New energy technologies
- 2. ’éĪ COAL: The first major break through is the application of fluidized bed technology for the coal gasification, carbonization and combustion. presently pressurised fluidized bed technology is being developed to further improve the performance. ADVANTAGES: 1) High combustion efficiency. 2) fuel flexibility. 3) corrosion caused by alkali compounds in ash significantly reduced. 4) uniform temperature. 5) Operation is simple.
- 3. OIL: Improved efficiencies in the range of 5-15% are reported. Oil burner design has been improved in terms of primary air and secondary air mixing and combustion. power consumption was much smaller than that of conventional mechanical pressure atomisation . GAS: It has become economical to run long distances pipelines for the gas to be transported several 100kms to the place where it can be used. Biogas from rural, urban and industrial waste is another area presently under development.
- 4. NON CONVENTIONAL ENERGY SOURCES 1) Solar energy 2) Wind energy 3) Energy from biomass and bio gas 4) Energy plantation 5) Tidal energy 6) Geo thermal energy 7) Magneto hydro dynamics generator
- 5. SOLAR ENERGY SUNŌĆÖs energy can be utilized as thermal and photovoltaics this can be a major source of power. The solar power on earthŌĆÖs surface is 10^16 watts. Utilization of solar energy is of great importance to India since it lies in a temperature climate of the region where sunlight is abundant.
- 6. APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR ENERGY 1) Solar water heating. 2) Solar cookers. 3) Food refrigeration. 4) Solar drying. 5) Solar distillation. 6) Heating and cooling of buildings. 7) Solar ponds.
- 7. WIND ENERGY ŌĆó Winds are caused by two factors. 1) Heating and cooling of atmosphere 2) The rotation of earth with respect to atmosphere, and its motion around the sun. ŌĆó The energy available in winds over the earthŌĆÖs surface is estimated to be 1.6*10^7MW.
- 8. Types of windmills ’éŚ Horizontal axis 1) Multi blade type wind mill 2) Sail type wind mill 3) Propeller type wind mill ’éŚ Vertical axis 1) Savonius type 2) Darrieus type
- 9. ENERGY PLANTATION ’éŚ For large production electrical power the use of fire wood as a fuel for the boilers of a conventional power plant is suggested this approach is called the energy plantation.
- 10. Bio mass ’éŚ Biomass is produced in nature through photosynthesis achieved by solar energy conversion. H2O + CO2 = CH2O + O2 ’éŚ Biomass resources 1) Traditional solid form 2) Non traditional form 3) Fermentation
- 11. BIO GAS ’ü▒ The main source of production of biogas is wet cow dung or wet live stock waste. ’ü▒ The other sources of biogas are: 1) Vegetable waste 2) Crop residue 3) Pig manures 4) Algae
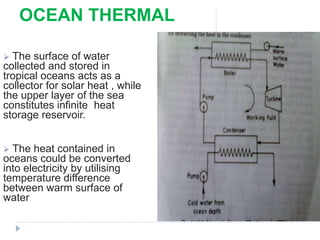
- 12. OCEAN THERMAL ’āś The surface of water collected and stored in tropical oceans acts as a collector for solar heat , while the upper layer of the sea constitutes infinite heat storage reservoir. ’āś The heat contained in oceans could be converted into electricity by utilising temperature difference between warm surface of water
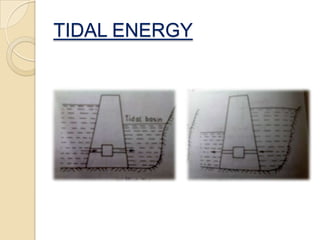
- 13. TIDAL ENERGY
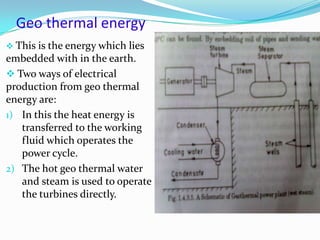
- 14. Geo thermal energy ’üČ This is the energy which lies embedded with in the earth. ’üČ Two ways of electrical production from geo thermal energy are: 1) In this the heat energy is transferred to the working fluid which operates the power cycle. 2) The hot geo thermal water and steam is used to operate the turbines directly.
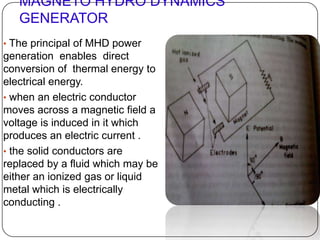
- 15. MAGNETO HYDRO DYNAMICS GENERATOR ŌĆó The principal of MHD power generation enables direct conversion of thermal energy to electrical energy. ŌĆó when an electric conductor moves across a magnetic field a voltage is induced in it which produces an electric current . ŌĆó the solid conductors are replaced by a fluid which may be either an ionized gas or liquid metal which is electrically conducting .
- 16. THANK YOU