Network topologies
- 1. Computer Network Topologies Maninder Kaur professormaninder@gmail.com
- 2. What is a Topology? • Network topologies describe the ways in which the elements of a network are mapped. They describe the physical and logical arrangement of the network nodes. • The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals
- 3. Different Types of Topologies • Bus Topology • Star Topology • Ring Topology • Mesh Topology • Tree Topology • Hybrid Topology
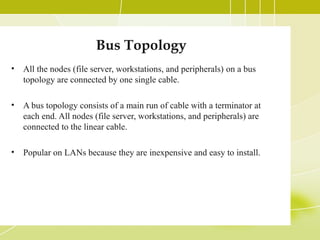
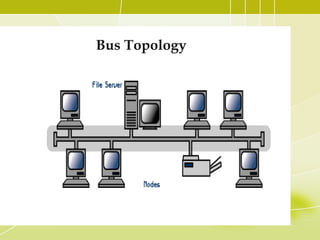
- 4. Bus Topology • All the nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) on a bus topology are connected by one single cable. • A bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end. All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable. • Popular on LANs because they are inexpensive and easy to install.
- 5. Bus Topology
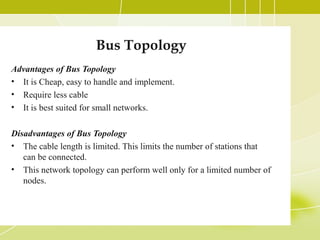
- 6. Bus Topology Advantages of Bus Topology • It is Cheap, easy to handle and implement. • Require less cable • It is best suited for small networks. Disadvantages of Bus Topology • The cable length is limited. This limits the number of stations that can be connected. • This network topology can perform well only for a limited number of nodes.
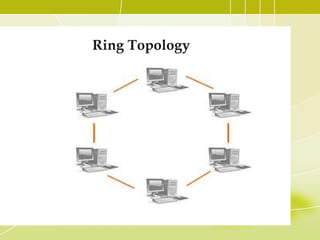
- 7. Ring Topology • In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighbours for communication purposes. • All messages travel through a ring in the same direction. • A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network. • To implement a ring network we use the Token Ring technology • A token, or small data packet, is continuously passed around the network. When a device needs to transmit, it reserves the token for the next trip around, then attaches its data packet to it.
- 9. Ring Topology Advantage of Ring Topology • Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit. • Easier to Mange than a Bus Network • Good Communication over long distances • Handles high volume of traffic Disadvantages of Ring Topology • The failure of a single node of the network can cause the entire network to fail. • The movement or changes made to network nodes affects the performance of the entire network.
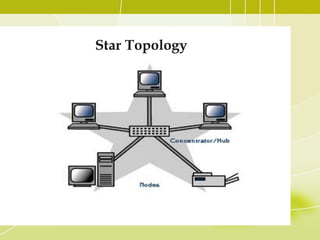
- 10. Star Topology • In a star network, each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) is connected to a central device called a hub. • The hub takes a signal that comes from any node and passes it along to all the other nodes in the network. • Data on a star network passes through the hub, switch, or concentrator before continuing to its destination. • The hub, switch, or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network. • The star topology reduces the chance of network failure by connecting all of the systems to a central node.
- 11. Star Topology
- 12. Star Topology Advantages of Star Topology • Easy to manage • Easy to locate problems (cable/workstations) • Easier to expand than a bus or ring topology. • Easy to install and wire. • Easy to detect faults and to remove parts. Disadvantages of Star Topology • Requires more cable length than a linear topology. • If the hub or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disabled. • More expensive because of the cost of the concentrators.
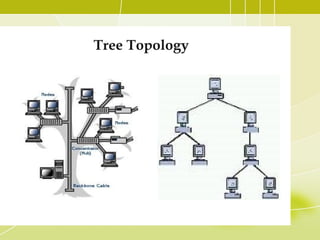
- 13. Tree Topology • A tree topology (hierarchical topology) can be viewed as a collection of star networks arranged in a hierarchy. • This tree has individual peripheral nodes which are required to transmit to and receive from one other only and are not required to act as repeaters or regenerators. • The tree topology arranges links and nodes into distinct hierarchies in order to allow greater control and easier troubleshooting. • This is particularly helpful for colleges, universities and schools so that each of the connect to the big network in some way.
- 14. Tree Topology
- 15. Tree Topology Advantages of a Tree Topology • Point-to-point wiring for individual segments. • Supported by several hardware and software vendors. • All the computers have access to the larger and their immediate networks. Disadvantages of a Tree Topology • Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used. • If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down. • More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
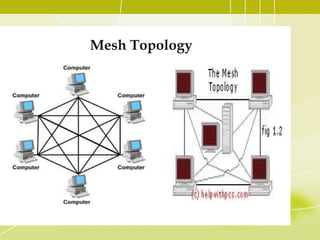
- 16. Mesh Topology • In this topology, each node is connected to every other node in the network. • Implementing the mesh topology is expensive and difficult. • In this type of network, each node may send message to destination through multiple paths. • While the data is travelling on the Mesh Network it is automatically configured to reach the destination by taking the shortest route which means the least number of hops.
- 17. Mesh Topology
- 18. Mesh Topology Advantage of Mesh Topology • • • No traffic problem as there are dedicated links. It has multiple links, so if one route is blocked then other routes can be used for data communication. Points to point links make fault identification easy. Disadvantage of Mesh Topology • There is mesh of wiring which can be difficult to manage. • Installation is complex as each node is connected to every node. • Cabling cost is high.
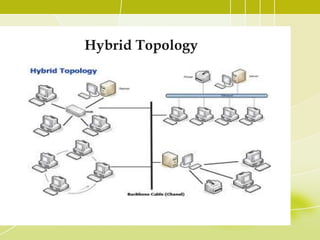
- 19. Hybrid Topology • A combination of any two or more network topologies. • A hybrid topology always accrues when two different basic network topologies are connected. • It is a mixture of above mentioned topologies. Usually, a central computer is attached with sub-controllers which in turn participate in a variety of topologies
- 20. Hybrid Topology
- 21. Hybrid Topology Advantages of a Hybrid Topology • • It is extremely flexible. It is very reliable. Disadvantages of a Hybrid Topology • Expensive
- 22. THANKS A LOT HAVE A NICE DAY