Newton laws
0 likes288 views
This document explains Isaac Newton's three laws of motion through examples and diagrams. Newton's First Law states that objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Friction and gravity are examples of forces that cause moving objects to eventually stop. Newton's Second Law states that force equals mass times acceleration (F=ma). Newton's Third Law says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction - when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal force back on the first.
1 of 33
























Ad
Recommended
law of inertia
law of inertiaHeart Break Institution
╠²
- Galileo conducted experiments rolling balls down inclined planes and concluded that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force like friction. This tendency of objects to resist changes in their motion is called inertia.
- Newton later formalized this as his first law of motion, stating that objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- An object's inertia is determined by its mass, with more massive objects requiring greater forces to change their state of motion. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is distinct from its weight, which is the gravitational force acting on it.law of torts rohit
law of torts rohitRohit Unnikrishnan
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's major contributions and laws of motion. It covers:
- Newton formulated calculus, discovered that white light is composed of rainbow colors, invented the reflecting telescope, established the laws of motion, and developed the theory of universal gravitation.
- Newton's First Law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- Newton's Second Law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object0708 laws of_motion
0708 laws of_motionpragash a
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's major contributions and laws of motion. It covers:
- Newton formulated calculus, discovered that white light is composed of rainbow colors, invented the reflecting telescope, established the laws of motion, and developed the theory of universal gravitation.
- Newton's First Law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- Newton's Second Law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the objectChapter 3 newtons first law of motion
Chapter 3 newtons first law of motion watsonma12
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts from a physics textbook chapter about motion and forces. It discusses Aristotle's early definitions of natural and violent motion. It then covers Galileo's ideas that challenged Aristotle, including that friction is needed to stop an object in motion, and that inertia causes objects to remain in motion without a force. Galileo provided evidence for these ideas through experiments with rolling balls on inclined planes. The document also discusses Newton's first law of motion formalizing the concept of inertia. It explains that mass is a measure of an object's inertia, and defines inertia and mass. Finally, it addresses how the idea of inertia refutes early arguments against Copernicus' theory of a moving Earth.Forces and motion ch3.1
Forces and motion ch3.1Emily Neistadt
╠²
This document provides an overview of forces and motion, including Newton's three laws of motion. It defines key terms like force, mass, weight, and inertia. It explains that force is needed to cause an object to start or stop moving, while mass resists changes in motion. It also discusses how gravity affects all objects, but air resistance only affects lower-mass objects like feathers at terminal velocity. Newton's three laws are that unbalanced forces cause acceleration, forces cause acceleration proportional to mass, and for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Newton's Laws of motion
Newton's Laws of motion Kim Boggio
╠²
This document summarizes Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The second law defines force as mass times acceleration. Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are given for each law, such as friction slowing moving objects and the reaction force when hitting a baseball being the force applied to the bat by the ball.Sec.3&4 newton's laws-of_motion[1]
Sec.3&4 newton's laws-of_motion[1]Hamdy Karim
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion:
1) An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Friction causes objects to slow down.
2) The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force. F=ma.
3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples include a bird's wings pushing air down to lift itself up.Forces & Motion
Forces & Motionmlong24
╠²
The document is a chapter about forces and motion from a science textbook. It covers three main topics:
1) Gravity and falling objects, explaining that gravity causes all objects to accelerate at the same rate when falling, and air resistance increases with speed until terminal velocity is reached.
2) Newton's Laws of Motion, including his first law of inertia, second law relating force, mass and acceleration, and third law of equal and opposite forces.
