Naeem Project Presentation FP 23 Welcome to My Presentation.pptx
- 1. Welcome to my presentation Presented by: Naeem Rahman Roll: 449 Reg. no: WUB 14/16/15/449 Batch: 15th Department of Pharmacy World University of Bangladesh Supervised by: Zubair Khalid Labu Head of the Department Department of Pharmacy World University of Bangladesh
- 2. Presentation on: A Review Report on Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases in Bangladesh
- 3. Objective Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the estimation of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 1 in 4 deaths in the United States are caused by CVDs each year. They also says, about 17.9 million deaths (32.1% of the death by any disease) were resulted globally by the CVDs in 2015, up from 12.3 million (25.8%) in 1990. Over three quarters of CVD deaths take place in low- and middle-income countries according to the World Health Organization (WHO); contribution of South Asian countries (India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Maldives) is the highest proportion as compared to any other regions globally. The CVDs are alarmingly increasing in Bangladesh over the last 2 decades. The purpose of this project is to highlight on the current scenario of cardiovascular diseases in Bangladesh.
- 4. Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of some diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels, keeping the heart or blood vessels away from working properly. If our heart doesnât pump the blood properly, this prevents blood from being delivered to many important parts of our body, which can cause serious illness, and even death. Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide. Coronary artery disease and stroke account for 80% of CVD deaths in males and 75% of CVD deaths in females globally. Older adults are comparatively in high risk; about 37% of people between the age of 40-60 have CVDs in United States, while 71% between the age of 60-80, and 85% of people over the age of 80. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the dysfunction of heart or blood vessels, which includes coronary artery disease, stroke, congestive heart failure, congenital heart disease, peripheral artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, pulmonary heart disease, etc. Although some people are born with certain types of CVD, most people develop these as a result of poor lifestyle (eating unhealthy foods, not getting enough exercise, or using tobacco). Besides, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, obesity, high blood cholesterol, and excessive alcohol consumption are also some big reasons.
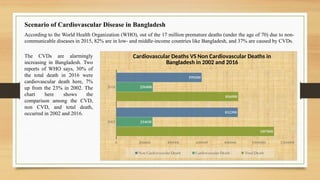
- 5. Scenario of Cardiovascular Disease in Bangladesh According to the World Health Organization (WHO), out of the 17 million premature deaths (under the age of 70) due to non- communicable diseases in 2015, 82% are in low- and middle-income countries like Bangladesh, and 37% are caused by CVDs. 2002 2016 0 200000 400000 600000 800000 1000000 1200000 1107000 856000 254610 256800 852390 599200 Cardiovascular Deaths VS Non Cardiovascular Deaths in Bangladesh in 2002 and 2016 Non Cardiovascular Death Cardiovascular Death Total Death The CVDs are alarmingly increasing in Bangladesh. Two reports of WHO says, 30% of the total death in 2016 were cardiovascular death here, 7% up from the 23% in 2002. The chart here shows the comparison among the CVD, non CVD, and total death, occurred in 2002 and 2016.
- 6. Types, Causes and Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases The class of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) include: 1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Coronary artery disease (CAD), or coronary/ischemic heart disease (CHD/IHD), is the disease of the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart muscle, involving the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of plaque in the arteries of the heart. Types of CAD include- i. Stable angina: A typical presentation of stable angina is chest discomfort and associated symptoms precipitated by some activity, such as running, walking, etc. (with minimal or non-existent symptoms at rest). Figure: Coronary Artery Disease ii. Unstable angina: Unstable angina (UA) may occur unpredictably at rest (a serious indicator of an impending heart attack). iii. Myocardial infarction (MI): This occurs when damage to the heart muscle is caused. The most common symptom is chest pain, that lasts for more than a few minutes. Causes: The CADs possess a number of risk factors including high blood pressure, tobacco, excessive alcohol, diabetes, poor diet and lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, depression, etc.
