Neglected Diabetic Foot.pptx
- 1. Neglected Diabetic Foot Dr Abdulhakim Altamimi University of Aden Yemen
- 2. • Diabetes mellitus has become an epidemic worldwide . • Foot problems are an associated complication • Diabetic foot ulcer will complicate the disease in more than 15% of these people during their lifetime . • Foot ulcer precede more than 80% of non traumatic lower limb amputation
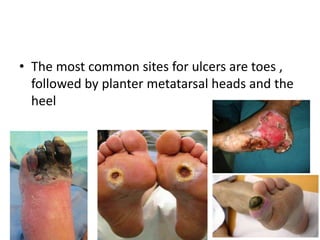
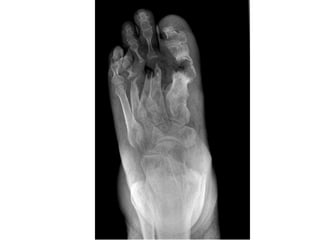
- 3. • The most common sites for ulcers are toes , followed by planter metatarsal heads and the heel
- 4. • Foot risk factors : • Peripheral neuropathy • Peripheral arterial diseases • Foot deformity • Others
- 5. • Although known risk factors for non-insulin- dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) such as family history, obesity and central distribution of fat are important in the elderly, aging itself seems to be a stronger risk factor.
- 6. Why it is neglected ? –Patient factors –Disease factors –Treating Doctors factors –Society and health system factors
- 7. Neglected Diabetic Foot • It is a disaster condition in the foot of diabetic patient due to deficiency of awareness towards the complications resulting from uncontrolled blood sugar , lack of seeking a proper help as well as poor health care • The patient may present in a condition that limb salvageable is questionable
- 8. • Understanding reasons for the neglect of foot screening during the annual review of people with diabetes enables the development of solutions for this omission. • This can be solved by identified the reasons within the context of health care delivery systems in terms of the professional, social, political and economic aspects of this screening.
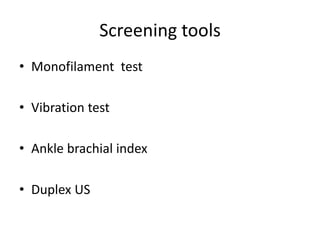
- 9. Screening tools • Monofilament test • Vibration test • Ankle brachial index • Duplex US
- 10. • Prevention services are infrequently provided to high-risk patients. • In the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) Guidance 2015,
- 11. Five key elements that underpin prevention of foot problems • 1- Identification of the at-risk foot . • 2- Regular inspection and examination of the at-risk foot . • 3-Education of patient, family and healthcare providers. • 4- Routine wearing of appropriate footwear . • 5- Treatment of pre-ulcerative signs.
- 12. Diabetic foot classification • Wagner – Megget’s classification • University of Texas • PEDIS classification • Amit Kumar classification
- 13. • Foot lesions constitute an increasing public health problem and also have substantial economic consequences. • The professionals involved in these activities, make up the multidisciplinary team, which is composed of medical specialists (diabetologist, internist, orthopedic, vascular surgeon, radiologist, cardiologist, etc) and prepared and trained professionals, such as nurses and podiatrists.
- 14. • The best solution for patient education to be beneficial in prevention may yet have to be investigated. • patient education and find the most effective methods to promote the correction of habits and wrong attitudes. • Education to the patient family and relative may help in prevention of disabling foot complications
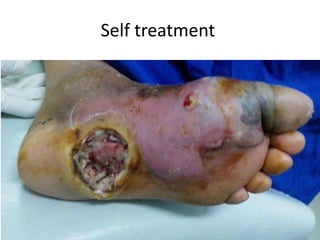
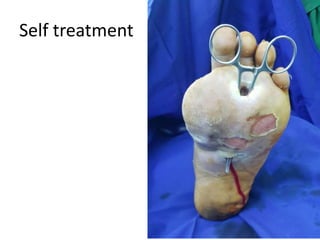
- 17. Self treatment
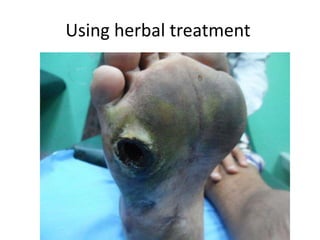
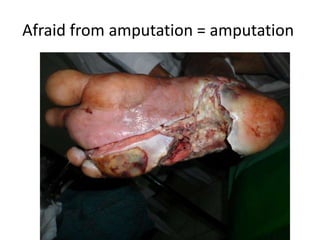
- 18. Afraid from amputation = amputation
- 19. Self treatment
- 20. Conclusions • Foot at risk for ulcer should be suspected in all patient with diabetes • Presence of diabetic foot ulcer is potentially carrying a high risk for severe infection • Long standing ulcer = osteomyelitis may be there • Long standing ulcer = foreign body is suspected
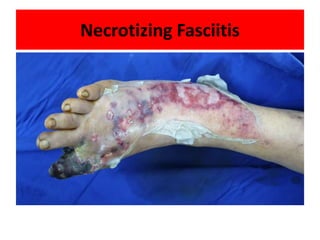
- 24. • Neglecting from the patient and underestimation from the care giver may lead to a complication by which the limb is lost ( major amputation ) • Neglecting from the patient and underestimation from the care giver may lead to a complication by which the live is lost
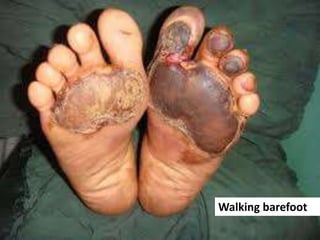
- 25. Walking barefoot
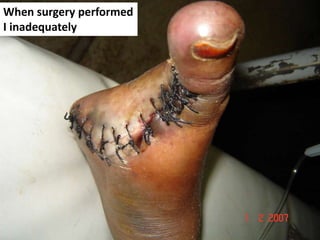
- 26. When surgery performed I inadequately
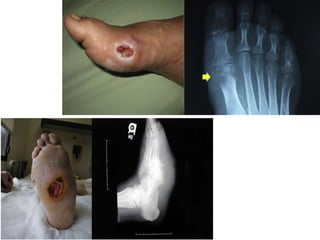
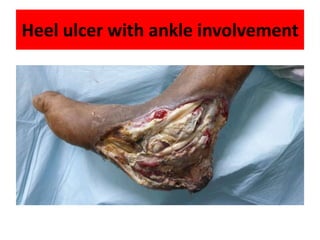
- 28. Heel ulcer with ankle involvement
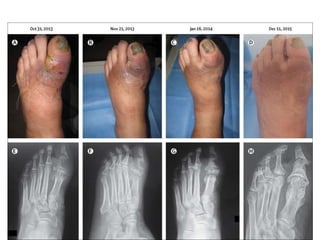
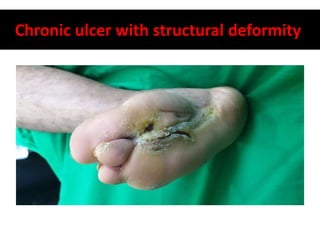
- 29. Chronic ulcer with structural deformity
- 30. Thank you for your attention