3) Momentum, defining it as the product of mass and velocity, and explaining the law of conservation of momentum whereby the total momentum in a system remains constant during collisions or interactions.Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion spwburleson
╠²
This document outlines Newton's three laws of motion, explaining the principles of force, mass, and acceleration. It illustrates each law using relatable examples, such as cars in collisions, throwing a ball, and bumper cars at amusement parks, while emphasizing the concepts of inertia, action/reaction forces, and their implications. The material is designed for a 9th-grade physical science curriculum, with additional resources for further learning.NewtonÔÇÖs laws of motion
NewtonÔÇÖs laws of motionJoy Fulgar
╠²
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Galileo was the first to discover and describe inertia, observing that objects resist changes to their motion due to their mass. Newton later formalized inertia as his first law of motion. MOTION (force & motion) (Teach)
MOTION (force & motion) (Teach)Moira Whitehouse
╠²
This document discusses force and motion, including Newton's three laws of motion. It explains that an object's motion changes when a force acts upon it. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force. Friction is introduced as a force that opposes motion. The document discusses the two main types of friction - static and sliding friction - and how friction depends on the surfaces in contact and an object's mass. Methods for reducing friction, such as lubrication and rolling motion, are also covered.ICT Lesson Plan on Newton's Third law of Motion
ICT Lesson Plan on Newton's Third law of MotionRenjini Mohan
╠²
This document outlines a 45 minute physics lesson plan for 9th standard students on Newton's third law of motion and conservation of momentum. The lesson uses presentations, activities, and sample problems to help students understand key concepts. Students view presentations on examples of Newton's third law like a tea bag rocket. They analyze experiments showing conservation of momentum with moving balls. They also solve a sample problem calculating momentum before and after a gun is fired. The goal is for students to grasp that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, and that the total momentum of a system remains constant.First Law of Motion- Law of Inertia
First Law of Motion- Law of InertiaAnabelle Montevirgen
╠²
The document explains Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, illustrating how objects resist changes in their state of motion through various experiments. It discusses practical applications of this law in real-life scenarios, such as the effects observed during sudden stops in vehicles and the use of seatbelts. The document aims to enhance understanding of inertia through hands-on activities and inquiries related to everyday experiences.U1 module 1 forces and motion
U1 module 1 forces and motionLea Lacar
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion. It begins by defining key terms like force, inertia, and acceleration. It then explains each of Newton's three laws: (1) an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, (2) acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass, and (3) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are provided to illustrate Newton's laws, such as how gravity causes free fall acceleration. Balanced and unbalanced forces are also distinguished.Ccps force, motion & energy workshop #2
Ccps force, motion & energy workshop #2 Vu Phu
╠²
This document provides an overview of a grant-funded project to teach force, motion, and energy concepts to teachers. It includes background on the grant, connections to state science standards, effective teaching practices like hands-on investigations and technology use, and examples of challenges and activities to teach concepts like projectile motion. Pre- and post-assessments are discussed to measure impact on student learning. The goal is to help teachers feel more comfortable and excited about teaching force, motion, and energy topics.Force motion-magnetism
Force motion-magnetismCarlos Prada
╠²
The document discusses physics concepts related to forces and motion. Part 1 covers forces, including defining a force, balanced and unbalanced forces, and Newton's laws of motion. Part 2 discusses motion concepts such as position, speed, velocity, and how to calculate speed. Key ideas are that forces cause motion or changes in motion, and that balanced forces result in no net force while unbalanced forces do result in a net force and acceleration.3 laws of motion
3 laws of motionShubham Rohila
╠²
1) Motion is defined as a change in position of an object over time relative to a reference point. Uniform motion means equal distances traveled in equal time intervals while non-uniform motion means unequal distances.
2) Newton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object's motion and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
3) The second law states that acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. The third law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.Chapter 2 Physical Science
Chapter 2 Physical ScienceShelly Ferguson
╠²
- Relative motion occurs when an object's position changes relative to a reference point. Distance is how far an object moves while displacement is the distance and direction from the starting point.
- Speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. Average speed is the total distance divided by total time. Instantaneous speed is the speed at a given moment. Motion over time can be shown on a distance-time graph.
- Velocity includes both speed and direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity and occurs when an object changes its speed or direction. Forces can cause changes in an object's motion.Forces & Changes in Motion
Forces & Changes in MotionStephen Taylor
╠²
The document compares the world record breaking skydives of Joe Kittinger in 1960 and Felix Baumgartner in 2012, noting that Baumgartner jumped from a higher altitude of 39,045m compared to Kittinger's 31,300m, allowing Baumgartner to reach a higher maximum speed of 1342.8 km/h over Kittinger's 988km/h. The document also explores the factors like air pressure and density that influence terminal velocity and made Baumgartner's higher jump necessary to break the speed of sound record.Physics ppt
Physics pptMehak Sukhramani
╠²
1) Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
2) Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
3) Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, such that the mutual forces of interaction between two bodies are equal and opposite.Force and motion
Force and motion Weerachat Martluplao
╠²
Forces and motion are discussed in this document. It defines a force as a push or pull and explains that all motion is due to forces acting on objects. Motion is defined as a change in an object's position over time. Balanced and unbalanced forces are compared, with unbalanced forces being able to cause motion. Common forces like gravity, friction, and air resistance are described. Examples are provided to illustrate key concepts around forces.Newtons laws fact sheet cards
Newtons laws fact sheet cardsAndrew_Cox
╠²
Newton's three laws of motion are:
1) An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
2) The acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, expressed by F=ma.
