imaging techniques by using no ionizing radiation and allowing cross-sectional imaging in any plane with good contrast resolution.Ct Basics



Ct BasicsPramod Krishnan
Ėý
Computerized tomography (CT) was pioneered by Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack in the 1970s. CT uses X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the body. The first CT scanners used a translate-rotate design, while later generations used multiple detectors and spiral scanning for faster, more detailed imaging. Image reconstruction uses back projection to convert attenuation measurements into pixel values and display slices. CT provides excellent anatomical detail and is widely used for diagnosing conditions of the brain, blood vessels, lungs and other organs.BASICS of CT Head



BASICS of CT HeadKunal Mahajan
Ėý
The document provides guidance on reading head CT scans for physicians. It outlines the basic principles of CT scanning, including its history and components. It then reviews normal neuroanatomy as seen on head CT scans, illustrating various anatomical structures and landmarks visible in different axial sections. The document aims to help physicians accurately interpret CT findings to diagnose and treat time-sensitive conditions without specialist assistance.Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
Ėý
Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
ðĄ Key Topics Covered:
âïļ Viable air & surface sampling best practices
âïļ USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
âïļ How to analyze & trend viable sample data
âïļ Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
ðĨ Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
ðĒ Stay informedâfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
Ėý
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH Guidelines



Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH GuidelinesKHUSHAL CHAVAN
Ėý
This presentation covers the stability testing of pharmaceutical dosage forms according to ICH guidelines (Q1A-Q1F). It explains the definition of stability, various testing protocols, storage conditions, and evaluation criteria required for regulatory submissions. Key topics include stress testing, container closure systems, stability commitment, and photostability testing. The guidelines ensure that pharmaceutical products maintain their identity, purity, strength, and efficacy throughout their shelf life. This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical professionals, researchers, and regulatory experts.Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management â A Comprehensive Overview



Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management â A Comprehensive OverviewDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
Ėý
This presentation provides a detailed yet concise overview of Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It covers the definition, etiology (causes), different types, signs & symptoms, and common triggers of asthma. The content highlights both allergic (extrinsic) and non-allergic (intrinsic) asthma, along with specific forms like exercise-induced, occupational, drug-induced, and nocturnal asthma.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, student, or someone looking to understand asthma better, this presentation offers valuable insights into the condition and its management.BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
Ėý
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdf



X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdfMohd Faraz
Ėý
An X-ray generator is a crucial device used in medical imaging, industry, and research to produce X-rays. It operates by accelerating electrons toward a metal target, generating X-ray radiation. Key components include the X-ray tube, transformer assembly, rectifier system, and high-tension circuits. Various types, such as single-phase, three-phase, constant potential, and high-frequency generators, offer different efficiency levels. High-frequency generators are the most advanced, providing stable, high-quality imaging with minimal radiation exposure. X-ray generators play a vital role in diagnostics, security screening, and industrial testing while requiring strict radiation safety measures.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (14)
Perception And Coordination Revised



Perception And Coordination RevisedTosca Torres
Ėý
The document discusses sensory perception and coordination. It defines key terms like sensory reception, kinesthetics, stereognosis, and visceral sensation. It describes the four aspects of the sensory process - stimulus, receptor, impulse conduction, and perception. It discusses factors that can affect sensory perception like environment, previous experience, and illness. It also outlines nursing interventions to promote normal sensory perception like stimulation, sensory aids, positioning, joint mobility exercises, ambulation assistance, and assistive devices.Ct carotid and cerebral



Ct carotid and cerebralMithlesh shah
Ėý
CT carotid and cerebral angiography is used to study the neck arteries (carotid arteries) and brain arteries (cerebral arteries) using a CT scanner. It can detect aneurysms, narrowing of arteries in the brain, abnormal blood vessels, stenosis, and narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. The procedure involves inserting a cannula if needed, obtaining plain CT images of the neck and brain, injecting contrast dye using a pressure injector, and obtaining images of the arteries. It can help determine the risk of future strokes and identify issues like strictures of the carotid arteries.Roentgenology of skull



