Net force practice quiz 2[1]
- 1. Posted by Imran Mirza These are the types of problems that you will see on the quizzes. Use this practice quiz as a gauge for your understanding of physics. The answers are on the last page. No peeking! Part A: 1. Complete the following statement: The term net force most accurately describes A) the mass of an object B) the inertia of an object. C) the quantity that causes displacement. D) the quantity that keeps an object moving. E) the quantity that changes the velocity of an object 2. A net force F is required to give an object with mass m an acceleration a. If a net force 6 F is applied to an object with mass 2m, what is the acceleration on this object? A) a B) 2a C) 3a D) 4a E) 6a Use the following to answer questions 3-6: A 2.0-kg object moves in a straight line on a horizontal frictionless surface. The graph shows the velocity of the object as a function of time. The various equal time intervals are labeled using Roman numerals: I, II, III, IV, and V. The net force on the object always acts along the line of motion of the object. 3. Which section(s) of the graph correspond to a condition of zero net force? A) V only B) III only C) II and IV D) II, III, and IV E) I, III, and V 1
- 2. Posted by Imran Mirza 4. Which section of the graph corresponds to the application of the largest constant net force? A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V 5. In which section of the graph is the magnitude of the net force decreasing? A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V 6. In which section(s) of the graph is the net force changing? A) I and III B) II and IV C) III D) IV E) I and V 7. A 15-N net force is applied for 6.0 s to a 12-kg box initially at rest. What is the speed of the box at the end of the 6.0 s interval? A) 1.8 m/s B) 15 m/s C) 3.0 m/s D) 30 m/s E) 7.5 m/s 8. An apple crate with a weight of 225 N accelerates along a frictionless surface as the crate is pulled with a force of 14.5 N as shown in the drawing. What is the horizontal acceleration of the crate? A) 1.40 m/s2 B) 0.427 m/s2 C) 1.29 m/s2 D) 0.597 m/s2 E) 0.644 m/s2 2
- 3. Posted by Imran Mirza 9. A rock is thrown straight up from the earth's surface. Which one of the following statements concerning the net force acting on the rock at the top of its path is true? A) It is equal to the weight of the rock. B) It is instantaneously equal to zero. C) Its direction changes from up to down. D) It is greater than the weight of the rock. E) It is less than the weight of the rock, but greater than zero. 10. Two point masses m and M are separated by a distance d. If the distance between the masses is increased to 3d, how does the gravitational force between them change? A) The force will be one-third as great. B) The force will be one-ninth as great. C) The force will be three times as great. D) The force will be nine times as great. E) It is impossible to determine without knowing the numerical values of m, M, and d. 11. An astronaut orbits the earth in a space capsule whose height above the earth is equal to the earth's radius. How does the weight of the astronaut in the capsule compare to her weight on the earth? A) It is equal to her weight on earth. B) It is equal to one-half of her weight on earth. C) It is equal to one-third of her weight on earth. D) It is one-fourth her weight on earth. E) It is equal to one-sixteenth her weight on earth. 12. A 2.00-kg projectile is fired at an angle of 20.0°. What is the magnitude of the force exerted on the projectile when it is at the highest position in its trajectory? A) 19.6 N B) 14.7 N C) 9.80 N D) 4.90 N E) zero 13. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force acting on a 79.5-kg student due to a 60.0-kg student sitting 2.25 m away in the lecture hall? A) 3.14 × 10−9 N B) 2.82 × 10−8 N C) 7.91 × 10−10 N D) 1.41 × 10−7 N E) 6.29 × 10−8 N 3
- 4. Posted by Imran Mirza Part B Use the following to answer questions 1-2: A force P pulls on a crate of mass m on a rough surface. The figure shows the magnitudes and directions of the forces that act on the crate in this situation. W represents the weight of the crate. FN represents the normal force on the crate, and f represents the frictional force. 1. Which statement best describes the motion of the crate? A) The crate must be at rest. B) The crate must be moving with constant velocity. C) The crate must be moving with constant acceleration. D) The crate may be either at rest or moving with constant velocity. E) The crate may be either at rest or moving with constant acceleration. 2. What is the magnitude of FN, the normal force on the crate? A) 57 N B) 80 N C) 160 N D) 196 N E) 230 N 3. An automobile's wheels are locked as it slides to a stop from an initial speed of 30.0 m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.200 and the road is horizontal, approximately how long does it take the car to stop? A) 6.00 s B) 7.57 s C) 15.3 s D) 22.5 s E) 30.0 s Imran Mirza bss.imranmirza@yahoo.com +92 333 6515500 Beaconhouse Schools System Canal Side A-Level campus, Lahore, Pakistan 4