3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Law of interaction
Law of interactionmaryjane0116
╠²
According to Newton, whenever objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other. For example, when a bird flies, it pushes air downwards with its wings, and the air reacts by pushing the wings upwards, providing lift. Similarly, when a rocket launches, the hot gases push down on the rocket, while the rocket pushes up on the gases, providing thrust. Newton's third law of motion explains these interacting equal and opposite forces that produce motion.Force and Motion Review
Force and Motion Reviewcrautry
╠²
Forces are pushes or pulls that have both size and direction. Newton's Laws of Motion describe how forces cause motion or changes in motion - an object at rest stays at rest unless a force acts on it, force equals mass times acceleration, and for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document reviews key concepts about forces, motion, speed, velocity, acceleration, and Newton's Laws through definitions, formulas, examples, and video clips to help explain these important physics concepts.Unbalanced Forces Cause Motion
Unbalanced Forces Cause Motiondeawscience
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion and related concepts like force, mass, inertia, gravity, friction, and air resistance. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's second law relates the acceleration of an object to the net force acting on it. Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Sehs 4.3.biomechanics iii
Sehs 4.3.biomechanics iiistrowe
╠²
Newton's three laws of motion describe the relationship between an object's motion and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that objects at rest will stay at rest and moving objects will keep moving unless acted on by an outside force. The second law relates the acceleration of an object to the net force acting on it and its mass. The third law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. These laws help explain phenomena in sports such as how starting blocks aid sprinting and how force generation allows football players to affect other players' motions.Motion and Laws of motion
Motion and Laws of motionAshittaZacharia
╠²
1) An unbalanced external force is needed to change the motion of an object. Galileo observed that objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest, unless an external force acts upon them.
2) Newton further studied Galileo's ideas and formulated his three laws of motion. Newton's first law formalizes the idea that objects resist changes to their motion.
3) Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass. It can be expressed as: Force = Mass ├ù Acceleration.NewtonÔÇÖs third law of motion
NewtonÔÇÖs third law of motionamandayoung313
╠²
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document provides examples of this law, such as bumper cars pushing against each other with equal forces in opposite directions. It also explains that it can be difficult to identify the action-reaction pair when one object is much more massive than the other and does not noticeably move, such as the Earth when a person walks on it. The document asks the reader to think of additional examples of Newton's third law of motion.0708 laws of_motion
0708 laws of_motionThembeka Madonsela
╠²
The document outlines Newton's three laws of motion, explaining the concepts of inertia, force, and action-reaction relationships. It discusses how objects at rest and in motion interact with unbalanced forces, along with the implications of weight and gravity. Examples are provided to illustrate each law, demonstrating their fundamental principles in real-world scenarios.0708_laws_of_motion.ppt
0708_laws_of_motion.pptkelvinencarnacion3
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's major scientific contributions and laws of motion. It explains Newton's three laws of motion: 1) Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2) Force equals mass times acceleration. 3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. It provides examples of how these laws apply to objects like balls, books, rockets, and describes concepts like inertia, balanced forces, unbalanced forces, and terminal velocity. Friction and gravity are identified as unbalanced forces that act on moving objects.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion spwburleson
╠²
This document outlines Newton's three laws of motion, explaining the principles of force, mass, and acceleration. It illustrates each law using relatable examples, such as cars in collisions, throwing a ball, and bumper cars at amusement parks, while emphasizing the concepts of inertia, action/reaction forces, and their implications. The material is designed for a 9th-grade physical science curriculum, with additional resources for further learning.NewtonÔÇÖs laws of motion
NewtonÔÇÖs laws of motionJoy Fulgar
╠²
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Galileo was the first to discover and describe inertia, observing that objects resist changes to their motion due to their mass. Newton later formalized inertia as his first law of motion. MOTION (force & motion) (Teach)
MOTION (force & motion) (Teach)Moira Whitehouse
╠²
This document discusses force and motion, including Newton's three laws of motion. It explains that an object's motion changes when a force acts upon it. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force. Friction is introduced as a force that opposes motion. The document discusses the two main types of friction - static and sliding friction - and how friction depends on the surfaces in contact and an object's mass. Methods for reducing friction, such as lubrication and rolling motion, are also covered.ICT Lesson Plan on Newton's Third law of Motion
ICT Lesson Plan on Newton's Third law of MotionRenjini Mohan
╠²
This document outlines a 45 minute physics lesson plan for 9th standard students on Newton's third law of motion and conservation of momentum. The lesson uses presentations, activities, and sample problems to help students understand key concepts. Students view presentations on examples of Newton's third law like a tea bag rocket. They analyze experiments showing conservation of momentum with moving balls. They also solve a sample problem calculating momentum before and after a gun is fired. The goal is for students to grasp that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, and that the total momentum of a system remains constant.First Law of Motion- Law of Inertia
First Law of Motion- Law of InertiaAnabelle Montevirgen
╠²
The document explains Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, illustrating how objects resist changes in their state of motion through various experiments. It discusses practical applications of this law in real-life scenarios, such as the effects observed during sudden stops in vehicles and the use of seatbelts. The document aims to enhance understanding of inertia through hands-on activities and inquiries related to everyday experiences.U1 module 1 forces and motion
U1 module 1 forces and motionLea Lacar
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion. It begins by defining key terms like force, inertia, and acceleration. It then explains each of Newton's three laws: (1) an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, (2) acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass, and (3) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are provided to illustrate Newton's laws, such as how gravity causes free fall acceleration. Balanced and unbalanced forces are also distinguished.Ccps force, motion & energy workshop #2
Ccps force, motion & energy workshop #2 Vu Phu
╠²
This document provides an overview of a grant-funded project to teach force, motion, and energy concepts to teachers. It includes background on the grant, connections to state science standards, effective teaching practices like hands-on investigations and technology use, and examples of challenges and activities to teach concepts like projectile motion. Pre- and post-assessments are discussed to measure impact on student learning. The goal is to help teachers feel more comfortable and excited about teaching force, motion, and energy topics.Force motion-magnetism
Force motion-magnetismCarlos Prada
╠²
The document discusses physics concepts related to forces and motion. Part 1 covers forces, including defining a force, balanced and unbalanced forces, and Newton's laws of motion. Part 2 discusses motion concepts such as position, speed, velocity, and how to calculate speed. Key ideas are that forces cause motion or changes in motion, and that balanced forces result in no net force while unbalanced forces do result in a net force and acceleration.3 laws of motion
3 laws of motionShubham Rohila
╠²
1) Motion is defined as a change in position of an object over time relative to a reference point. Uniform motion means equal distances traveled in equal time intervals while non-uniform motion means unequal distances.
