New features of sql server 2005
- 1. Agenda History of MS SQL Server Introduction to SQL Server Enhanced UI for MS SQL Server 2005 New Features of SQL Server 2005 References
- 2. History of MS SQL Server
- 3. In 1988, Microsoft released its first version of SQL Server. It was designed for the OS/2 platform and was developed jointly by Microsoft and Sybase. During the early 1990s, Microsoft began to develop a new version of SQL Server for the NT platform. In 1994, Microsoft and Sybase formally ended their partnership. In 1995, Microsoft released version 6.0 of SQL Server. This release was a major rewrite of SQL Server's core technology. History of MS SQL Server
- 4. History of MS SQL Server In 1997, Microsoft released version 6.5 Enterprise Edition. In 1998, Microsoft released version 7.0 of SQL Server, which was a complete rewrite of the database engine. In 2000, Microsoft released SQL Server 2000. SQL Server version 2000 is Microsoft's most significant release of SQL Server to date. In 2005 , Microsoft released SQL Server 2005 and now the latest version is SQL Server 2008.
- 5. Introduction to SQL Server
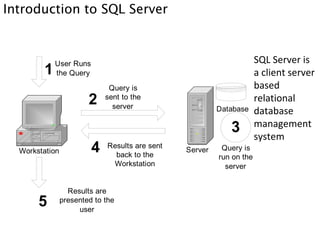
- 6. Introduction to SQL Server SQL Server is a client server based relational database management system
- 7. Enhanced UI for MS SQL Server 2005
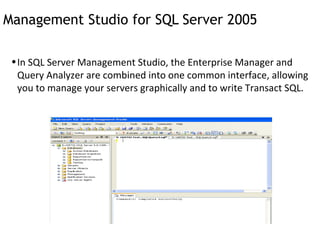
- 8. Management Studio for SQL Server 2005 In SQL Server Management Studio, the Enterprise Manager and Query Analyzer are combined into one common interface, allowing you to manage your servers graphically and to write Transact SQL.
- 9. Management Studio for SQL Server 2005 To make life easier, the SQL Server Management Studio includes an updated Template Explorer (View | Template Explorer or [Ctrl][Alt]T) that lays out the structure of more than 100 objects and tasks in Transact SQL, including administrative tasks like backing up and restoring databases.
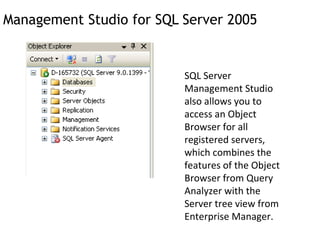
- 10. Management Studio for SQL Server 2005 SQL Server Management Studio also allows you to access an Object Browser for all registered servers, which combines the features of the Object Browser from Query Analyzer with the Server tree view from Enterprise Manager.
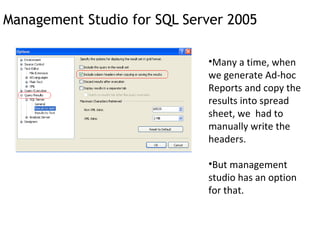
- 11. Management Studio for SQL Server 2005 Many a time, when we generate Ad-hoc Reports and copy the results into spread sheet, we had to manually write the headers. But management studio has an option for that.
- 12. Few New Features of MS SQL Server 2005
- 13. Few New Features of SQL Server 2005 C ommon T able E xpressions Improved Error Handling DDL Triggers Query Notifications Row_Number() PIVOT operators
- 14. Common Table Expression (CTE) A common table expression is an expression that returns a temporary named result set from a simple┬Āor complex query,┬Ādefined within the execution scope of a SELECT , INSERT , UPDATE , or DELETE statement. A CTE is a "temporary result set" that exists only within the scope of a single SQL statement.
- 15. Syntax of Common Table Expression A Common Table Expression contains three core parts: The CTE name (this is what follows the WITH keyword) The column list ( optional ) The query (appears within parentheses after the AS keyword)
- 16. Example for Common Table Expression
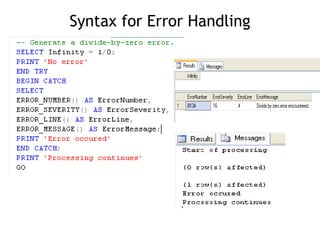
- 17. Improved Error Handling It introduces soft error control into T-SQL, the same kind available in standard programming languages. With TRY/CATCH , errors can be taken care of on the server side without involving the client side at all.
- 18. Syntax for Error Handling
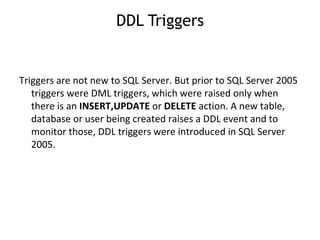
- 19. DDL Triggers Triggers are not new to SQL Server. But prior to SQL Server 2005 triggers were DML triggers, which were raised only when there is an INSERT,UPDATE or DELETE action. A new table, database or user being created raises a DDL event and to monitor those, DDL triggers were introduced in SQL Server 2005.
- 20. Syntax for DDL Triggers CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name ON { ALL SERVER | DATABASE } [ WITH <ddl_trigger_option> [ , ...n ] ] { FOR | AFTER } { event_type | event_group } [ ,... n ] AS { sql_statement [ ; ] [ ... n ] | EXTERNAL NAME < method specifier > [ ; ] }
- 21. Query Notifications SQL Server 2005 introduced query notifications, new functionality that allows an application to request a notification from SQL Server when the results of a query change. Query notifications allow programmers to design applications that query the database only when there is a change to information that the application has previously retrieved.
- 22. Query Notifications ..Cont Applications can take advantage of query notifications to reduce round trips to the database. With query notifications, the application issues a command that contains a query and a request for notification. The application caches the results of the query or dynamic content generated from the query results. When the application receives the query notification, the application clears the cached content.
- 23. ROW_NUMBER() Returns the sequential number of a row within a partition of a result set, starting at 1 for the first row in each partition. Syntax:
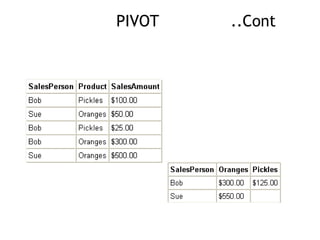
- 24. PIVOT In earlier versions of SQL Server there was not a simple way to create cross-tab queries, but a new option in SQL Server 2005 has made this a bit easier. What this allows you to do is to turn query results on their side, so instead of having results listed down like the listing below, you have results listed across.
- 25. PIVOT ..Cont
- 26. PIVOT ..Cont
- 27. There are three pieces that need to be understood in order to construct the query The SELECT statement The query that pulls the raw data to be prepared The PIVOT expression PIVOT ŌĆ”Cont







![Management Studio for SQL Server 2005 To make life easier, the SQL Server Management Studio includes an updated Template Explorer (View | Template Explorer or [Ctrl][Alt]T) that lays out the structure of more than 100 objects and tasks in Transact SQL, including administrative tasks like backing up and restoring databases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newfeaturesofsqlserver2005-100531234016-phpapp02/85/New-features-of-sql-server-2005-9-320.jpg)






![Syntax for DDL Triggers CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name ON { ALL SERVER | DATABASE } [ WITH <ddl_trigger_option> [ , ...n ] ] { FOR | AFTER } { event_type | event_group } [ ,... n ] AS { sql_statement [ ; ] [ ... n ] | EXTERNAL NAME < method specifier > [ ; ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newfeaturesofsqlserver2005-100531234016-phpapp02/85/New-features-of-sql-server-2005-20-320.jpg)