Naming-Ionic-and-Covalent-Compound-NEW-VERSION.pptx
- 1. Chemical Names and Formulas Overview ŌĆóMetals and Non-Metals ŌĆóIons and Ionic Charges ŌĆóTypes of Compounds ŌĆóSystematic Names -Writing Names and Formulas
- 2. Which side is ionic/covalent?
- 3. Objectives: ŌĆó Identify Ionic and Covalent Compound. ŌĆó Describe binary and ternary compound. ŌĆó Name and write chemical formula. * Ionic Compound * Covalent Compound
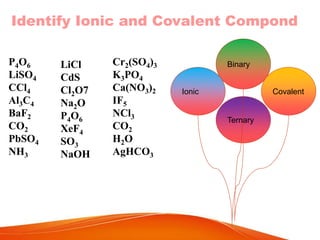
- 4. Identify Ionic and Covalent Compond P4O6 LiSO4 CCl4 Al3C4 BaF2 CO2 PbSO4 NH3 LiCl CdS Cl2O7 Na2O P4O6 XeF4 SO3 NaOH Cr2(SO4)3 K3PO4 Ca(NO3)2 IF5 NCl3 CO2 H2O AgHCO3 Binary Ionic Covalent Ternary
- 5. How will you describe a ternary compound?
- 6. Naming Compounds ’ü« General Information ’ü« Binary Ionic Compounds ’ü« Ternary Ionic Compounds/Poly-atomic Ions ’ü« Naming w/metals that have more than 1 charge (Transition Metals) ’ü« Molecular Compounds
- 7. Metals and Nonmetals ’ü« Stairway Of Division on Periodic Table ’ü« C, P, Se, I, Rn and to the right are non- metals ’ü« B, Si, As, Ge, Sb, Te, Po, At are semi- metals ’ü« All others are metals
- 8. Ions ’ü« Cations ’ü« Positively Charged Atoms ’ü« i.e. Na + ’ü« Anions ’ü« Negatively Charged Atoms ’ü« i.e. Cl -
- 10. IONIC CHARGES ’ü« Group I -> ’ü« Group II -> ’ü« Group III -> ’ü« Group IV -> 1+ 2+ 3+ 4+
- 11. IONIC CHARGES ’ü« Group V -> ’ü« Group VI -> ’ü« Group VII -> ’ü« Group VIII -> 3- 2- 1- Noble Gases
- 12. ’ü«Ionic Compounds ŌĆó composed of positive and negative ions. ŌĆó usually formed from a metal and non-metal. ŌĆó these elements are not attached to one another.
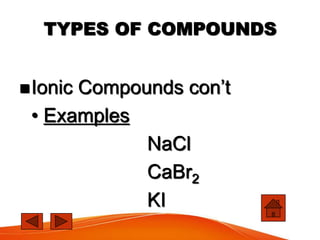
- 13. TYPES OF COMPOUNDS ’ü«Ionic Compounds conŌĆÖt ŌĆó Examples NaCl CaBr2 KI
- 14. ’ü« Definition ŌĆó shows the kind and numbers of atoms in the smallest representative unit of the substance. ’ü« i. e. NaCl
- 15. ’ü« A formula unit is the lowest whole number ratio of ions in an ionic compound. ’ü« i.e. Na2Cl2 -> NaCl ’ü« There is no such thing as a molecule of NaCl!!!!!!!!!
- 16. ’ü« If charges cancel, just write the symbols Na+1 Cl-1 NaCl ’ü« If charges do not cancel, criss-cross: Ca+2 Cl-1 CaCl2 ***Do not move the charge, only the number ***Do not write the 1
- 17. NAMING COMPOUNDS ’ü« Your ability to name compounds and write formulaŌĆÖs hinges on your ability to recognize whether a compound is Ionic or Covalent.