2) Newton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object's motion and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
3) The second law states that acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. The third law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.Chapter 2 Physical Science
Chapter 2 Physical ScienceShelly Ferguson
╠²
- Relative motion occurs when an object's position changes relative to a reference point. Distance is how far an object moves while displacement is the distance and direction from the starting point.
- Speed is the distance traveled per unit of time. Average speed is the total distance divided by total time. Instantaneous speed is the speed at a given moment. Motion over time can be shown on a distance-time graph.
- Velocity includes both speed and direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity and occurs when an object changes its speed or direction. Forces can cause changes in an object's motion.Forces & Changes in Motion
Forces & Changes in MotionStephen Taylor
╠²
The document compares the world record breaking skydives of Joe Kittinger in 1960 and Felix Baumgartner in 2012, noting that Baumgartner jumped from a higher altitude of 39,045m compared to Kittinger's 31,300m, allowing Baumgartner to reach a higher maximum speed of 1342.8 km/h over Kittinger's 988km/h. The document also explores the factors like air pressure and density that influence terminal velocity and made Baumgartner's higher jump necessary to break the speed of sound record.Physics ppt
Physics pptMehak Sukhramani
╠²
1) Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
2) Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
3) Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, such that the mutual forces of interaction between two bodies are equal and opposite.Force and motion
Force and motion Weerachat Martluplao
╠²
Forces and motion are discussed in this document. It defines a force as a push or pull and explains that all motion is due to forces acting on objects. Motion is defined as a change in an object's position over time. Balanced and unbalanced forces are compared, with unbalanced forces being able to cause motion. Common forces like gravity, friction, and air resistance are described. Examples are provided to illustrate key concepts around forces.Newtons laws fact sheet cards
Newtons laws fact sheet cardsAndrew_Cox
╠²
Newton's three laws of motion are:
1) An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
2) The acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on it and its mass, expressed by F=ma.
3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Law of interaction
Law of interactionmaryjane0116
╠²
According to Newton, whenever objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other. For example, when a bird flies, it pushes air downwards with its wings, and the air reacts by pushing the wings upwards, providing lift. Similarly, when a rocket launches, the hot gases push down on the rocket, while the rocket pushes up on the gases, providing thrust. Newton's third law of motion explains these interacting equal and opposite forces that produce motion.Force and Motion Review
Force and Motion Reviewcrautry
╠²
Forces are pushes or pulls that have both size and direction. Newton's Laws of Motion describe how forces cause motion or changes in motion - an object at rest stays at rest unless a force acts on it, force equals mass times acceleration, and for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document reviews key concepts about forces, motion, speed, velocity, acceleration, and Newton's Laws through definitions, formulas, examples, and video clips to help explain these important physics concepts.Unbalanced Forces Cause Motion
Unbalanced Forces Cause Motiondeawscience
╠²
The document discusses Newton's three laws of motion and related concepts like force, mass, inertia, gravity, friction, and air resistance. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's second law relates the acceleration of an object to the net force acting on it. Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Sehs 4.3.biomechanics iii
Sehs 4.3.biomechanics iiistrowe
╠²
Newton's three laws of motion describe the relationship between an object's motion and the forces acting upon it. The first law states that objects at rest will stay at rest and moving objects will keep moving unless acted on by an outside force. The second law relates the acceleration of an object to the net force acting on it and its mass. The third law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. These laws help explain phenomena in sports such as how starting blocks aid sprinting and how force generation allows football players to affect other players' motions.Motion and Laws of motion
Motion and Laws of motionAshittaZacharia
╠²
1) An unbalanced external force is needed to change the motion of an object. Galileo observed that objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest, unless an external force acts upon them.
