neurohumoral transmission in cns
- 1. Neurohumoral Transmission in CNS K Ravi kumar M.Pharm 1st semester Reg no: 170604017 Department of pharmacology Manipal university
- 2. CONTENTS ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Neurohumoral transmission ŌĆó Neurotransmitters ŌĆó Neurodegenerative diseases ŌĆó Conclusion ŌĆó References
- 4. Anatomic organisation of the cns
- 5. Chemical mediators in the CNS ŌĆó Small molecules ŌĆó Biogenic amines ŌĆó Serotonin ŌĆó Dopamine ŌĆó Histamine ŌĆó Epinephrine ŌĆó Norepinephrine ŌĆó Amino acids ŌĆó Glutamate ŌĆó Aspartate ŌĆó GABA ŌĆó Glycine ŌĆó Others ŌĆó Acetylcholine ŌĆó Nitric oxide ŌĆó Neuromodulators ŌĆó Neuropeptide-y ŌĆó Substance-p ŌĆó Lipid mediators ŌĆó prostaglandins ŌĆó Growth factors ŌĆó Nerve growth factor ŌĆó Brain derived growth factor
- 6. Chemical mediators in the CNS Mediator type Examples Targets Mainfuntional role Small molecule mediators Glutamate ,GABA, Acetylcholine, Dopamine ,5HT Ligangated ion channels G-PCR Fast & slow synaptic neurotransmission Neuromodulation Neuropeptides Substance P, Neuropeptide Y Endorphins G-PCR Neuromodulation Lipid mediators Prostaglandins Endocannabinoids G-PCR Neuromodulation Neutrophins Cytokines Nerve growth factor Kinase-linked receptors Neuronal growth , survival & functional plasticity
- 8. Metabolism and release of aminoacids
- 11. NMDA receptor
- 12. Ionotropic glutamate receptors NMDA AMPA Kainate Agonists Glutamate Aspartate Glycine D-serin Glutamate AMPA Quisqualate Glutamate Antagonists Ap-5,CPP NBQX NBQX ACET Modulators Polyamines Cyclothiazide Piracetam Channel blockers Phencyclidine Ketamine Remacidine Location Postsynaptic Glial cells Post synaptic Glial cells Pre & post synaptic Function Synaptic plasticity Excitotoxicity Fast epsp Fast epsp Presynaptic inhibition
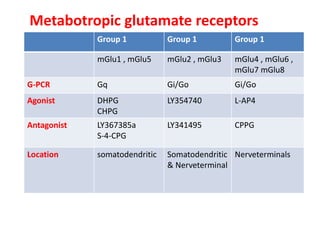
- 13. Metabotropic glutamate receptors Group 1 Group 1 Group 1 mGlu1 , mGlu5 mGlu2 , mGlu3 mGlu4 , mGlu6 , mGlu7 mGlu8 G-PCR Gq Gi/Go Gi/Go Agonist DHPG CHPG LY354740 L-AP4 Antagonist LY367385a S-4-CPG LY341495 CPPG Location somatodendritic Somatodendritic & Nerveterminal Nerveterminals
- 16. GABA Receptors
- 17. Glycine ŌĆó Glycine particularly present in high concentrations in the grey matter of spinal cord
- 18. Properties of Inhibitory amino acid receptors GABAA GABAB Glycine Agonist Muscimol Gaboxadol Baclofen Glycine Taurine Antagonist Bicuculline Gabazine 2-hydroxy- saclofen Channel blocker Picrotoxin Strychnine Effector mechanism Ligandgated chloride channel GPCR Ligandgated chloride channel Location GABAergic neurons Pre & post synaptic Postsynaptic mainly in brain stem &spinal cord
- 19. BIOGENIC AMINES
- 20. Dopamine pathway
- 21. Dopamine pathway in Brain
- 22. DOPAMINE Receptors D1 D5 D2 D3 D4 D1 D2 Corpus striatum Hippocampus hypothalamus Substantia nigra Limbic system Midbrain Medulla oblongata Excitatory Inhibitory
- 23. 5HT PATHWAY
- 25. Serotonin pathway in the brain
- 26. 5HT receptors 5HT1 5HT2 5HT3 5HT4 GPCR GPCR GPCRIONOTROPIC Inhibitory Excitatory Ligandgated Excitatory cAMP IP3 & DAG NA+, K+ cAMP
- 27. Receptors Location Agonists Antagonists 5HT1A 5HT1B 5HT1D 5HT1F CNS Vascular smooth muscles Blood vessels Uterus, heart, GIT Buspirone Ergotamine 5-CT Trip tans Trip tans Ergotamine Methiothepin Ergotamine 5HT2A 5HT2B CNS,PNS Smooth muscles Gastric fundus LSD Methysergide Cyproheptadiene 5HT3 PNS,CNS Chloromethyl biguanide Granisetron Ondansetron 5HT4 GIT Metoclopramide
- 28. ’āś Neurodegenerative diseases ŌĆó Parkinsonism ŌĆó It is defined as a neurodegenerative disorder of extrapyramidal Nigrostriatal pathway ŌĆó Therapy : MAO & COMT inhibitors ŌĆó Alzhiemers ŌĆó loss of cholinergic neurons results in shrinkage of the brain and other pathological conditions ŌĆó Therapy : Nootropic agents ŌĆó Antiamyloid antibodies ŌĆó NMDA receptor blocker
- 29. ’āś Huntington ’āś Depletion of GABA neurons ’āś Therapy : GABA-B Agonist ’āś Ischaemic Brain Damage ’āś Decrease blood supply results in hypoxia ’āś Therapy : NMDA receptor blocker
- 30. CONCLUSION ŌĆó The optimistic view is that a better understanding of the particular functions of the many molecular subtypes of these targets, and the design of more subtype- specific ligands, will lead to future breakthroughs.
- 31. References 1. Bleakman, D., Lodge, D., 1998. Neuropharmacology of AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 37, 187ŌĆō204. (Review giving molecular and functional information on these receptors), 2. Barnard, E.A., 2000. The molecular architecture of GABAA receptors. In: M├Čhler, H. (Ed.), Pharmacology of GABA and glycine neurotransmission. Handbook of experimental pharmacology 150. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 79ŌĆō100. (Authoritative review on the molecular subtypes of GABAA receptors
- 32. 3. Bylund, D.B., 2007. Receptors for norepinephrine and signal transduction pathways. In: Ordway, G.A., Schwartz, M.A., Frazer, A. (Eds.), Brain norepinephrine. Cambridge University Press, London. Head, G.A., Mayorov, D.N., 2006. Imidazoline receptors, novel agents and therapeutic potential. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 4, 17ŌĆō32. (Provides an update on the elusive imidazoline receptors