National AIDS Program under UHC
- 1. 1
- 2. 2
- 3. ŌĆóThailand and Indonesia are similar in many ways. ŌĆóThailand has about 500,000 sq.km. in area and 67 million of population, a quarter smaller than Indonesia. ŌĆóThe economy has performed well in recent years, and was then upgraded to an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank in 2011. ŌĆóThe GDP per capita in 2010 was a little bit more than 5 thousand USD with 3.9% of total health expenditure. ŌĆóLife expectancy at birth was 71 years in male and 76 years in female. ŌĆóHIV prevalence in adult is approximately 1.3%. 3
- 4. ŌĆóMore than one thousand hospitals are operated within the government sector with more than one hundred thousand beds, distributed from urban metropolitan level to rural district area. The service bed per population ratio is approximately 1 to 600. ŌĆóThe health units which take responsibility in sub-district level are primary care units and community health centers. ŌĆóCurrently, there are more than ten thousand primary care unit and fifty thousand community health centers cover all over the country. 4
- 5. ŌĆóRatio of health personnel can be shown in this table. 5
- 6. ŌĆóThere are three main health protection scheme in Thailand: 1. Civil servant medical benefit scheme for government employee, 2. Social security scheme for private sector employee, 3. Universal health coverage scheme for the rest of Thai people. ŌĆóEach scheme still has its own history and administration. 6
- 7. ŌĆóFirstly, Civil Servant Medical Benefit Scheme, which is provided for government employees, contributes around 8% of total population and totally funded by government. ŌĆóSecondly, Social Security Scheme, which is provided for private sector employees, contributes around 15% of total population. It is funded by tripartite contribution between government, employees and employers. ŌĆóLastly, Universal Health Coverage Scheme, which is provided for the rest of population, contributes around 15% of total population. The budget is totally funded by government. 7
- 8. ŌĆóThis table demonstrates benefit packages which are provided free of charge to all HIV people. ŌĆóThey are classified into 4 categories: 1. Asymptomatic PWHA with CD4 more than 350, in this group no ART is needed, just provides regular CD4 check up every 6 m. 2. Symptomatic or asymptomatic PWHA with CD4 350 or less, this group of people needs ART as well as routine lab monitoring such as blood chemistry, CD4, viral load and drug resistance. 3. HIV positive mother, in this group, ARV for HIV prevention from mother to child is provided as well as CD4 monitoring. 4. Babies who born from HIV positive mother, ARV for prevention and infant formula are supplied as well as DNA PCR for diagnosis. 8
- 9. ŌĆóFirst Thai AIDS case was reported in 1984. ŌĆóBefore 2000, Anti-retroviral treatment was under research settings. ŌĆóPMTCT program was first implemented in 2000. ŌĆóA pilot study on national access to ART was started in 2001 in order to prepare for the system. ŌĆóIn 2003, National Health Security Act was issued, still, ART was not included in the benefits. ŌĆóNot until 2006 that Universal access for ART has been implemented. 9
- 10. ŌĆóBefore universal access to ART, HIV/AIDS contributed the highest DALY loss and the leading cause of death among Thai population. ŌĆóIt infected young and middle generation who are still in working age especially laborers and agriculturists who are in the poorest and least educated groups. ŌĆóHIV/AIDS still overwhelms these vulnerable group of people by decreasing household income but increasing personal health expenditure. 10
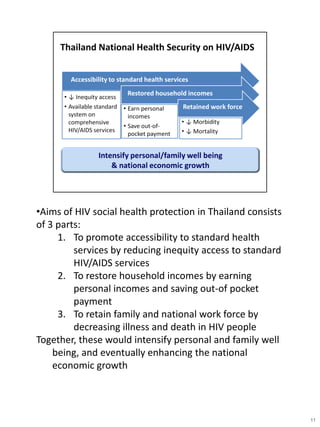
- 11. ŌĆóAims of HIV social health protection in Thailand consists of 3 parts: 1. To promote accessibility to standard health services by reducing inequity access to standard HIV/AIDS services 2. To restore household incomes by earning personal incomes and saving out-of pocket payment 3. To retain family and national work force by decreasing illness and death in HIV people Together, these would intensify personal and family well being, and eventually enhancing the national economic growth 11
- 12. ŌĆóBefore implementing the national ART program, some economists predicted that the total resources needed would touch at least 200 mUSD within 2012, or even more than 460 mUSD in case of good adherence to treatment ŌĆóThis made policy makers hesitated to invest for the project for some time. ŌĆóFortunately, this assumption was proved untrue soon after. 12
- 13. ŌĆóThis graph shows the number of PWHA is increasing over time. ŌĆóIt is estimated that the number of PWHA receiving ART in next coming year will increase up to 174,400, which is 50% increase compare to 2009. ŌĆóDespite of that increasing, during 2009 to 2013, the average ART budget remains stable at around 100 mUSD. ŌĆóHow could we make it ? 13
- 14. ŌĆóThe major components of ART budget is ARV drugs. ŌĆóIn Thailand, about 75% of ART program contributes to ARV drugs, 20% to lab, and the rest 5% to others. ŌĆóNormally, the global ARV prices itself continue to drop gradually. ŌĆóAs a result of TRIPŌĆÖs flexibility, the cost of ARV in Thailand falls dramatically. ŌĆóAverage unit cost of first and second line ARV falls to nearly 50% during past 5 years. ŌĆóAccordingly, central procurement and flexibility of TRIPS Agreement are the most important mechanisms in controlling ARV prices. 14
- 15. 15