Roentgenology of skullakshay_gursale
Ėý
The document discusses the anatomy and radiographic evaluation of the skull, describing the bones that make up the cranial vault and facial skeleton, landmarks and sutures, skull projections including PA, lateral, Towne's view and submentovertical views, and anatomical structures visible on each view such as sinuses, foramina and cervical spine. Standard exposure factors are provided for the various skull radiographic projections.Basic anatomy Views -importance and positioning Interpretation Skull radiography



Basic anatomy Views -importance and positioning Interpretation Skull radiographyairwave12
Ėý
The document provides instructions for various skull and sinus x-ray views including positioning, collimation, and interpretation guidelines. Key views covered include PA, Caldwell, Chamberlain-Townes, lateral, base, Schuller's, Water's, sinus lateral, and basilar views. Proper positioning is emphasized to ensure quality images and evaluation of important anatomical structures like the sinuses, orbits, and temporomandibular joints.Lumbar puncture 



Lumbar puncture Aravind Ravi
Ėý
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is performed to obtain cerebrospinal fluid for diagnostic purposes. It carries risks such as post-lumbar puncture headache, infection, and nerve injury. The procedure involves positioning the patient, prepping and draping the skin, administering local anesthesia, and inserting a spinal needle between lumbar vertebrae to collect CSF samples for analysis. Complications are usually minor but can include headache, back pain, bleeding, or neurological issues and may require treatment.Understanding ultrasound



Understanding ultrasoundMohammad Amir
Ėý
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures. It has several medical applications such as visualizing soft tissues, assessing blood vessels, and guiding procedures. The document discusses how ultrasound works, including how sound waves are produced and reflected to form images, and factors that affect image quality such as frequency, attenuation, and gain. Ultrasound is a valuable medical imaging tool when used by an operator with the proper knowledge and skills to acquire and interpret the images.Basics of CT Scan



Basics of CT ScanDr. Sreedhar Rao
Ėý
CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body by combining x-rays with computer technology. CT scans are useful for diagnosing many medical conditions by allowing physicians to examine tissues and organs. While CT scans provide valuable medical information with minimal risks, they do involve exposure to radiation, so the benefits must be weighed against the risks for each individual patient's circumstance.Basics of Ultrasound



Basics of UltrasoundDr. Sreedhar Rao
Ėý
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body in real-time without using radiation. It is widely used due to its availability, low cost, speed, and ability to show internal structures and blood flow. Common uses include examining organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys, as well as guiding procedures, imaging breasts and blood vessels, and assessing fetal development in pregnancies. The procedure works by a transducer sending sound waves into the body and receiving echoes to create images based on the return signal.Computer Tomography (CT Scan)



Computer Tomography (CT Scan)Likan Patra
Ėý
Computed tomography (CT scan) is a medical imaging procedure that uses computer-processed X-rays to produce tomographic images or 'slices' of specific areas of the body. These cross-sectional images are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical disciplines.X ray



X rayWaliullah Wali
Ėý
This document provides an overview of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques. It discusses the principles, methods, applications, advantages, and limitations of both XRD and XRF. XRD is described as a technique that uses X-ray scattering from crystalline materials to determine their atomic structure, while XRF involves bombarding a material with X-rays and analyzing the characteristic secondary X-rays emitted to determine its elemental composition. A variety of applications are outlined for each technique in fields such as materials science, geology, and chemistry.Basic principles of CT scanning



Basic principles of CT scanningHareesha N Gowda, Dayananda Sagar College of Engg, Bangalore
Ėý
This presentation gives an information about Basic principles of CT scanning covering the syllabus of Non Destructive testing Mri ppt



Mri pptshonimaindiaultrasound
Ėý
MRI uses magnetism and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues in the body. It was developed based on principles of nuclear magnetic resonance and the first MRI exam took 5 hours to produce one image. Key components of an MRI scanner include powerful magnets to align hydrogen nuclei in tissues, gradient coils to localize images, and radiofrequency coils to transmit signals and receive returning signals used to construct images. MRI provides advantages over other imaging techniques by using no ionizing radiation and allowing cross-sectional imaging in any plane with good contrast resolution.Ct Basics



