Java- Nested Classes
- 1. Nested Classes in Java
- 2. www.tothenew.com Agenda ‚ùñ Nested Classes ‚ùñ Inner Classes ‚ùñ Types of Inner Classes ‚û¢ Local inner class ‚û¢ Anonymous inner class ‚ùñ .new operator ‚ùñ .this operator
- 3. www.tothenew.com Nested Classes ‚ûîNested class is a class which is declared inside another class or interface class OuterClass { ... static class StaticNestedClass { ... } class InnerClass { ... } }
- 4. www.tothenew.com Advantages of Nested Classes ➔ It is a way of logically grouping classes that are only used in one place ➔ Can access all the members of outer class including private data members and methods. ➔ Can be declared private, public,protected, or package private, unlike regular classes that can only be declared public or package private. ➔ It increases encapsulation as itself can be declared private and still access Outer class’ private members ➔ It can lead to more readable and maintainable code as it places the code closer to where it is used.
- 5. www.tothenew.com Inner Classes ‚ûîInner class or non-static nested class is a class i.e. declared inside the class or interface ‚ûîAn inner class is associated with an instance of its enclosing class and has direct access to that object's methods and fields class Outer_class{ ... class Inner_class{ ... } }
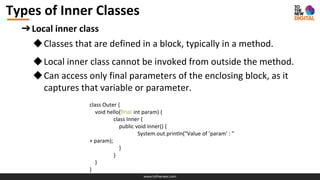
- 6. www.tothenew.com Types of Inner Classes ➔Local inner class ◆Classes that are defined in a block, typically in a method. ◆Local inner class cannot be invoked from outside the method. ◆Can access only final parameters of the enclosing block, as it captures that variable or parameter. class Outer { void hello(final int param) { class Inner { public void inner() { System.out.println("Value of ’param’ : " + param); } } } }
- 7. www.tothenew.com Types of Inner Classes ➔Local inner class ◆Can’t have static data members(unless declared final) and static methods. public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String []args){ class abc { static int b=6; public static void inner(){ System.out.println("Value of ’b’ : "+b); } } } } public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String []args){ class abc { static final int b=6; public void inner(){ System.out.println("Value of ’b’ : "+b); } } } }
- 8. www.tothenew.com Types of Inner Classes ‚ûîAnonymous inner class ‚óÜ Local Classes that have no name are known as anonymous inner class ‚óÜ Help make code more concise by allowing to declare and instantiate a class at the same time ‚óÜ Used when a local class is to be used only once ‚óÜ Used to override method of class or interface Button btn = new Button(); btn.setText("Say 'Hello World'"); btn.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() { @Override public void handle(ActionEvent event) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } });
- 9. www.tothenew.com .this Operator ‚ûî Refers to the current instance of the class. Example: Home.this ‚ûî In a simple class, saying Home.this and this will be equivalent. This expression is only used in cases where there is an inner class, and one needs to refer to the enclosing class. class Hello { class World { public void doSomething() { Hello.this.doAnotherThing(); // Here, "this" alone would refer to the instance of // the World class, so one needs to specify that the // instance of the Hello class is what is being referred to. } } public void doAnotherThing() { } }
- 10. www.tothenew.com .new Operator ‚ûî Creates an object of the inner class type. ‚ûî An Inner class has a reference to a specific instance of its outer class public class Outer { private final String message; Outer(final String message) { this.message = message; } public class Inner { private final String message; public Inner(final String message) { this.message = message; } public void foo() { System.out.println(Outer.this.message + message); } } public static void main(final String args[]) { new Outer("Hello").new Inner("World").foo(); } }
- 11. www.tothenew.com 1. How to decide if a class should be made an inner class or not? 2. When shouldn’t Inner classes be used? 3. Advantages of Inner classes over Local Classes? 4. Is it possible to create an anonymous class which isn’t an inner class? If yes, how? 5. What will be the names of the class files created for Outer.java having a nested class, named ‘Inner’? 6. Which modifiers can be applied to the inner class? 7. Which modifiers can be applied to method local inner class? 8. Create a class Library, that takes details(Name & Author) of Books from the user to add the Book to the Library and displays the details of all the books present in the Library. Book is an inner class. Display a menu to the user : i. Add a book to the Library. ii. Display current books in the Library. iii. Exit Exercises 9. Explain the last line : class OuterClass { static class Inner1 { static class Inner2 { class Inner3 { class Inner4 { } }}} } class Test { OuterClass.Inner1.Inner2.Innner3.Inner4 outerClass = new OuterClass.Inner1.Inner2().new Inner3().new Inner4(); }






![www.tothenew.com
Types of Inner Classes
‚ûîLocal inner class
◆Can’t have static data members(unless declared final) and
static methods.
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String []args){
class abc {
static int b=6;
public static void inner(){
System.out.println("Value of ’b’
: "+b);
}
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String []args){
class abc {
static final int b=6;
public void inner(){
System.out.println("Value of
’b’ : "+b);
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f814b924-268b-46c9-aaf1-bdc7de45e1d6-160813192154/85/Java-Nested-Classes-7-320.jpg)


![www.tothenew.com
.new Operator
‚ûî Creates an object of the inner class type.
‚ûî An Inner class has a reference to a specific instance of its outer class
public class Outer {
private final String message;
Outer(final String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public class Inner {
private final String message;
public Inner(final String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public void foo() {
System.out.println(Outer.this.message + message);
}
}
public static void main(final String args[]) {
new Outer("Hello").new Inner("World").foo();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f814b924-268b-46c9-aaf1-bdc7de45e1d6-160813192154/85/Java-Nested-Classes-10-320.jpg)

