presentation on matrix
- 1. PRESENTED BY: Nikhi jain Salini bhadoria Gunjan dwivedi Shilpi barua Ritu Tomar
- 2. ï‚— It is an collection of elements which is arranges in rows columns. ï‚— It is the Combination of linear equation. ï‚— It is Represented by these symbols: ï‚— , , e.g. - 3*3
- 3. 1. Row matrices – A matrices which has only one row called row matrices e.g.- [123]1*3 2. Column matrices – A matrices which has only one column is called column matrices e.g. –
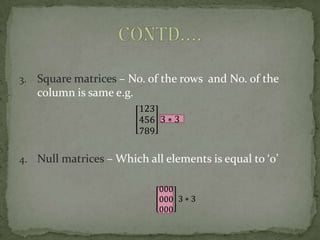
- 4. 3. Square matrices – No. of the rows and No. of the column is same e.g. 4. Null matrices – Which all elements is equal to ‘0’
- 5. 5. Identity matrices – A square matrices who’s main diagonal is assinty value ‘1’ and each of the other element is ‘0’ e.g. - , 6. Diagonal matrices – A square matrices all of who’s element expect those in the leading diagonal are ‘0’ e.g. -
- 6. 7. Scalar matrices – A diagonal matrices in which all the elements of main diagonal is same called scalar matrices e.g.- 3*3 8. Triangular matrices – there are two types: - Upper triangular – All the below elements are ‘0’ Lower triangular – All the above elements are ‘0’
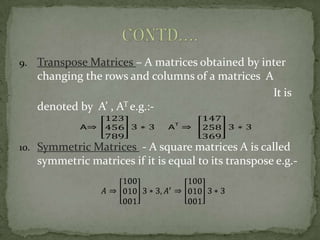
- 7. 9. Transpose Matrices – A matrices obtained by inter changing the rows and columns of a matrices A It is denoted by A’ , AT e.g.:- A AT 10. Symmetric Matrices - A square matrices A is called symmetric matrices if it is equal to its transpose e.g.-
- 8. 11. Skew Matrices - if A’ = -A is called skew matrices e.g.- 2*2 12. Equal Matrices – If two matrices order and there corresponding element is same is called equal matrices If X
- 9. 13. Algebraic Matrices – There are three type:- i. Addition method - for addition of two matrices the order must be same e.g.:- A +
- 10. ii.Subtraction method –For subtraction of two matrices the order must be same. Example:- A A-B
- 11. Multiplication of method – iii. Example:-



![1. Row matrices – A matrices which has only one row
called row matrices e.g.-
[123]1*3
2. Column matrices – A matrices which has only one
column is called column matrices e.g. –](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-130323092558-phpapp02/85/presentation-on-matrix-3-320.jpg)