- 7. Figure: PAD resulting in necrosis of multiple toes 2. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply blood to the heart or brain. Symptoms include leg pain (while walking), bluish skin or cold skin in the affected leg. Causes: Factors contributing to increased risk include age, sex, smoking, high blood pressure, high sugar and cholesterol, etc. 3. Pulmonary Heart Disease (PHD) Pulmonary heart disease (PHD) is the enlargement and failure of the right ventricle of the heart. Chronic PHD usually results in right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), whereas acute PHD usually results in dilatation. Causes: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), COPD, primary pulmonary hypertension, blood clots in the lungs, interstitial lung disease, sickle cell anemia, etc. are the main causes of PHD. Figure: Right ventricular hypertrophy
- 8. ii. Idiopathic: Idiopathic diseases (Moyamoya) are those that occur spontaneously without a known reason. iii. Acquired: The acquired cerebrovascular disease is caused by atherosclerosis, embolism, aneurysms, and arterial dissections. Figure: Illustration of a cerebral aneurysm 5. Heart Failure (HF) Heart failure (HF) is that condition when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain the blood flow to meet the body's needs. Shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling are the common symptoms. Causes: The reasons behind the cerebrovascular disease consists of the following three types: i. Congenital: These are medical conditions (Arteriovenous malformations and germinal matrix hemorrhage) that are present at birth. 4. Cerebrovascular Disease These are diseases of the blood vessels supplying blood to the brain, including a variety of medical conditions affecting the cerebral circulation vessels. The most common presentation is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke, and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke.
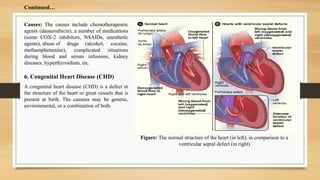
- 9. Causes: The causes include chemotherapeutic agents (daunorubicin), a number of medications (some COX-2 inhibitors, NSAIDs, anesthetic agents), abuse of drugs (alcohol, cocaine, methamphetamine), complicated situations during blood and serum infusions, kidney diseases, hyperthyroidism, etc. 6. Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) A congenital heart disease (CHD) is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. The causees may be genetic, environmental, or a combination of both. Figure: The normal structure of the heart (in left), in comparison to a ventricular septal defect (in right) ContinuedâĶ
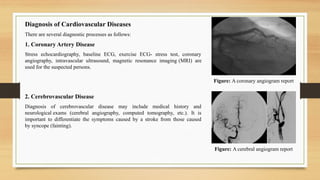
- 10. Figure: A coronary angiogram report Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases There are several diagnostic processes as follows: 1. Coronary Artery Disease Stress echocardiography, baseline ECG, exercise ECG- stress test, coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used for the suspected persons. 2. Cerebrovascular Disease Diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease may include medical history and neurological exams (cerebral angiography, computed tomography, etc.). It is important to differentiate the symptoms caused by a stroke from those caused by syncope (fainting). Figure: A cerebral angiogram report
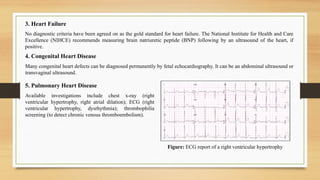
- 11. 3. Heart Failure No diagnostic criteria have been agreed on as the gold standard for heart failure. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NIHCE) recommends measuring brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) following by an ultrasound of the heart, if positive. 5. Pulmonary Heart Disease Available investigations include chest x-ray (right ventricular hypertrophy, right atrial dilation); ECG (right ventricular hypertrophy, dysrhythmia); thrombophilia screening (to detect chronic venous thromboembolism). Figure: ECG report of a right ventricular hypertrophy 4. Congenital Heart Disease Many congenital heart defects can be diagnosed permanently by fetal echocardiography. It can be an abdominal ultrasound or transvaginal ultrasound.
