Nc rna in molecular oncology
- 22. Target Genes KEGG Pathway LncRNA-miRNA Interaction miRNA-miRNA Interaction Bioinformatics Gene Class Target Genomic Location Disease Search Bioinformatics
Editor's Notes
- #6: Non-coding RNA comprise a much larger portion of the human genome than protein-coding RNA, which comprise <┬Ā3% of the genome. Non-coding RNAs are arbitrarily classified into short and┬Ālong non-coding RNAbased on transcript size. LncRNA can be designated as Intergenic, Intronic, Enhancer, Sense, Antisense, or Bidirectional based on their genomic location relative to that of nearby protein-coding genes.
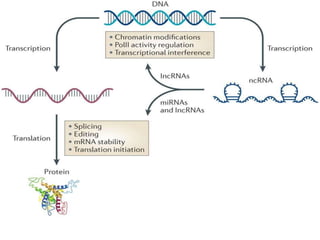
- #7: Regulatory functions of ncRNAs are involved in all the stages of the central dogma of biology. Genetic information flows from DNA (the genotype) to RNA (with thick black lines). RNA (the phenotype) then decodes proteins (from a mRNA) and/or ncRNAs (from a transcript or a mRNA). Regulatory ncRNAs control gene expression (shown in dashed lines), whereas structural ncRNAs (e.g., ribosomal and transfer RNAs) are involved in protein synthesis (shown in thin doubled-line). ncRNA symbology: mi, micro; nc, non-coding; pi, piwi; rasi, repeat-associated small interfering; si, short interfering; sn, small nuclear; sno, small nucleolar; r, ribosomal; t, transfer; SRP, signal recognition particle; TF, transcription factor. Figure is modified with kind permission from┬Ā
- #10: Schema depicting miRNA biogenesis and function. Primary miRNA transcript (pri-miRNA) is transcribed by RNA polymerase II/III in the nucleus, forming an elongated RNA hairpin structure that is subsequently cleaved by Drosha into a small stem-loop structure of~70 nt,(pre-miRNA).Pre-miRNA is exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm by exportin-5 and the loop is cleaved after the pre-miRNA is loaded onto Dicer, producing a double-stranded structure of miRNA and antisense miRNA*.The latter is typically degraded, whereas the long (~22 nt) mature miRNA strand is incorporated into the miRNA-induced silencing complex (mRISC), leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression.Mature miRNA levels are regulated via binding to ceRNAs such circular(c) RNAs, pseudogenes, and lncRNAs, which act as a sponge to prevent miRNA binding to target mRNAs
- #15: lncRNAs associated with hallmarks of cancer. LncRNAs have been implicated in key hallmarks of cancer and can contribute to the onset and progression of cancer.
- #19: ADVANTAGES vs. DISADVANTAGES
- #23: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG): is a database resource for understanding high-level functions and utilities of the biological system from molecular-level information generated by experimental technologies.
- #34: towards a new era for the management of cancer
- #38: Strategies to target┬ĀlncRNA. (A)┬ĀGene transcription: DNA-binding elements can target the genomic locus to alter lncRNA transcription. (B)┬ĀTranscript destabilization/degradation:┬ĀsiRNAs┬Ā(19ŌĆō30┬Ānt long double-stranded RNAs) can bind to complementary lncRNA sequences through RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex). ASO and Gapmers (8ŌĆō50┬Ānt long┬Āsingle-stranded DNAs or RNAs┬Ācan carry out sequence specific and┬ĀRNase┬ĀH-mediated lncRNA degradation.┬ĀRibozymes┬Ā(single-stranded RNA in neutral condition) can undergo cellular processing to expose the hammerhead structure of the binding arms that bind with target sites and result in cleavage of the target lncRNA. (C)┬ĀBlock interactions. Small synthetic molecules can block binding of lncRNAs with┬Āprotein, DNA, RNA or other interacting complexes by associating with specific binding pockets. (D)┬ĀFunctional disruption:┬ĀAptamers┬Ā(3- dimensional short RNA or DNA oligonucleotides) can bind at specific structural regions to target lncRNA and antagonize their association with their binding partners.