Naranjilla Micro-Propagation
- 2. Project Objectives • Improve upon previous study (standardize procedure for micro- propagation of naranjilla) • Original sample size not large enough for data to be statistically supported • Check for differences between seeds bought at market and seeds from INIAP (Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Agropecuarias)
- 3. Naranjilla background • Distribution: indigenous to Sierra of Ecuador and Colombia • So far unable to be grown outside of South America • Characteristics: fruiting shrub that grows up to 8ft (2.5m) tall, with a thick spiny stem (no spines when cultivated) and wooly leaves up to 2ft (60cm) long • covered in fine purple hair when young • Fragrant white flowers • Juicy orange fruit, covered in brown fur until ripe • grows at 3,000 - 8,000 ft above sea level • Susceptible to nematodes (roundworms) • Low genetic diversity • Uses: eaten raw, made into juice, jam, pies, etc.
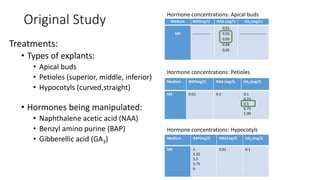
- 4. Original Study Treatments: • Types of explants: • Apical buds • Petioles (superior, middle, inferior) • Hypocotyls (curved,straight) • Hormones being manipulated: • Naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) • Benzyl amino purine (BAP) • Gibberellic acid (GA3) Hormone concentrations: Apical buds Hormone concentrations: Petioles Hormone concentrations: Hypocotyls Medium BAP(mg/l) NAA (mg/l) GA3 (mg/L) MS -------------- 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 ---------------------- Medium BAP(mg/l) NAA (mg/l) GA3 (mg/l) MS 0.01 4.5 0.1 0.25 0.5 0.75 1.00 Medium BAP(mg/l) NAA(mg/l) GA3 (mg/l) MS 5 5.25 5.5 5.75 6 0.01 0.1
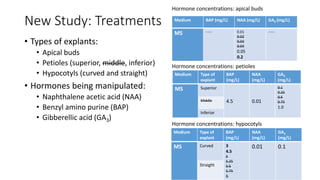
- 5. New Study: Treatments • Types of explants: • Apical buds • Petioles (superior, middle, inferior) • Hypocotyls (curved and straight) • Hormones being manipulated: • Naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) • Benzyl amino purine (BAP) • Gibberellic acid (GA3) Medium BAP (mg/L) NAA (mg/L) GA3 (mg/L) MS ----- 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.2 ----- Hormone concentrations: apical buds Hormone concentrations: petioles Hormone concentrations: hypocotyls Medium Type of explant BAP (mg/L) NAA (mg/L) GA3 (mg/L) MS Superior 4.5 0.01 0.1 0.25 0.5 0.75 1.0 Middle Inferior Medium Type of explant BAP (mg/L) NAA (mg/L) GA3 (mg/L) MS Curved 3 4.5 5 5.25 5.5 5.75 6 0.01 0.1 Straight
- 6. Procedure: growing the plants 1) Market seeds are cleaned and disinfected 1) 3 min in alcohol 70% 2) 18 min in hypochlorite 2.5% and 4-5 drops of tween, stirring every 3 min 3) 5 washes with sterile deionized water 2) Seeds are planted in autoclaved MS medium, under sterile camera, 10 seeds per jar 3) Jars are covered with saran wrap and placed under light
- 7. Study Treatments: Apical Buds • What they are: AKA terminal bud, the very top of a growing plant, where new leaves emerge • Procedure: All leaves are removed, stem is cut just below most recent leaves, planted right-side-up • Treatments: NAA .01 mg/L, NAA .05 mg/L, NAA .20 mg/L 0.01NAA 0.05 NAA 0.20 NAA
- 8. Study Treatments: Petioles • What they are: The stalk attaching the leaf to the stem of a plant • Procedure: roots are removed, stalk is cut in 3, discarding the middle, leaves are removed, and petioles are cut from the main stem, placed in medium on their side • Treatments: BAP 4.5 (mg/L)/NAA 0.01 (mg/L)/GA3 1.0 (mg/L) Superior: Inferior:
- 9. Study Treatments: Hypocotyls • What they are: Stem below the first leaves • Procedure: curved: as soon as a stem begins to emerge, the seed and any roots or leaves are cut away, hypocotyl is planted on its side straight: the plant is allowed to grow until the stem is straight, at which point the stem is cut directly below the first leaves and approx. 6mm down, hypocotyl is planted on its side • Treatments: BAP 3 (mg/L), BAP 4.5 (mg/L), BAP 6 (mg/L)/NAA .01 (mg/L)/GA3 0.1 (mg/L)
- 10. Results: Apical Buds Number of leaves (avg. per explant) Length of stem (avg. per explant) Length of root cm (avg. per explant) 0.01 mg/L NAA 4.85 2.5 cm 2.27 cm 0.05 mg/L NAA 4.95 3.58 cm 1.66 cm 0.20 mg/L NAA 4.90 2.93 cm 1.56 cm 4.8 4.82 4.84 4.86 4.88 4.9 4.92 4.94 4.96 0.01 0.05 0.2 numberofleaves(avg.) Concentration of NAA (mg/L) Number of leaves 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 0.01 0.05 0.2 Length(cm) Concentration of NAA (mg/L) Stems and Roots length of stem Length of root
- 11. Next Steps • Collect data on petioles and hypocotyls • Employ micro-propagation protocol for conservation programs • Micro-propagation protocol can also be used to cultivate modified naranjilla plants for further study
Editor's Notes
- Apical buds: NAA in concentration 0.03 mg/L yielded the largest leaves, highest number of leaves, and longest roots; NAA in concentration 0.02 mg/L yielded the longest stems Petioles: inferior petioles yielded the largest sprouts and leaves, GA3 in concentration 0.5 mg/L was marginally better in terms of number and size of sprouts, GA3 in concentration 1.0 mg/L yielded the greatest number of leaves Hypocotyls: curved hypocotyls produced larger sprouts; neither type of hypocotyl (curved or straight) nor the concentration of hormones in the medium had a significant effect on any other parameters