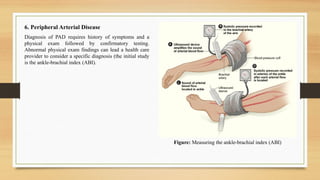
- 12. 6. Peripheral Arterial Disease Diagnosis of PAD requires history of symptoms and a physical exam followed by confirmatory testing. Abnormal physical exam findings can lead a health care provider to consider a specific diagnosis (the initial study is the ankle-brachial index (ABI). Figure: Measuring the ankle-brachial index (ABI)
- 13. Management of Cardiovascular Diseases The management process of the CVDs are done in two ways- prevention, and treatment. The prevention process is basically almost same to almost all the CVDs, whereas the treatment processes (non-pharmacological, pharmacological, and surgical treatment) vary. The overall management process is displayed in below: ï§ Adequate physical exercise. ï§ Avoiding smoking. ï§ Keeping the normal cholesterol level. ï§ Having healthy and balanced diet. ï§ Decreasing obesity or controlling the weight. ï§ Keeping a controlled blood pressure. ïķ Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases According to the World Health Organization (WHO), up to 90% of CVDs may be preventable by avoiding the following established risk factors-
- 14. Figure: Half an hour of swimming can burn 350 calories Figure: Balanced and healthy diet ContinuedâĶ Figure: Jogging as an effective form of exercise
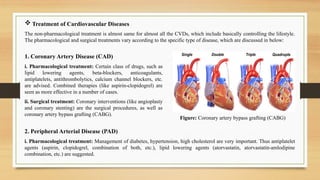
- 15. ïķ Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases The non-pharmacological treatment is almost same for almost all the CVDs, which include basically controlling the lifestyle. The pharmacological and surgical treatments vary according to the specific type of disease, which are discussed in below: 1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) i. Pharmacological treatment: Certain class of drugs, such as lipid lowering agents, beta-blockers, anticoagulants, antiplatelets, antithrombolytics, calcium channel blockers, etc. are advised. Combined therapies (like aspirin-clopidogrel) are seen as more effective in a number of cases. ii. Surgical treatment: Coronary interventions (like angioplasty and coronary stenting) are the surgical procedures, as well as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Figure: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) 2. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) i. Pharmacological treatment: Management of diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol are very important. Thus antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel, combination of both, etc.), lipid lowering agents (atorvastatin, atorvastatin-amlodipine combination, etc.) are suggested.
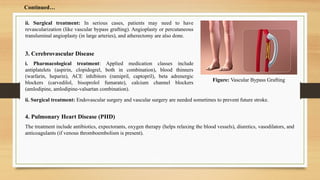
- 16. 3. Cerebrovascular Disease i. Pharmacological treatment: Applied medication classes include antiplatelets (aspirin, clopidogrel, both in combination), blood thinners (warfarin, heparin), ACE inhibitors (ramipril, captopril), beta adrenergic blockers (carvedilol, bisoprolol fumarate), calcium channel blockers (amlodipine, amlodipine-valsartan combination). ii. Surgical treatment: In serious cases, patients may need to have revascularization (like vascular bypass grafting). Angioplasty or percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (in large arteries), and atherectomy are also done. Figure: Vascular Bypass Grafting ii. Surgical treatment: Endovascular surgery and vascular surgery are needed sometimes to prevent future stroke. 4. Pulmonary Heart Disease (PHD) The treatment include antibiotics, expectorants, oxygen therapy (helps relaxing the blood vessels), diuretics, vasodilators, and anticoagulants (if venous thromboembolism is present). ContinuedâĶ
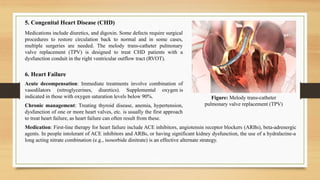
- 17. Chronic management: Treating thyroid disease, anemia, hypertension, dysfunction of one or more heart valves, etc. is usually the first approach to treat heart failure, as heart failure can often result from these. 5. Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) Medications include diuretics, and digoxin. Some defects require surgical procedures to restore circulation back to normal and in some cases, multiple surgeries are needed. The melody trans-catheter pulmonary valve replacement (TPV) is designed to treat CHD patients with a dysfunction conduit in the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT). 6. Heart Failure Figure: Melody trans-catheter pulmonary valve replacement (TPV) Acute decompensation: Immediate treatments involve combination of vasodilators (nitroglycerines, diuretics). Supplemental oxygen is indicated in those with oxygen saturation levels below 90%. Medication: First-line therapy for heart failure include ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-adrenergic agents. In people intolerant of ACE inhibitors and ARBs, or having significant kidney dysfunction, the use of a hydralazine-a long acting nitrate combination (e.g., isosorbide dinitrate) is an effective alternate strategy.
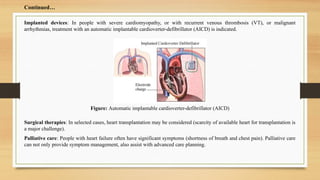
- 18. Figure: Automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) ContinuedâĶ Implanted devices: In people with severe cardiomyopathy, or with recurrent venous thrombosis (VT), or malignant arrhythmias, treatment with an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD) is indicated. Surgical therapies: In selected cases, heart transplantation may be considered (scarcity of available heart for transplantation is a major challenge). Palliative care: People with heart failure often have significant symptoms (shortness of breath and chest pain). Palliative care can not only provide symptom management, also assist with advanced care planning.
