networking in cyber security basics of data communication
- 1. Subject: Data Communication and Network Unit 1: Introduction Presented by ŌĆō Prof. P. P. Patil-Niphade
- 2. Network Software Network software encompasses a broad range of software used for design, implementation, and operation and monitoring of computer networks. Functions of Network Software Helps to set up and install computer networks Enables users to have access to network resources in a seamless manner Allows administrations to add or remove users from the network Helps to define locations of data storage and allows users to access that data Helps administrators and security system to protect the network from data breaches, unauthorized access and attacks on a network Enables network virtualizations
- 3. Types of Networks Software Network storage software: software that manages the storage and backup of data on a network. Data archiving software: software that compresses and stores old or infrequently used data on a network. Patch management software: software that updates and fixes the software on a network. Security surveillance software: software that monitors and protects the network from threats and attacks. Asset management software: software that tracks and controls the hardware and software assets on a network.
- 4. Wireless Networks Computer networks that are not connected by cables are called wireless networks. They generally use radio waves for communication between the network nodes. They allow devices to be connected to the network while roaming around within the network coverage.
- 6. Types of Wireless Networks Wireless LANs ŌłÆ Connects two or more network devices using wireless distribution techniques. Wireless MANs ŌłÆ Connects two or more wireless LANs spreading over a metropolitan area. Wireless WANs ŌłÆ Connects large areas comprising LANs, MANs and personal networks.
- 7. Design Issues The following are the design issues for the layers: ŌĆó Reliability: It is a design issue of making a network that operates correctly even when it is made up of unreliable components. ŌĆó Addressing: There are multiple processes running on one machine. Every layer needs a mechanism to identify senders and receivers. ŌĆó Error Control: It is an important issue because physical communication circuits are not perfect. Many error detecting and error correcting codes are available. Both sending and receiving ends must agree to use any one code. ŌĆó Flow Control: If there is a fast sender at one end sending data to a slow receiver, then there must be flow control mechanism to control the loss of data by slow receivers. There are several mechanisms used for flow control such as increasing buffer size at receivers, slow down the fast sender, and so on. Some process will not be in position to accept randomly long messages. This property leads to mechanisms for disassembling, transmitting and the reassembling messages.
- 8. Contd.. ŌĆó Multiplexing and De-multiplexing: If the data has to be transmitted on transmission media separately, it is inconvenient or expensive to setup separate connection for each pair of communicating processes. So, multiplexing is needed in the physical layer at sender end and de-multiplexing is need at the receiver end. ŌĆó Scalability: When network gets large, new problem arises. Thus scalability is important so that network can continue to work well when it gets large. ŌĆó Routing: When there are multiple paths between source and destination, only one route must be chosen. This decision is made on the basis of several routing algorithms, which chooses optimized route to the destination. ŌĆó Confidentiality and Integrity: Network security is the most important factor. Mechanisms that provide confidentiality defend against threats like eavesdropping. Mechanisms for integrity prevent faulty changes to messages.
- 9. Network Models ŌĆóOSI Reference Model ŌĆóTCP/IP Model
- 10. OSI Reference Model OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It has been developed by ISO ŌĆō ŌĆśInternational Organization for StandardizationŌĆś, in the year 1984. It is a 7-layer architecture with each layer having specific functionality to perform. All these 7 layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one person to another across the globe. The seven layers of the OSI Model are a physical layer, data link layer, network layer, transport layer, session layer, presentation layer, and application layer.
- 11. OSI Model
- 12. OSI Reference Model The main functions of each of the layers are as follows ŌłÆ Physical Layer ŌłÆ Its function is to transmit individual bits from one node to another over a physical medium. Data Link Layer ŌłÆ It is responsible for the reliable transfer of data frames from one node to another connected by the physical layer. Network Layer ŌłÆ It manages the delivery of individual data packets from source to destination through appropriate addressing and routing. Transport Layer ŌłÆIt is responsible for delivery of the entire message from the source host to destination host. Session Layer ŌłÆ It establishes sessions between users and offers services like dialog control and synchronization. Presentation Layer ŌłÆ It monitors syntax and semantics of transmitted information through translation, compression, and encryption. Application Layer ŌłÆ It provides high-level APIs (application program interface) to the users.
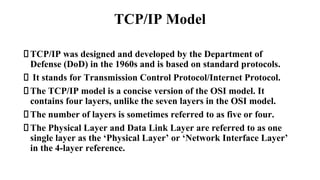
- 13. TCP/IP Model TCP/IP was designed and developed by the Department of Defense (DoD) in the 1960s and is based on standard protocols. It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The TCP/IP model is a concise version of the OSI model. It contains four layers, unlike the seven layers in the OSI model. The number of layers is sometimes referred to as five or four. The Physical Layer and Data Link Layer are referred to as one single layer as the ŌĆśPhysical LayerŌĆÖ or ŌĆśNetwork Interface LayerŌĆÖ in the 4-layer reference.
- 15. Why TCP/IP Model ? The main work of TCP/IP is to transfer the data of a computer from one device to another. The main condition of this process is to make data reliable and accurate so that the receiver will receive the same information which is sent by the sender. To ensure that, each message reaches its final destination accurately, the TCP/IP model divides its data into packets and combines them at the other end, which helps in maintaining the accuracy of the data while transferring from one end to another end.
- 16. How Does the TCP/IP Model Work? Whenever we want to send something over the internet using the TCP/IP Model, the TCP/IP Model divides the data into packets at the senderŌĆÖs end and the same packets have to be recombined at the receiverŌĆÖs end to form the same data, and this thing happens to maintain the accuracy of the data. TCP/IP model divides the data into a 4-layer procedure, where the data first go into this layer in one order and again in reverse order to get organized in the same way at the receiverŌĆÖs end.
- 17. Thank You