Mysql 2007 Tech At Digg V3
- 1. Technology at digg.com Elliott White III - Eli Tim Ellis - Time
- 2. What's all this then? History of Tech at Digg Standard Setup Memcached Purpose Driven MySQL Server Pools Sharding Other MySQL details
- 3. History of Tech at Digg Initially one Linux server with Apache 1.3 and PHP 4.x MySQL 4.0 and myisam tables & MySQL full-text search Started with as many open source packages as possible for rapid development. ImageMagick, Ispell, prototype/scriptaculous, etc Grew quick. One server became two. myisam become innodb. We moved to 3 servers, Apache 2.x, MySQL master-slave?replication, started using memcached, moved to PHP 5.x & hired a dba And then the pace picked up yet again...
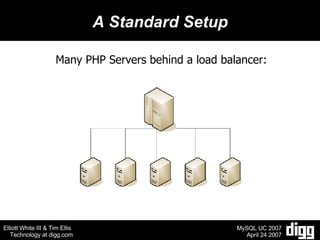
- 4. A Standard Setup Many PHP Servers behind a load balancer:
- 5. A Standard Setup Many MySQL slaves, talking to a master
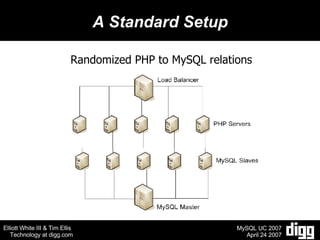
- 6. A Standard Setup Randomized PHP to MySQL relations
- 7. Memcached What is it & Why use it? Why not just pregenerate pages of content? Performance gains: Caching certain chunks of data that may be used on many different pages. From that, still being able to dynamically create the page, but using cached data.
- 8. Memcached Server Farm Issues to be solved: Allowing for Failover and Redundancy Removing or ignoring stale data upon machine failure Stopping perpetuation of database slave lag Making the actual decisions of what and when to cache Solution: Write generic code that understands your data.
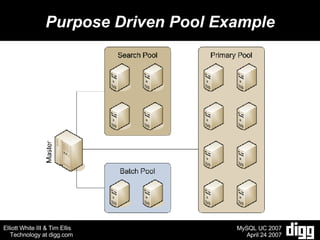
- 9. Purpose Driven MySQL Pools Creating separate slave pools, that are close to identical in order to isolate high database load.
- 10. Purpose Driven Pool Example
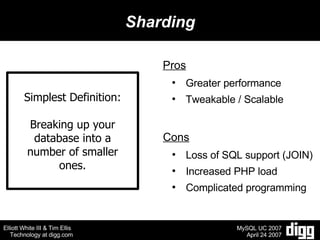
- 11. Sharding Simplest Definition: Breaking up your database into a number of smaller ones. Pros Greater performance Tweakable / Scalable Cons Loss of SQL support (JOIN) Increased PHP load Complicated programming
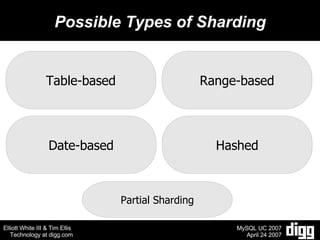
- 12. Possible Types of Sharding Table-based Range-based Date-based Hashed Partial Sharding
- 13. How MySQL Can Do Sharding Partition tables Federated tables MySQL Cluster (NDB) Which of these technologies does Digg use? None of them They weren't ready when we needed them
- 14. Digg MySQL Specifics Mix of MySQL 5.0 versions: 5.0.22, 5.0.27, 5.0.30, 5.0.32 A single MySQL 4.1 supporting Cacti MySQL installation & patching done via Debian apt 5.0 performs fine for us compared to 4.1 OLTP DBs are InnoDB & OLAP DB is MyISAM InnoDB backup DB for dumps and slave creation InnoDB recovery faster after slave hardware dies MyISAM great for loads and date-versioned DBs
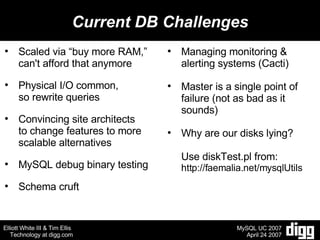
- 15. Current DB Challenges Scaled via ^buy more RAM, ̄ can't afford that anymore Physical I/O common, so rewrite queries Convincing site architects to change features to more scalable alternatives MySQL debug binary testing Schema cruft Managing monitoring & alerting systems (Cacti) Master is a single point of failure (not as bad as it sounds) Why are our disks lying? Use diskTest.pl from: http://faemalia.net/mysqlUtils
- 16. Any Questions? For this presentation and more: http://eliw.com/ Visit http://digg.com/