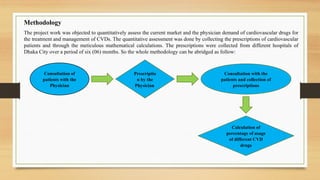
- 19. Methodology The project work was objected to quantitatively assess the current market and the physician demand of cardiovascular drugs for the treatment and management of CVDs. The quantitative assessment was done by collecting the prescriptions of cardiovascular patients and through the meticulous mathematical calculations. The prescriptions were collected from different hospitals of Dhaka City over a period of six (06) months. So the whole methodology can be abridged as follow: Consultation of patients with the Physician Prescriptio n by the Physician Consultation with the patients and collection of prescriptions Calculation of percentage of usage of different CVD drugs
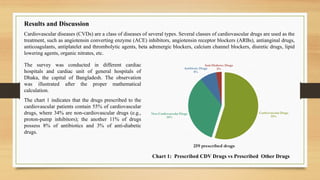
- 20. Chart 1: Prescribed CDV Drugs vs Prescribed Other Drugs Results and Discussion Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a class of diseases of several types. Several classes of cardiovascular drugs are used as the treatment, such as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), antianginal drugs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet and thrombolytic agents, beta adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretic drugs, lipid lowering agents, organic nitrates, etc. Cardiovascular Drugs 55% Non-Cardiovascular Drugs 34% Antibiotic Drugs 8% Anti-Diabetec Drugs 3% 259 prescribed drugs The survey was conducted in different cardiac hospitals and cardiac unit of general hospitals of Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. The observation was illustrated after the proper mathematical calculation. The chart 1 indicates that the drugs prescribed to the cardiovascular patients contain 55% of cardiovascular drugs, where 34% are non-cardiovascular drugs (e.g., proton-pump inhibitors); the another 11% of drugs possess 8% of antibiotics and 3% of anti-diabetic drugs.
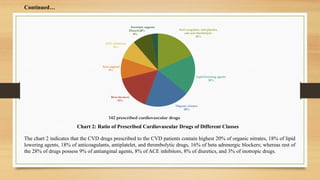
- 21. Anti-coagulant, anti-platelet, and anti-thrmbolytic 18% Lipid lowering agents 18% Organic nitrates 20% Beta blockers 15% Anti-anginal 9% ACE inhibitors 8% Diuretics 8% Inotropic aagents 3% 142 prescribed cardiovascular drugs Chart 2: Ratio of Prescribed Cardiovascular Drugs of Different Classes ContinuedâĶ The chart 2 indicates that the CVD drugs prescribed to the CVD patients contain highest 20% of organic nitrates, 18% of lipid lowering agents, 18% of anticoagulants, antiplatelet, and thrombolytic drugs, 16% of beta adrenergic blockers; whereas rest of the 28% of drugs possess 9% of antianginal agents, 8% of ACE inhibitors, 8% of diuretics, and 3% of inotropic drugs.
- 22. Conclusion Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide and in all regions except Africa; and it is also estimated that over 23 million people will die from these diseases each year by 2030. The risk of these diseases are increased significantly in Bangladesh over the last two decades, as well as the amount of CVD deaths. From 1986 to 2006, the age-standardized cardiovascular disease mortality rates increased by 30-fold (from 16 deaths per 100,000 to 483 deaths per 100,000) among males and 47-fold (from 7 deaths per 100,000 to 330 deaths per 100,000) in females in Bangladesh. Although this study is a reflection of the current alarming CVD situation in Bangladesh, but unfortunately, no accurate and organized document in Bangladesh is found yet, as this type of survey is very rare here. Therefore, a nation-wide survey is badly needed to find out more accurate current epidemiological aspects of CVD in Bangladesh. Although the treatment of cardiovascular diseases are being developed worldwide, the development rate is not seen as that remarkable in Bangladesh so far. Besides, it has been observed from most of the research that, prevention by maintaining a controlled lifestyle is the best policy in this case. Thus controlling the lifestyle should be the motto of cardiovascular management for a country like Bangladesh.
- 23. THANK YOU