Network switch
- 2. NETWORK SWITCH ï A network switch is a device used to connect network segments or network devices. ï Network switch receive messages and send them to the targeted audience. ï It is a telecommunication device that uses the packet switching to receive,process and forward data to the destination address.
- 4. Contd.. ï Network switch forwards data to one or multiple devices that need to receive it. ï Switches are the multiport network bridges that process and forward data at the data link layer(layer 2 of OSI model). ï The switches that process data at the network layer or above it, known as layer 3 switches or multi-layer switches.
- 5. APPLICATIONS OF SWITCHES ï A switch can manage the flow of data across the network. ï A network switch plays an integeral part in most modern Ethernet LANs.Mid to large sized LANs contain a number of linked managed switches. ï Switches are also used in SOHO(Small Office/Home Office) applications that typically uses a single switch to access the various broadband servioces an d the services like voice over internet protocol.
- 6. °äīĮēÔģŲŧåâĶ ï A switch is a device used in a computer network to physically connect the devices together. ï Each network device is connected to a switch is identified using a MAC address or a hardware address.Therefore,a switch is also considered as a intelligent network hub. ï A switch can trensfer data to any of the other devices at a time using half duplex mode or full duplex mode.
- 7. FUNCTIONS & ROLE ï A switch may operate at one or more layers of the OSI model as data link layer,network layer,transport layer,etc.A device that operate simultaneously at more than one of these layers,called as Multilayer switch. ï Devices that interconnect at layer 3 are called Routers,thatâs why layer 3 switches are also known as Routers. ï For commercial use,it is possible to connect different types of networks such as Ethernet,Fibre Channel,RapidIO,ATM,etc.This connectivity can be at any layers.
- 8. Contd,.. ï Generally,switches do not provide any network security.Therefore,some vendors provide firewall and network intrusion detection system to provide more security. ï Switch is used to create a mirror image of data that can go to external device.Ince most switch port mirroring provides only one mirrored stream,network hubs can be useful for fanning out data to several read-only analyzers,such as intrusion detection system and packet sniffers.
- 9. TYPES/LAYER-SPECIFIC FUNCTIONALITY ï Layer 1 Switch or Hub ï Layer 2 switch ï Layer 3 switch ï Layer 4-7 switch(multi-layered switch)
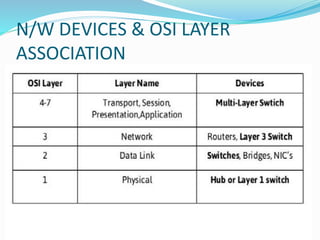
- 10. N/W DEVICES & OSI LAYER ASSOCIATION
- 11. LAYER1 SWITCH ï A network hub is simply a network device that does not manage any of the traffic coming through it.Any packet entering through a port is repeated on every other port.So the packet collissions effect the entire network. ï Can not filter messages,propagate to all connected devices. ï Not intelligent to find out best path for data packets.
- 12. PORT MIRRORING ï Layer 1 switches perform function called port mirroring. ï This helps to send network packets from one switch port to another switch port.
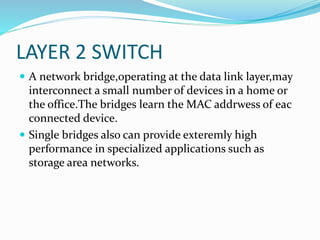
- 13. LAYER 2 SWITCH ï A network bridge,operating at the data link layer,may interconnect a small number of devices in a home or the office.The bridges learn the MAC addrwess of eac connected device. ï Single bridges also can provide exteremly high performance in specialized applications such as storage area networks.
- 14. 4 forwarding methods ï Store and Forward :- The switch buffers and verifies each frame before forwarding it. ï§ Perform error-checking before sending network frames. ï§ Highly reliable and slow. ï Cut Through :- The switch reads only up to the frameâs hardware address before starting to forward it. ï§ No error checking performed. ï§ Look up destination and forward it. ï§ Performance penalty.
- 15. °äīĮēÔģŲŧåâĶ ï Fragment Free :- It checks the first 64 bytes of the frame,where addressing information is stored.Collisions shuld be detected and tehn that frames will not be forwarded. ï§ It attempts to retain the benefits of both store & froward and cut through. ï§ Error checking is left for the end device.
- 16. °äīĮēÔģŲŧåâĶ ï Adaptive Switching :- A method of automatically selecting between the other three modes.
- 17. LAYER 3 SWITCH ï Most the fuctions are performed by a router. ï The most common capability of layer 3 is awareness of IP multicast through IGMP snooping. ï In this layer,switch can increase their efficiency by delivering more traffic. ï
- 18. LAYER 4 SWITCH ï Layer-4 switch is vendor-dependent. ï It may contain firewall,VPN concentrator and IP Security gateway. ï It is responsible for the analysis and control of network traffic at transport layer. ï Eg. Cisco 3560 L4 switch
- 19. Contd..
- 20. LAYER 7 SWITCH ï This may distribute loads based on Uniform Resource Locator . ï It may include a web cache and participate in a content delivery network.
- 21. °äīĮēÔģŲŧåâĶ
- 22. ADVANTAGES ï The number of broadcast domains gets decreased. ï Unlike hub,switches are more hardware oriented. ï It can make use of CAM table for port to MAC mapping. ï Unlike router,multi ports of switches are available in lower cost. ï It helps in logical segmentation by supporting VLAN.
- 23. DISADVANTAGE ï Proper designing and configuration is required if multicast packets are being handled. ï While limiting broadcasts,switches are not as good as routers.
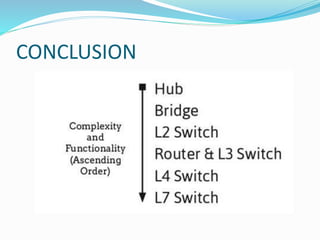
- 24. CONCLUSION