Ct BasicsPramod Krishnan
Ėý
Computerized tomography (CT) was pioneered by Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack in the 1970s. CT uses X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the body. The first CT scanners used a translate-rotate design, while later generations used multiple detectors and spiral scanning for faster, more detailed imaging. Image reconstruction uses back projection to convert attenuation measurements into pixel values and display slices. CT provides excellent anatomical detail and is widely used for diagnosing conditions of the brain, blood vessels, lungs and other organs.BASICS of CT Head



BASICS of CT HeadKunal Mahajan
Ėý
The document provides guidance on reading head CT scans for physicians. It outlines the basic principles of CT scanning, including its history and components. It then reviews normal neuroanatomy as seen on head CT scans, illustrating various anatomical structures and landmarks visible in different axial sections. The document aims to help physicians accurately interpret CT findings to diagnose and treat time-sensitive conditions without specialist assistance.Recently uploaded (20)
Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
Ėý
Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
ðĄ Key Topics Covered:
âïļ Viable air & surface sampling best practices
âïļ USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
âïļ How to analyze & trend viable sample data
âïļ Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
ðĨ Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
ðĒ Stay informedâfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
Ėý
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH Guidelines



Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH GuidelinesKHUSHAL CHAVAN
Ėý
This presentation covers the stability testing of pharmaceutical dosage forms according to ICH guidelines (Q1A-Q1F). It explains the definition of stability, various testing protocols, storage conditions, and evaluation criteria required for regulatory submissions. Key topics include stress testing, container closure systems, stability commitment, and photostability testing. The guidelines ensure that pharmaceutical products maintain their identity, purity, strength, and efficacy throughout their shelf life. This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical professionals, researchers, and regulatory experts.Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management â A Comprehensive Overview



Asthma: Causes, Types, Symptoms & Management â A Comprehensive OverviewDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
Ėý
This presentation provides a detailed yet concise overview of Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It covers the definition, etiology (causes), different types, signs & symptoms, and common triggers of asthma. The content highlights both allergic (extrinsic) and non-allergic (intrinsic) asthma, along with specific forms like exercise-induced, occupational, drug-induced, and nocturnal asthma.
Whether you are a healthcare professional, student, or someone looking to understand asthma better, this presentation offers valuable insights into the condition and its management.BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
Ėý
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdf



X-Ray-Generators-and-Transformers final.pdfMohd Faraz
Ėý
An X-ray generator is a crucial device used in medical imaging, industry, and research to produce X-rays. It operates by accelerating electrons toward a metal target, generating X-ray radiation. Key components include the X-ray tube, transformer assembly, rectifier system, and high-tension circuits. Various types, such as single-phase, three-phase, constant potential, and high-frequency generators, offer different efficiency levels. High-frequency generators are the most advanced, providing stable, high-quality imaging with minimal radiation exposure. X-ray generators play a vital role in diagnostics, security screening, and industrial testing while requiring strict radiation safety measures.Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
Ėý
Hingula(Cinnabar)
Synonyms - Churna Parada, Darada, Mleccha, Rasagarbha,Rasodbhava,
Shukatunda, Hamsapada, Lohagna
Mineralogical Identification
Chemical Formula- HgS
Chemical name- mercury sulfide
Nature â Crystalline
Colour- Bright Red
Crystal- Trigonal.
Clevage- -
Diaphaneity- Transparent to Translucent
Fracture- Uneven
Tenacity- Brittle
Lustre- Vitreous
Streak- Red
Sp. Gravity- 8 to 8.1
Hardness- 2 to 2.5
Sources
- It is found near volcanic region and near mercury mines(extracted).
- It is associated with other minerals like Stibnite, pyrite, realgar, calcite etc.
- Almaden (Spain), California, Texas.
Types
1) Charmara
2) Shukhatunda
3) Hamsapada ( Ap 2/69)
1) Khanija
2) Kritrima (RT 9/4)
Grahya ad Agrahyata
āĪāĪŠāĪū āĪāĨāĪļāĨāĪŪ āĪĩāĪ°āĨāĪĢāĪūāĪ: āĪŠāĨāĪ·āĪĢ āĪļāĨāĪŪāĪĻāĨāĪđāĪ°: |
āĪŪāĪđāĨāĪāĨāĪĩāĪūāĪēāĨ āĪāĪūāĪ°āĪŠāĨāĪ°āĨāĪĢāĨ āĪđāĪŋāĪāĪāĨāĪē: āĪķāĨāĪ°āĨāĪ·āĨāĪ āĪāĪāĨāĪŊāĪĪāĨ || RT 9/3
Doshas
Andya( Blindness)
Kshinata
Klama
Bhrama
Moha
Prameha ( AP 2/73)
Shodhana
1) Grahya Hingula ChurnaâArdraka rasa bhavana(7)--Shuddhahingula (RT 9/12)
Marana
Other Processing Techniques
Satwa Patana
-Shuddha HingulaâAdhaha patana/Urdhwa patana -Satva (Parada) (RRS â 3/144)
Yogas
Hinguleshwar rasa
Anandabhairava Rasa,
Mrutunjaya Rasa,
Tribhuvana keerti Rasa, etc.
Research Updates
A CONCEPTUAL REVIEW ON HINGULA (CINNABAR- HgS)
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/1237
EXTRACTION OF PARAD FROM HINGULA, A TRADITIONAL AYURVEDIC METHOD
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323601866_EXTRACTION_OF_PARAD_FROM_HINGULA_A_TRADITIONAL_AYURVEDIC_METHOD
DrMahantesh.B.Rudrapuri,
M.D.(Ayu) FAGE , PGDYT
HOD Department of Rasa Shastra&BhaishajyaKalpana
Shri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical College,
INCHAL â 591 102, Dist: Belgaum
Mob: 9972710790
Description of Beta thalassemia its cause and management.