2) Newton further studied Galileo's ideas and formulated his three laws of motion. Newton's first law formalizes the idea that objects resist changes to their motion.
3) Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass. It can be expressed as: Force = Mass ├ù Acceleration.NewtonÔÇÖs third law of motion
NewtonÔÇÖs third law of motionamandayoung313
╠²
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document provides examples of this law, such as bumper cars pushing against each other with equal forces in opposite directions. It also explains that it can be difficult to identify the action-reaction pair when one object is much more massive than the other and does not noticeably move, such as the Earth when a person walks on it. The document asks the reader to think of additional examples of Newton's third law of motion.Similar to Newton laws (20)
0708 laws of_motion
0708 laws of_motionThembeka Madonsela
╠²
The document outlines Newton's three laws of motion, explaining the concepts of inertia, force, and action-reaction relationships. It discusses how objects at rest and in motion interact with unbalanced forces, along with the implications of weight and gravity. Examples are provided to illustrate each law, demonstrating their fundamental principles in real-world scenarios.0708_laws_of_motion.ppt
0708_laws_of_motion.pptkelvinencarnacion3
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's major scientific contributions and laws of motion. It explains Newton's three laws of motion: 1) Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2) Force equals mass times acceleration. 3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. It provides examples of how these laws apply to objects like balls, books, rockets, and describes concepts like inertia, balanced forces, unbalanced forces, and terminal velocity. Friction and gravity are identified as unbalanced forces that act on moving objects.Newton's_laws_of_motion, 1st, 2nd and 3rd.
Newton's_laws_of_motion, 1st, 2nd and 3rd.Tamonash Jana
╠²
The document outlines Newton's contributions to physics, including laws of motion and gravitation. It explains Newton's three laws: inertia, the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, and action-reaction pairs. Practical examples illustrate these concepts and clarify how different forces affect motion.0708_laws_of_motion.ppt
0708_laws_of_motion.pptZedZaoirseZaid
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's major scientific contributions and laws of motion. It explains Newton's three laws of motion: 1) Objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2) Force equals mass times acceleration. 3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. It provides examples of how these laws apply to objects like balls, books, rockets, and bugs colliding with surfaces. Friction and gravity are identified as unbalanced forces that cause moving objects to eventually stop.newtons laws of_motion
newtons laws of_motionLily Rose
╠²
This document discusses Isaac Newton's three laws of motion and related concepts like inertia, balanced forces, unbalanced forces, and gravity. Newton's three laws are: 1) Objects at rest tend to stay at rest and objects in motion tend to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2) Force equals mass times acceleration. 3) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document provides examples and explanations of how these laws apply to real-world situations like a ball rolling to a stop due to friction or an object in space propelling itself back to a shuttle by throwing an object.Newton laws
Newton lawsaimorales
╠²
Objects in motion will remain in motion and objects at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Things stop moving due to forces like friction and gravity. Newton's laws state that (1) objects resist changes in motion, (2) force equals mass times acceleration, and (3) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Gurun. ppt
Gurun. pptGurun Anand
╠²
This document summarizes Newton's three laws of motion as presented by student G urunjit. Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's second law establishes that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the object's mass. Newton's third law expresses that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are provided for each law.Law of inertia
Law of inertiamaryjane0116
╠²
The document discusses Newton's laws of motion through examples and activities. It begins by introducing inertia and having students relate experiences of sudden stops or starts in vehicles. Several activities are described to illustrate inertia, such as placing a coin on paper and removing the paper quickly. The document then summarizes Newton's three laws of motion, defines key terms like force, mass, and acceleration, and provides examples of how the laws apply in various situations like throwing a ball or stubbing a toe.Laws of motion
Laws of motionKimette Witt
╠²
Newton's First Law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. It further explains that an object's inertia causes it to resist any change in its motion. Newton's Second Law establishes that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. Newton's Third Law specifies that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.Bs ed,gen sc,unit # 10,11,12,laws of motion.