- 5. Posted by Imran Mirza Use the following to answer questions 4-6: Two blocks rest on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown. The surface between the top and bottom blocks is roughened so that there is no slipping between the two blocks. A 30-N force is applied to the bottom block as suggested in the figure. 4. What is the acceleration of the "two block" system? A) 1 m/s2 B) 2 m/s2 C) 3 m/s2 D) 6 m/s2 E) 15 m/s2 5. What is the force of static friction between the top and bottom blocks? A) zero B) 10 N C) 20 N D) 25 N E) 30 N 6. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction necessary to keep the top block from slipping on the bottom block? A) 0.05 B) 0.10 C) 0.20 D) 0.30 E) 0.40 7. A crate rests on the flatbed of a truck which is initially traveling at 15 m/s on a level road. The driver applies the brakes and the truck is brought to a halt in a distance of 38 m. If the deceleration of the truck is constant, what is the minimum coefficient of friction between the crate and the truck that is required to keep the crate from sliding? A) 0.20 B) 0.30 C) 0.39 D) 0.59 E) This cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the crate. 5
- 6. Posted by Imran Mirza 8. In an experiment with a block of wood on an inclined plane, with dimensions shown in the figure, the following observations are made: (1) If the block is placed on the inclined plane, it remains there at rest. (2) If the block is given a small push, it will accelerate toward the bottom of the incline without any further pushing. Which is the best conclusion that can be drawn from these observations? A) The coefficient of kinetic friction must be negative. B) Both coefficients of friction must be less than 0.25. C) Both coefficients of friction must be greater than 0.25. D) The coefficient of static friction must be less than the coefficient of kinetic friction. E) The coefficient of static friction is greater than 0.25 while the coefficient of kinetic friction is less than 0.25. 9. A rock is suspended from string and accelerates downward. Which one of the following statements concerning the tension in the string is true? A) The tension points downward. B) The tension is less than the weight of the rock. C) The tension is equal to the weight of the rock. D) The tension is greater than the weight of the rock. E) The tension is independent of the magnitude of the rock's acceleration. 10. In a tug-of-war, 5 men on each team pull with an average force of 500 N each. What is the tension in the center of the rope? A) zero B) 100 N C) 500 N D) 2500 N E) 5000 N Imran Mirza bss.imranmirza@yahoo.com+ 92 333 6515500 Beaconhouse Schools System Canal Side A-Level campus, Lahore, Pakistan 6
- 7. Posted by Imran Mirza 11. A muscle builder holds the ends of a massless rope. At the center of the rope, a 15-kg ball is hung as shown. What is the tension in the rope if the angle θ in the drawing is 4.5°? A) 1900 N B) 940 N C) 470 N D) 230 N E) 150 N 12. Two sleds are hooked together in tandem as shown in the figure. The front sled is twice as massive as the rear sled. The sleds are pulled along a frictionless surface by an applied force F. The tension in the rope between the sleds is T. Determine the ratio of the magnitudes of the two forces, T/F. A) 0.25 B) 0.33 C) 0.50 D) 0.67 E) 2.0 13. A 10-kg block is pushed against a vertical wall by a horizontal force of 100 N as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction, µ s, between the block and the wall is 0.60; and the coefficient of kinetic friction, µ k, is 0.40. Which one of the following statements is true if the block is initially at rest? A) The total force exerted on the block by the wall is horizontally directed. B) The block slides down the wall with an acceleration of magnitude 3.8 m/s2. C) The block will slide down the wall because the force of static friction can be no larger than 60 N. D) The block will remain at rest because the coefficient of static friction is greater than the coefficient of kinetic friction. E) The block will slide down the wall because the coefficient of kinetic friction is less than the coefficient of static friction. 7
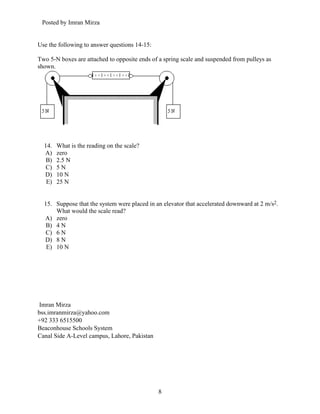
- 8. Posted by Imran Mirza Use the following to answer questions 14-15: Two 5-N boxes are attached to opposite ends of a spring scale and suspended from pulleys as shown. 14. What is the reading on the scale? A) zero B) 2.5 N C) 5N D) 10 N E) 25 N 15. Suppose that the system were placed in an elevator that accelerated downward at 2 m/s2. What would the scale read? A) zero B) 4 N C) 6 N D) 8 N E) 10 N Imran Mirza bss.imranmirza@yahoo.com +92 333 6515500 Beaconhouse Schools System Canal Side A-Level campus, Lahore, Pakistan 8
- 9. Posted by Imran Mirza 16. A spring scale is loosely fastened to the ceiling of a railway car. When a 1.0-kg block is hung from the scale, it reads 12 N and is oriented as shown in the figure. What is the approximate acceleration of the car as measured by an observer at rest on the ground outside of the car? A) 7 m/s2 to the right B) 7 m/s2 to the left C) 12 m/s2 to the right D) 12 m/s2 to the left E) It is impossible to calculate since the angle θ has not been given. 17. A 4-kg block and a 2-kg block can move on the horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks are accelerated by a +12-N force that pushes the larger block against the smaller one. Determine the force that the 2-kg block exerts on the 4-kg block. A) −12 N B) −4 N C) zero D) +4 N E) +8 N Imran Mirza bss.imranmirza@yahoo.com +92 333 6515500 Beaconhouse Schools System Canal Side A-Level campus, Lahore, Pakistan 9
- 10. Answer Key for Part A: 1. E 2. C 3. C 4. C 5. A 6. E 7. E 8. D 9. A 10. B 11. D 12. A 13. E Answer Key for Part B 1. D 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. B 8. E 9. B 10. d 11. B 12. B 13. C 14. C 15. B 16. A 17. B Dear all teacher with lots of love and care. Get a copy and enjoy your teaching bss.imranmirza@yahoo.com +92 333 6513300 10