No Nalue Latent Images
- 1. Forensic Biometric Identification Solutions LLC.
- 2. Realizing an attorney can't be expected to keep up with all the information related to the forensic disciplines, we decided to do a series of brief informational presentations on latent fingerprint images. Fingerprints and Automated Fingerprint Identification Systems are an accurate and critical part of the judicial system, but they do have shortcomings which can result in incorrect fingerprint analysis and sometimes missed/bad identifications. Errors can occur as a result of fingerprint images not being analyzed thoroughly or when a fingerprint examiner makes a questionable or bad decision. The current adversarial judicial process is the most effective tool in minimizing the number of incomplete and inaccurate latent fingerprint errors, but for the system to work as intended it requires that attorneys have more useable information available on analyzing/processing latent fingerprints. As explained later in this presentation a missed suspect or victim exclusion can be as devastating to a case as a bad identification. This presentation is designed to provide information on the initial evaluation of the latent image and areas in the fingerprint process that should be weighed when confronted with a case involving latent images. The questions posed in this presentation should be as useful to the prosecution as a they are to a defense attorney, neither attorney wants to have any surprises in court.
- 3. The image does not need to be verifiable to be useable. If a determination of pattern or even if limited amount of minutiae detail is available the image can have value in excluding possible donors. Exclusion is the decision by a fingerprint examiner that there are sufficient features in disagreement to conclude that the two areas of friction ridge impressions did not originate from the same source. In some situations knowing the suspect or victim did not leave the latent image can be very significant in a case. Scientific Working Group on Friction Ridge Analysis Study and Technology (SWGFAST) guidelines: The standard for exclusion is disagreement of friction ridge details, the following conditions that must be satisfied: Determined by a competent examiner. Applied to all comparable anatomical areas. Presence of one *discrepancy is sufficient to exclude. Based on sufficient quantity and quality of the friction ridge details. * Discrepancy- The presence of friction ridge detail in one impression that does not exist in the corresponding area of another impression.
- 4. There are no national standard guidelines for the evaluation of latent images. There are commonly two approaches to the Determination of Value of Latent Images that are determined by Agency Policy. Approach #1: Only impressions of value for individualization are compared. Value for individualization indicates an impression that is deemed to be identifiable. When adopting this approach, impressions lacking value for individualization are not further compared. Approach #2: Impressions of value for individualization or exclusion are compared. Approach #1 limits the examiners ability to thoroughly process and evaluate the latent case, this can lead to an exclusion of information critical to a case. The ability to exclude can be a an integral part of a case.
- 5. The analysis and evaluation of the latent image to determine usability can be done at the crime scene or in the ID Laboratory based on Agency Policy. A determination on the image value made at the crime scene could result in latent images deemed no value being destroyed or filed away in a case folder. Evaluating and Analyzing the latent images at the ID laboratory will normally produce the best results. The ID Laboratory has the capability to apply software enhancements, utilize fiber optic lighting and magnification technique to assist in analyzing and evaluating the questionable latent image(s). Again while the images may not be identifiable they may contain enough information to exclude a victim or suspect. If the image from the crime scene can exclude the suspect it may be a significant factor in processing the latent case. It is important that the attorneys involved in the case thoroughly understand the process used by the agency in; evaluating latent images and whether the image(s) were categorized as useable or of no value and if policy dictates the no value images be destroyed or archived.
- 6. Fingerprint experts can reach different opinions on the same images? The experts analysis is based on training and experience this can result in a more experienced examiner placing a value on an image that the inexperienced examiner may determine has no value. The determination of image value is not a completely objective decision: 1) Value versus no value 2) Individualization versus inconclusive 3) Exclusion versus inconclusive 4) Individualization versus exclusion The criminal justice system relies on the skill of latent print examiners as experts, currently there is no generally accepted objective, measure to assess the skill of latent print examiners. For an initial analysis of incoming latent images an agency may utilize it’s most experienced examiner or it may utilize the least experienced, as a training exercise for the new examiner. The training and experience of the examiner can have a dramatic impact on the images an agency categorizes as no-value or useable.
- 7. Documentation of the image analysis and disposition of the latent image(s) again is based on Agency Policy. Many agencies document the final decision of the examiner in a computerized record but few go into detail on how they reached the no-value decision. Remember unlike individualizations the no-value decision is usually made by a single fingerprint examiner so you are relying on that individuals; training and experience. If the decision on image quality is made at the crime scene the individual may not be made by an experienced latent examiner that determines the value of the image and the conditions at the scene will not be conducive to a thorough accurate analysis.
- 8. Level 1 includes the general ridge flow and pattern configuration to include information enabling orientation, core and delta location, and distinction of finger versus palm. Level 2 detail includes formations, defined as a ridge ending, bifurcation, dot, or combinations thereof. The relationship of Level 2 detail enables individualization. Level 3 detail includes all dimensional attributes of a ridge, such as ridge path deviation, width, shape, pores, edge contour, incipient ridges, breaks, creases, scars and other permanent details.
- 9. SWGFAST Guidelines; an exclusion decision can be based on: Level 1 detail, when sufficient pattern area and orientation indicators are available absent any significant distortion. If significant distortion is observed, an exclusion decision can only be reached by considering both Level 1 and Level 2 details. Level 2 detail, an exclusion decision can be based on Level 2 when sufficient disagreement has been observed. Level 3 details, cannot be the sole factor in exclusion decisions. Level 3 details have to be considered in conjunction with Level 1 and Level 2 details.
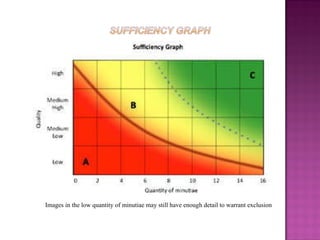
- 10. Images in the low quantity of minutiae may still have enough detail to warrant exclusion
- 11. While we would be more than willing to assist you in any case work needs, we are hope this presentation will give you some basic information for any of your future latent fingerprint case work. The information contained attorneys working for the prosecution or defense. If you need more detailed information on latent fingerprints please contact us, in today’s electronic world Forensic Biometric Identification Solutions LLC. can assist attorney’s in NY or CA as easily as we can attorneys in Omaha NE.
- 12. Ěý
- 13. Exclusion The determination by an examiner that there is sufficient quality and quantity of detail in disagreement to conclude that two areas of friction ridge impressions did not originate from the same source. No Value(Inconclusive) The determination by an examiner that there is neither sufficient agreement to individualize, nor sufficient disagreement to exclude. Individualization The determination by an examiner that there is sufficient quality and quantity of detail in agreement to conclude that two friction ridge impressions originated from the same source. Level 1 includes the general ridge flow and pattern configuration to include information enabling orientation, core and delta location, and distinction of finger versus palm. Level 2 detail includes formations, defined as a ridge ending, bifurcation, dot, or combinations thereof. The relationship of Level 2 detail enables individualization. Level 3 detail includes all dimensional attributes of a ridge, such as ridge path deviation, width, shape, pores, edge contour, incipient ridges, breaks, creases, scars and other permanent details.
Editor's Notes
- #13: While you are doing the exercises I will pass out by business card.