Description of Beta thalassemia its cause and management.KIMS
Ėý
All about Beta Thalassemia etiology , pathology , manifestation and treatment & prevention..MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
Ėý
Unit 1: Introduction to Histological and Cytological techniques
ï· Differentiate histology and cytology
ï· Overview on tissue types
ï· Function and components of the compound light microscope
ï· Overview on common Histological Techniques:
o Fixation
o Grossing
o Tissue processing
o Microtomy
o Staining
o Mounting
ï· Application of histology and cytologySolubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...



Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...KHUSHAL CHAVAN
Ėý
This presentation provides an in-depth understanding of solubilization and its critical role in pharmaceutical formulations. It covers:
Definition & Mechanisms of Solubilization
Role of surfactants, micelles, and bile salts in drug solubility
Factors affecting solubilization (pH, polarity, particle size, temperature, etc.)
Methods to enhance drug solubility (Buffers, Co-solvents, Surfactants, Complexation, Solid Dispersions)
Advanced approaches (Polymorphism, Salt Formation, Co-crystallization, Prodrugs)
This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical scientists, formulation experts, regulatory professionals, and students interested in improving drug solubility and bioavailability.Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level Curriculum



Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level CurriculumDr Ovels
Ėý
Sudurpaschim province psc ( lok sewa aayog) medical officer 8th level syllabusLocal Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable Patients



Local Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable PatientsReza Aminnejad
Ėý
Local anesthetics are a cornerstone of pain management, but their use requires special consideration in vulnerable groups such as pediatric, elderly, diabetic, or obese patients. In this presentation, weâll explore how factors like age and physiology influence local anesthetics' selection, dosing, and safety. By understanding these differences, we can optimize patient care and minimize risks.
PresentaciÃģ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025



PresentaciÃģ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025Badalona Serveis Assistencials
Ėý
PresentaciÃģ que va acompanyar la demostraciÃģ prà ctica de metge d'InnovaciÃģ JosÃĐ Ferrer sobre el projecte Benestar de BSA, nom d'IDIAP Pere Gol, el 5 de març de 2025 a l'estand de XarSMART al Mobible Word Congress. Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdf



Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdfMedicoseAcademics
Ėý
Title: Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption â A Comprehensive Overview
Description:
This lecture provides a detailed and structured explanation of the mechanisms regulating tubular reabsorption in the kidneys. It explores how different physiological and hormonal factors influence glomerular filtration and reabsorption rates, ensuring fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
ð Who Should Read This?
This presentation is designed for:
âïļ Medical Students (MBBS, BDS, Nursing, Allied Health Sciences) preparing for physiology exams.
âïļ Medical Educators & Professors looking for structured teaching material.
âïļ Healthcare Professionals (doctors, nephrologists, and physiologists) seeking a refresher on renal physiology.
âïļ Postgraduate Students & Researchers in the field of medical sciences and physiology.
ð What Youâll Learn:
â
Local Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
âïļ Glomerulo-Tubular Balance â its mechanism and clinical significance
âïļ Net reabsorptive forces affecting peritubular capillaries
âïļ Role of peritubular hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures
â
Hormonal Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
âïļ Effects of Aldosterone, Angiotensin II, ADH, and Natriuretic Peptides
âïļ Clinical conditions like Addisonâs disease & Conn Syndrome
âïļ Mechanisms of pressure natriuresis and diuresis
â
Nervous System Regulation
âïļ Sympathetic Nervous System activation and its effects on sodium reabsorption
ðĐš Clinical Correlations & Case Discussions
âïļ How renal regulation is altered in hypertension, hypotension, and proteinuria
âïļ Comparison of Glomerulo-Tubular Balance vs. Tubulo-Glomerular Feedback
This presentation provides detailed diagrams, flowcharts, and calculations to enhance understanding and retention. Whether you are studying, teaching, or practicing medicine, this lecture will serve as a valuable resource for mastering renal physiology.
ðĒ Keywords for Easy Search:
#Physiology #RenalPhysiology #TubularReabsorption #GlomeruloTubularBalance #HormonalRegulation #MedicalEducation #NephrologyDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Its Management Protocol



Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Its Management ProtocolDr Anik Roy Chowdhury
Ėý
Dr. Anik Roy Chowdhury
MBBS, BCS(Health), DA, MD (Resident)
Department of Anesthesiology, ICU & Pain Medicine
Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital (ShSMCH)physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ØģØĪاŲ.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ØģØĪاŲ.pptxamralmohammady27
Ėý
ŲŲ ØđŲØŊŲ ŲاØĻ ØŠŲØĻ ØĢŲ ؊اØĻŲØŠ ŲاŲ
power point show
ŲŲŲŲØđŲ ØŽØŊا ŲŲ Ų
ØąØ§ØŽØđØĐ ØģØąŲØđØĐ ŲŲŲØĐ Ø§ŲاŲ
ØŠØاŲ
ŲاŲŲŲ ŲŲØŊØą ŲØđŲ
Ų Øا؎ØĐ ŲØđŲ
ŲŲا
ŲØīŲØąØ§ ŲŲØŊŲØŠŲØąØĐ ŲŲاŲ ØđŲŲ ØŠØŽŲ
ŲØđØĐ ØĢØģØĶŲØĐ Ø§ŲØĻŲŲHingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
Ėý
MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
Ėý
Mv perivalvular leak
- 1. Mitral Perivalvular LeakMitral Perivalvular Leak Luft MDLuft MD Feehan DOFeehan DO
- 4. Hole
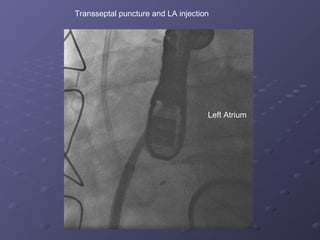
- 5. Transseptal puncture and LA injection Left Atrium
- 6. Crossing leak with stiff glidewire (LAO projection)
- 7. Advancement of LIMA catheter into LV in RAO Projection
- 8. Ventriculogram to prove location
- 9. âTug Testâ With Deployed Device
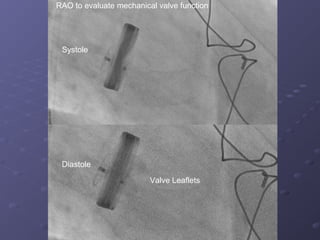
- 10. Systole Diastole Valve Leaflets RAO to evaluate mechanical valve function
- 11. LAO projection with no impingement on mechanical valve
- 12. Left ventriculogram (beat 3) with trace MR
- 13. DEVICE
- 14. Trace MR through the valve with no perivalvular MR by TEE