Bs ed,gen sc,unit # 10,11,12,laws of motion.Rakhshanda Hashmi
╠²
Newton's three laws of motion are summarized. Newton's First Law states that objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law states that force equals mass times acceleration. Newton's Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are provided to illustrate each law, such as friction slowing moving objects or gravity accelerating objects at the same rate but with different forces depending on their mass.Newton's laws of motion_564
Newton's laws of motion_564Pritam Sarkar
╠²
Isaac Newton made several important contributions including developing calculus, proposing that light is composed of colors in the visible spectrum, inventing the reflecting telescope, and establishing his three laws of motion and the universal law of gravitation. Newton's laws of motion describe the relationship between an object's mass, its motion (including changes in motion), and the applied force. The first law deals with inertia, the second law defines the relationship between an object's acceleration, mass, and the applied force, and the third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.Forces
ForcesPaula Mills
╠²
Forces can cause objects to move, change speed or direction, turn, bend or twist. Forces can be contact forces that act through direct physical contact, like pushing or pulling, or non-contact forces that act over a distance, like magnetism or gravity. Balanced forces cause no change in motion, while unbalanced forces cause acceleration or changes in speed or direction. Newton's three laws of motion describe how forces affect the motion of objects.laws of motion
laws of motionKavya Singhal
╠²
This document discusses Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion. Newton published his laws in his 1687 book "Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica", establishing the laws of classical mechanics. The laws state that 1) an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, 2) the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and 3) for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples are provided to help explain each law, such as tug of war demonstrating balanced forces, and kicking a soccer ball to impart unbalanced force. Key terms like inertia, acceleration, andNewton's 3 laws of Motion
Newton's 3 laws of Motionkoniasunset
╠²
Sir Isaac Newton discovered the three laws of motion in the late 1600s. Newton's First Law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law states that the force on an object equals its mass times its acceleration. Newton's Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.NEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION.pptx
NEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION.pptxMy own sweet home
╠²
This document summarizes Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion. It begins with background on Newton and his publication of the laws of motion in 1687. It then defines each law in 1-2 sentences: 1) An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2) The amount of force on an object equals its mass times its acceleration. 3) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The document then provides examples and explanations for each law.Newton laws of motion
Newton laws of motionNaveed Malik
╠²
This document summarizes Newton's three laws of motion. It explains that the first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The second law states that force equals mass times acceleration. The third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. It provides examples to illustrate each law, such as how inertia causes unrestrained passengers in a stopped car to continue moving forward, and how rockets are propelled upward by the equal and opposite reaction of exhaust gases pushing downward.Grade 8 Science IMs Q1 S1.ppt
Grade 8 Science IMs Q1 S1.pptJECKORO2
╠²
The document discusses Newton's laws of motion, including the definition of force, units of measurement for force, types of forces like friction and gravity, and Newton's three laws of motion - the law of inertia, the law of acceleration (F=ma), and the law of interaction (action-reaction forces). It provides examples and explanations of these fundamental physics concepts relating to force and motion.Newtons laws of_motion
Newtons laws of_motionWilliam McIntosh
╠²
Newton's laws of motion describe the fundamental principles of movement, including the law of inertia, the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration (F=ma), and the concept of action-reaction. The first law states that an object remains at rest or in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, the second law quantifies the effect of forces, and the third law emphasizes that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. These principles are illustrated through various examples of forces and motion, such as friction, propulsion, and the interaction of objects.Ad
Recently uploaded (19)
Personal letter personal letter personal letter.pptx
Personal letter personal letter personal letter.pptxGedeJuliana2
╠²
Personal letter personal letter personal letterPersonal letter personal letter personal letterAnalysis of Tausog Language English.pptx
Analysis of Tausog Language English.pptxMervieJadeBabao
╠²
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language English
Analysis of Tausog Language EnglishTypes of Information Sources (Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Sources)
Types of Information Sources (Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Sources)jenicahmendoza1
╠²
Sources of information come in various forms and serve different educational purposes. 2025-06-22 Abraham 04 (shared slides).pptx
2025-06-22 Abraham 04 (shared slides).pptxDale Wells
╠²
Lesson 4 of 9 in a Heritage Bible Master Class study of "Abraham: The Man God Called 'My Friend'"
Heritage Bible Master Class is a non-denominational Bible Class/Worship service that meets every Sunday morning at 10:15 at Heritage Palms Country Club, south of Fred Waring and east of Jefferson. Please join us.Japan's Media and Telecom Markets: Evolution, Global Competition, and NTT Law...
Japan's Media and Telecom Markets: Evolution, Global Competition, and NTT Law...Toshiya Jitsuzumi
╠²
Presentation at ICA2025 in Denver, CO. on June 16, 2025.Josaya - Abstract for the research of the youth development.pdf
Josaya - Abstract for the research of the youth development.pdfJosaya Injesi
╠²
This is my abstract. My first idea on the youFL Studio Crack Full Version [Latest 2025]
FL Studio Crack Full Version [Latest 2025]Jackson lithms
╠²
ƒæëØùíØùóØùºØùÿ:ØùûØùóØùúØù¼ ØùƒØù£ØùíØù× & ØùúØùöØùªØùº ØùÂØù╗ØÉôØù╝ ØùÜØù╝Øù╝Øù┤Øù╣Øù▓ ØùíØùÿØù¬ ØùºØù«Øù»> https://pcprocore.com/ ƒæêÔùÇ
FL Studio is a powerful digital audio workstation (DAW) used for music production. It's a complete software package that allows users to compose, arrange, record, edit, mix, and master music. Known for its intuitive design, especially for pattern-based music creation, FL Studio is popular among beginners and experienced producers alike.
