Nand flash memory
- 1. USB Flash drive Project Mohamed Fadel Buffon Storage Element NAND Flash Memory
- 2. Agenda ï What is NAND Flash? ïWhat does NAND Flash Controller do? ïWhat is ONFI? ïWhat are NAND Flash issues? ïWhat is wear leveling Technology?
- 3. What is NAND Flash? âĒ Non Volatile Memory. âĒ Programmable Memory. âĒ Portable Storage.
- 4. Diff. between NAND Flash & Others âĒ Serial Storage device. âĒ Long Access Time. âĒ Not RAM.
- 5. NAND Flash || NOR Flash
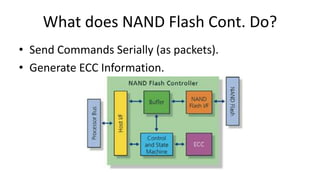
- 6. What does NAND Flash Cont. Do? âĒ Send Commands Serially (as packets). âĒ Generate ECC Information.
- 7. Commands
- 10. Storing 0 x x
- 11. Types of NAND Flash
- 12. Types of NAND Flash âĒ MLC offers higher storage density. âĒ But MLC is slower and less robust. âĒ MLC ï 10,000 erase/program cycle. âĒ SLC ï 100,000 erase/program cycle.
- 13. SLC NAND Flash
- 14. What is ONFI? âĒ Open Standard for device level NAND Flash interface. âĒ Supported by new NAND Flash devices.
- 15. ECC âĒ Is a good way to recover the wrong value. âĒ Can be implemented by: â Hardware (Faster). â Software. âĒ SLC ï 1-bit ECC correction per 512 bytes (which mean 24 ECC bits {Hamming Code}).
- 16. What are NAND Flash issues? âĒ Bad Blocks. âĒ Long Access Time. âĒ No Random Access. âĒ Short Life-time.
- 17. What is wear leveling? âĒ Divide Data to Segments. âĒ Distribute Segments on multi-pages. âĒ Re-map the logical address to physical address. âĒ Adv: â Extend the NAND Flash life-time.
- 18. What is RAM shadowing? âĒ Like External Cache Memory. âĒ Reasons: â Limit erase/program cycle. â Slow speed (compared to SDRAM).
- 19. Reference âĒ âNAND Flash FAQâ from Eureka Technology.