- 18. BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS ’ü« Binary means 2 elements ’ü« Ionic means a metal and a non-metal (or cation and anion) ’ü« Writing Formulas ŌĆó charges must balance so compound charge is neutral.
- 19. BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS ’ü«Writing Formulas from Names ŌĆó 1st word = CATION ŌĆó 2nd word = ANION name with ide ending.
- 20. BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS ’ü« NaBr ’ü« MgF2 ’ü«Sodium Bromide ’ü«Magnesium Fluoride
- 21. BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS ’ü« Potassium Chloride ’ü« Aluminum Oxide ŌĆó notice ending of name is ide! K+Cl- -> KCl Al2 3+O3 2- -> Al2O3
- 22. Polyatomic Ions ’ü«Definition ŌĆótightly bound groups of atoms that behave as a unit and carry a charge. ’ü«Example SO3 2- , NO2 -, ClO2 -
- 24. TERNARY IONIC COMPOUNDS ’ü«Ternary means 3 different elements ’ü«Usually contain Poly-atomic Ions ’ü«Ionic means cation and anion
- 25. ’ü«Ca2+CO3 2- CaCO3 Charges canceled. Just write the symbols ’ü«Calcium carbonate
- 26. TERNARY IONIC COMPOUNDS: Naming ’ü«Calcium Nitrate Notice the charges didnŌĆÖt cancel so they criss crossed ’ü«Ca+2 (NO3)-1 Ca(NO3)2
- 27. Naming with Transition Metals ’ü« First word = CATION ’ü« Second word = ANION ŌĆōThe Roman numeral will tell you the charge of the transition metal ŌĆōSilver (Ag) is an exception. ItŌĆÖs charge is +1
- 28. Elements with more than one oxidation state.
- 29. Naming Transition Metals ’ü«Copper (I) Oxide ’ü«Cu+1 O- 2 ’ü«Cu2O
- 30. Writing Formulas with Transition Metals ’ü«FeCl3 Fe+3 Cl-1 ’ü«FeCl2 Fe+2 Cl-1 ’ü«Iron (III) Chloride ’ü«Iron (II) Chloride *Backwards criss-cross to know the charge/Roman numeral
- 31. TYPES OF COMPOUNDS ’ü« Covalent/Molecular Compounds ŌĆó composed of molecules in which elements share electrons. ŌĆó usually composed of 2 nonmetals. ŌĆó these elements are attached
- 32. MOLECULAR FORMULA ’ü« Definition ŌĆó shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a molecule of a compound. ’ü« i. e. CO
- 33. TYPES OF COMPOUNDS ’ü« Molecular Compounds conŌĆÖt ŌĆóExamples CS2 SiO2 BF3
- 34. BINARY MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS ’ü«Binary means 2 elements ’ü«Molecular means 2 non- metals ’ü«NO ionic charges are present
- 35. Naming Binary Covalent/Molecular Compounds ’ü«Prefixes are used to show how many atoms are present in each molecule.
- 36. Covalent Prefixes ’ü« Mono (or no prefix) ŌĆō 1 ’ü« Di ŌĆō 2 ’ü« Tri ŌĆō 3 ’ü« Tetra ŌĆō 4 ’ü« Penta ŌĆō 5 ’ü« Hexa ŌĆō 6 ’ü« Hepta ŌĆō 7 ’ü« Octa ŌĆō 8 ’ü« Nona ŌĆō 9 ’ü« Deca ŌĆō 10
- 37. Writing Binary Molecular Compounds ’ü«CO2 ŌĆóno mono prefix is used on first element ’ü«Carbon Dioxide ŌĆó Di means 2 oxygens!!
- 38. Naming Binary Molecular Compounds ’ü«2 ways itŌĆÖs done! ŌĆó (prefix + element name) i.e. N2O dinitrogen monoxide
- 39. Naming Binary Molecular Compounds ŌĆó (prefix + element root + ide) i.e. PCl3 Phosphorous Trichloride ’ü«All binary compounds end in ide!!!