Briefing on the upcoming UNFSS +4 Stocktake
Briefing on the upcoming UNFSS +4 StocktakeFrancois Stepman
╠²
2 June 2025. Online network briefing session from the Netherlands Food Partnership about the upcoming UNFSS +4 Stocktake for the Dutch partner network
The global UN FSS+4 Stocktaking Moment (July 27ÔÇô29, 2025, in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, co-hosted by Ethiopia and Italy) aims to discuss progress made since the UN Food Systems Summit of 2021.
With just five years remaining until the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development horizon line, the UNFSS+4 will provide an opportunity to document progress, strengthen accountability, and unlock investments for transformative action.
The event spotlighted:
successful country-level transformations,
innovative practices,
challenges faced in fragile and conflict-affected settings,
and be part of broader efforts to shape a coherent global narrative on sustainable development and accelerate synergies between key SDG transitions.
This is the presentation of Mr. Khaled Eltaweel of the Food Systems Coordination Hub.
Google Algorithm Updates ÔÇô A Complete Guide for Digital Marketing Students.pdf
Google Algorithm Updates ÔÇô A Complete Guide for Digital Marketing Students.pdfNithinks37
╠²
Explore the most important Google algorithm updates that shaped the SEO landscape from Panda to Helpful Content. This presentation is designed for students and beginners in digital marketing to help them understand how Google's algorithms affect search rankings and how to stay updated with best practices.
ƒöì WhatÔÇÖs inside:
Overview of key algorithm updates (Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, BERT, etc.)
Real-life examples of algorithm impacts
SEO tips to align with GoogleÔÇÖs evolving standards
Easy-to-understand explanations for beginners
ƒôÜ Learn more about SEO and digital marketing at ƒæë https://nithinksofficial.com
Whether you're preparing for a course, training session, or just want to improve your SEO skills, this guide will help you build a solid foundation.
#GoogleAlgorithmUpdates #DigitalMarketing #SEOforBeginners #GoogleSEO #LearnSEO #nithinksofficial. https://nithinksofficial.com/Ad
Newton laws
- 2. NewtonÔÇÖs Contributions 1. Calculus 2. Light is composed of rainbow colors 3. Reflecting Telescope 4. Laws of Motion 5. Theory of Gravitation
- 3. NewtonÔÇÖs First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
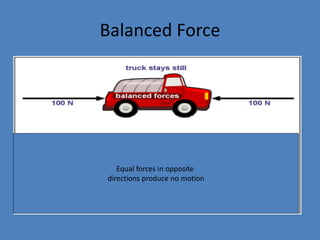
- 4. Balanced Force Equal forces in opposite directions produce no motion
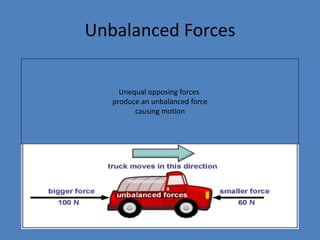
- 5. Unbalanced Forces Unequal opposing forces produce an unbalanced force causing motion
- 6. If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why donÔÇÖt moving objects keep moving forever? Things donÔÇÖt keep moving forever because thereÔÇÖs almost always an unbalanced force acting upon them. A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. If you throw a ball upwards it will eventually slow down and fall because of the force of gravity.
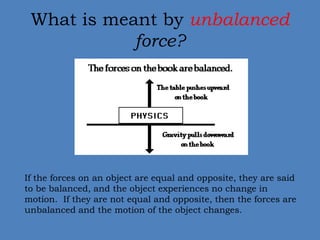
- 7. What is meant by unbalanced force? If the forces on an object are equal and opposite, they are said to be balanced, and the object experiences no change in motion. If they are not equal and opposite, then the forces are unbalanced and the motion of the object changes.
- 8. NewtonÔÇÖs First Law (law of inertia) ÔÇó MASS is the measure of the amount of matter in an object. ÔÇó It is measured in Kilograms
- 9. NewtonÔÇÖs First Law (law of inertia) ÔÇó INERTIA is a property of an object that describes how ______________________ the motion of the object much it will resist change to mass inertia ÔÇó more _____ means more ____
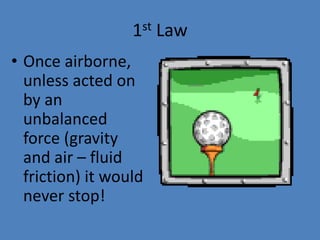
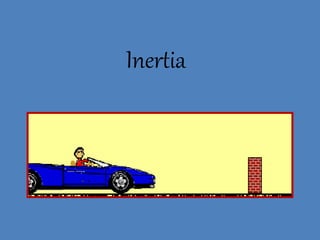
- 10. 1st Law ÔÇó Unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, this golf ball would sit on the tee forever.
