Noisy breathing in children
- 2. By : Dr hisham alrabty Pediatric consultant and pulmonologist
- 3. objectives: • Definition. • Anatomy. • Types. • Causes. • Clinical presentation. • Diagnosis. • Treatment.
- 4. Definition: breathing cycle is not hearable normally. So noisy breathing is hearable breathing on other words breathing with any noise. It happens due to obstruction to airways either upper or lower due to any cause like edema or foreign body or secretion.
- 5. Anatomy of R.S: Consists of an upper respiratory tract (nose to larynx) and a lower respiratory tract (trachea onwards) . OR Conducting portion transports air: includes the nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and progressively smaller airways, from the primary bronchi to the terminal bronchioles Respiratory portion carries out gas exchange: composed of small airways called respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts as well as air sacs called alveoli.
- 7. Types: Three common types are: 1. Stridor: due to obstruction of upper airways. 2. wheeze: due to obstruction to lower airways. 3. Grunting: due to expiration against partially closed epiglottis.
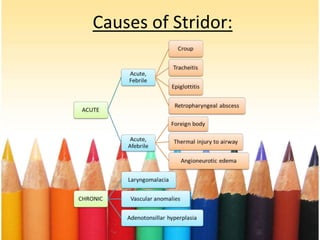
- 8. Causes: • Causes of stridor: 1. Croup: parainfluenza virus. 2. Epiglottitis: hemophilus influenza bacteria. 3. Laryngomalacia: congenital. 4. Hypocalcaemia: rickets. • Causes of wheeze: 1. Asthma: inflammatory. 2. Bronchiolitis: RSV. • Causes of grunting: Pneumonia: infections by bacteria and viruses.
- 9. Stridor: abnormal, high-pitched sound produced by turbulent airflow through a partially obstructed airway at the level of the supraglottis, glottis, subglottis, and/or trachea. Types of it either inspiratory due to laryngeal obstruction or expiratory due to tracheobronchial obstruction or biphasic doe to subglottic or glottic anomaly.
- 12. Wheeze: abnormal high-pitched or low-pitched sound heard either by unaided human ear or through stethoscope mainly during expiration. patterns of wheezing either Transient early wheezing (viral induced) or Persistent and recurrent wheezing (asthma).
- 13. Clinical presentation: • History. • symptoms. • Signs.
- 14. History: • Onset. • History of any associated symptom: fever. • Duration: • Family history: • Social: • Drug history: • History of previous illness or addmission:recurrence like asthma. • Travel history:
- 15. Symptoms: • Fever: pneumonia. • Cough: barking cough like croup. • Wheeze: bronchiolitis. • Stridor: croup. • Hoarseness: croup. • Feeding difficulty: pneumonia. • Drooling: epiglottitis. • Dyspnea.
- 16. Signs: • Cyanosis. • Tachypnea. • Apnea. • Flaring alae nasii. • Recessions. • Rhochi: asthma. • Rales: pneumonia. • Pleural rub.
- 17. Diagnosis: • Blood: Cbc,abg,esr,crp,culture. • X.ray: Cxr,lat.neck xr. • Specific: Immunoflouroceness,pcr,viral serology. • Direct laryngnscopy,bronchoscopy. • Ct,mri.
- 18. The radiographic changes of asthma are those of hyper inflated chest (flat diaphragm, square chest shape).
- 19. Laryngomalacia • Progressive airway obstruction on inspiration. • Note omega-shaped epiglottis.
- 20. Treatment: • Supportive: Humid oxygen,antipyretic,intravenous fluids. • Specific: Antibiotics,bronchodilators,steroids,antiviral. • Immunization: Monoclonal antibody in bronchiolitis.
- 21. Prognosis: It depends on the cause ranging from complete recovery to death.