Next generation satellite services
- 1. Next generation satellite services 1 September 2022 Andr├® Gomes
- 2. regulation made simple >35 Years of Experience 4x4 Covering 4 Sectors Across 4 Continents >270 Clients from 90 Different Countries 70 Countries Covered >70 Team Members 25 Different Nationalities 26 Different Languages who we are in numbers
- 4. ŌĆó Satellites/year: ŌĆó 1967: 143 ŌĆó 2020: 1200 ŌĆó 2021: 1778 ŌĆó Similar average for 10 years Satellites skyrocketing Source: Edison Group. Euroconsult.
- 5. Satellite manufacturing and launch revenues: very long tail Manufacturing and launch revenues Satellites per company 5 companies will launch 58% of new satellites until 2030
- 6. System Amazon Kuiper Guowang OneWeb SpaceX Starlink Telesat Lightspeed Planned satellites 3,276 12,992 648 12,000 30,000 298 Spectrum bands Ka Ka, V Ku, Ka V Ku, Ka, E Ku, Ka Orbital height (km) 590-630 1100 1200 335-570 328-614 1015-1325 Manufacturer ABL Space System (start-up) China SpaceSat (R&D and manufacturing) JV with Airbus Space X Thales-Alenia Space Approx. life 5-10 years Approx. data rates 100-400 Mbps Approx. costs LEO: US$ 10,000-20,000 per Kg Examples of mega-constellations
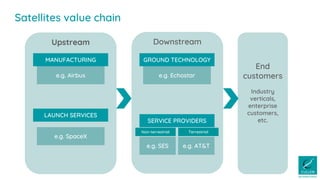
- 7. Downstream Upstream e.g. Airbus e.g. SpaceX GROUND TECHNOLOGY e.g. Echostar MANUFACTURING LAUNCH SERVICES e.g. SES SERVICE PROVIDERS Non-terrestrial Terrestrial e.g. AT&T End customers Industry verticals, enterprise customers, etc. Satellites value chain
- 8. Business models: relationship with telecoms operators Wholesale Retail Greenfield Brownfield - Distribution agreements (e.g. retail broadband) - Intermediate services (e.g. backhaul LTE and 5G; backup to navigation systems) Shareholder JSTL j.v.
- 9. Eutelsat & OneWeb Mergers and acquisitions
- 10. Amount Description Covered period US US$24.00bn Proposed funding for NASA in FY 2022. (But only US$224m for NASAŌĆÖs commercial LEO development programme). SpaceX (supplier of NASA). Proposed FY 2022 EU US$15.44bn Total budget of the EU Space Programme. (Proposed: US$2.69bn to be allocated for the Secure Connectivity Programme) 2021-2027 Japan US$4.50bn Total space-related budget (of these, US$71.4m are for satellite quantum cryptography R&D projects) 2022 China US$3.15bn First phase of deployment of the Hongyan constellation. (No information available on other constellations) 2016ŌĆō2021 Canada US$1.14bn (69% repayable loan and 31% equity) for Telesat Lightspeed 2021 UK US$1.00bn Equity stake in OneWeb 2020 Korea US$530.90m Space-related budget 2022 South Africa US$293.52m Government funding for the National Space AgencyŌĆÖs space infrastructure hub 2020 Singapore US$110.92m Flagship space technology development programme 2022 Relationships with governments
- 11. Key issues in satellite services regulation Licensing Interference and coexistence ŌĆó Satellite capacity and satellite services providers (concession/ licence/ authorisation) ŌĆó Earth stations (permit) ŌĆó Duration: 3-5-10-20 years, satellite lifespan ŌĆó Fees: per terminal or blanket licensing ŌĆó Regulators impose technical rules to avoid interference ŌĆó Service providers must avoid interferences/ report if existent Migration ŌĆó Each country has own coexistence parameters ŌĆó Varies per spectrum band ŌĆó Per spectrum band
- 12. Licensing requirements can be challenging
- 13. ŌĆó Technical characteristics & performance of new generation satellites present opportunities and challenges ŌĆó Some governments see new opportunities in this field. Direct funding, equity investor, as clients, or a combination of the above. Bridge coverage gaps, development opportunities for the domestic industry, competitive advantage. ŌĆó New dynamism in the industry. Incumbent groups, start-ups, new partnerships of different sizes. Vision and business models vary. ŌĆó Long-term promises: R&D on quantum cryptography for enhanced security, and on hybrid networks (combination of terrestrial and satellite in view of 6G). Main takeaways - opportunities
- 14. Main takeaways ŌĆō open issues ŌĆó Due to the current high CAPEX requirements, revenue uncertainties and short lifespan of LEO satellites, concerns over the economic sustainability of many of these systems. ŌĆó Capability to address "global" challenges (accidents, space debris, liabilities, how to collaborate, relations among governments) in an increasingly ŌĆ£crowdedŌĆØ satellite space.