- 11. What is this unbalanced force that acts on an object in motion? ÔÇó There are four main types of friction: ÔÇô Sliding friction: ice skating ÔÇô Rolling friction: bowling ÔÇô Fluid friction (air or liquid): air or water resistance ÔÇô Static friction: initial friction when moving an object
- 12. 1st Law ÔÇó Once airborne, unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air ÔÇô fluid friction) it would never stop!
- 13. Inertia
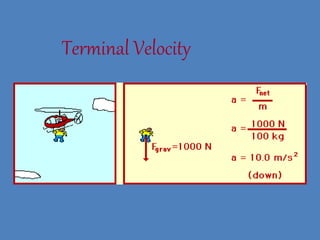
- 15. NewtonÔÇÖs Second Law Force equals mass times acceleration. F = ma
- 16. NewtonÔÇÖs Second Law ÔÇó Force = Mass x Acceleration ÔÇó Force is measured in Newtons ACCELERATION of GRAVITY(Earth) = 9.8 m/s2 ÔÇó Weight (force) = mass x gravity (Earth) MoonÔÇÖs gravity is 1/6 of the EarthÔÇÖs If you weigh 420 Newtons on earth, what will you weigh on the Moon? 70 Newtons If your mass is 41.5Kg on Earth what is your mass on the Moon?
- 17. NewtonÔÇÖs Second Law ÔÇó WEIGHT is a measure of the force of ________ gravity on the mass of an object Newtons ÔÇó measured in __________
- 18. NewtonÔÇÖs Second Law One rock weighs 5 Newtons. The other rock weighs 0.5 Newtons. How much more force will be required to accelerate the first rock at the same rate as the second rock? Ten times as much
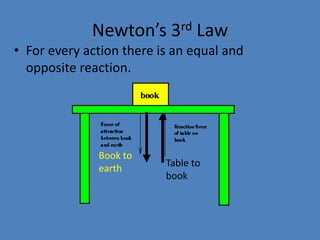
- 19. NewtonÔÇÖs Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- 20. NewtonÔÇÖs 3rd Law ÔÇó For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Book to earth Table to book
- 21. Think about it . . . What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When your toe exerts a force on a rock, the rock exerts an equal force back on your toe. The harder you hit your toe against it, the more force the rock exerts back on your toe (and the more your toe hurts).
- 22. NewtonÔÇÖs Third Law ÔÇó A bug with a mass of 5 grams flies into the windshield of a moving 1000kg bus. ÔÇó Which will have the most force? ÔÇó The bug on the bus ÔÇó The bus on the bug
- 23. NewtonÔÇÖs Third Law ÔÇó The force would be the same. ÔÇó Force (bug)= m x A ÔÇó Force (bus)= Mx a Think I look bad? You should see the other guy!
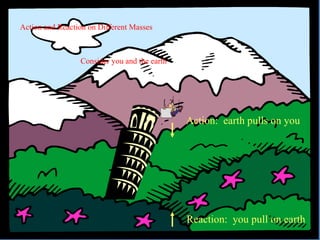
- 24. Action: earth pulls on you Reaction: you pull on earth Action and Reaction on Different Masses Consider you and the earth
- 25. Action: tire pushes on road Reaction: road pushes on tire
- 26. Reaction: gases push on rocket Action: rocket pushes on gases
- 27. Consider hitting a baseball with a bat. If we call the force applied to the ball by the bat the action force, identify the reaction force. (a) the force applied to the bat by the hands (b) the force applied to the bat by the ball (c) the force the ball carries with it in flight (d) the centrifugal force in the swing
- 28. NewtonÔÇÖs 3rd Law ÔÇó Suppose you are taking a space walk near the space shuttle, and your safety line breaks. How would you get back to the shuttle?
- 29. NewtonÔÇÖs 3rd Law ÔÇó The thing to do would be to take one of the tools from your tool belt and throw it is hard as you can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accelerate. At the same time, by Newton's third law, the tool is pushing back against you in the opposite direction, which causes you to accelerate back towards the shuttle, as desired.
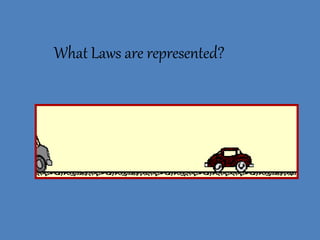
- 30. What Laws are represented?
- 32. Review NewtonÔÇÖs First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. NewtonÔÇÖs Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). NewtonÔÇÖs Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- 33. 1stlaw: Homer is large and has much mass, therefore he has much inertia. Friction and gravity oppose his motion. 2nd law: HomerÔÇÖs mass x 9.8 m/s/s equals his weight, which is a force. 3rd law: Homer pushes against the ground and it pushes back.