Nossi ch 3
- 1. Chapter 3 Voting and Elections Voting Systems Flaws of Voting Systems Weighted Voting Systems
- 2. Voting Systems Vote for your favorite of the following: Butterfinger Nestle Crunch ReeseŌĆÖs Skittles
- 3. Voting Systems The candy bar with the most votes is the winner. This method of choosing a winner is called: The Plurality Method
- 4. Voting Systems We will vote again for the Candy bars, but this time we will rank the choices:
- 5. Voting Systems Rank each candidate using 1 to 4, 1 is your favorite and 4 is your least favorite. (I will give out a ballot) Butterfinger Nestle Crunch ReeseŌĆÖs Skittles
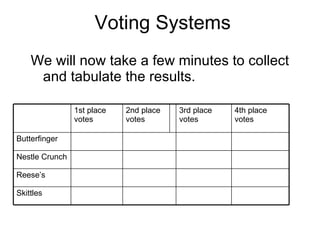
- 6. Voting Systems We will now take a few minutes to collect and tabulate the results. Skittles ReeseŌĆÖs Nestle Crunch Butterfinger 4th place votes 3rd place votes 2nd place votes 1st place votes
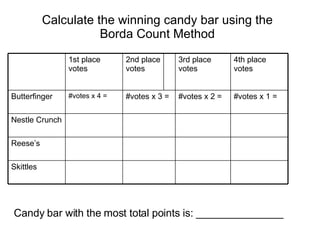
- 7. Borda Count Method Voters rank the m candidates. A voterŌĆÖs last choice gets one point, next-to-the-last choice gets two points and so on, until the voterŌĆÖs first choice gets m points. The candidate receiving the most points is selected.
- 8. Calculate the winning candy bar using the Borda Count Method Candy bar with the most total points is: _______________ Skittles ReeseŌĆÖs Nestle Crunch #votes x 1 = #votes x 2 = #votes x 3 = #votes x 4 = Butterfinger 4th place votes 3rd place votes 2nd place votes 1st place votes
- 9. Borda Count Method Variations of this method are widely used. The Heisman trophy winner is chosen by about 900 sportswriters and former Heisman trophy winners awarding 3 pts for a first place vote, 2 pts for a second place vote and 1 point for a 3rd place vote.
- 10. Borda Count Method Did the winning candy bar receive the most 1st place votes?
- 11. Plurality With Elimination Method LetŌĆÖs look at another method to choose a winning candy bar. In this method voters vote for one candidate. If a candidate receives a majority of votes, that candidate is selected.
- 12. Plurality With Elimination Method If no candidate receives a majority, eliminate the candidate(s) receiving the fewest votes, and do another round of voting.
- 13. Plurality With Elimination Method How many members of the class are present today? To win a majority of votes a candy bar would have to get _____ votes. (1/2 of those present +1)
- 14. Plurality With Elimination Method The candy bar receiving the least amount of votes was:_________ So, we eliminate that candy bar and vote for the remaining 3. Did one get a majority of votes?
- 15. Plurality With Elimination Method If no candy bar got a majority of votes, the candy bar receiving the least amount of votes is eliminated and vote for the remaining 2.
- 16. Plurality With Elimination Method This method is used to choose: The location for the Olympic Games The President of France
- 17. Plurality With Elimination Method We will study Example 3.4 which starts on pg 147 This example demonstrates the Plurality with elimination method along with using rankings.
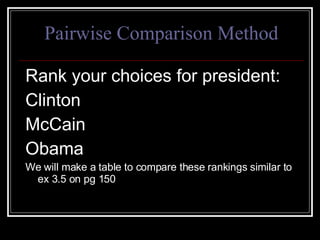
- 18. Pairwise Comparison Method A method for comparing pairs of candidates to determine a winner. For today we will use the 3 top presidential candidates to demonstrate this method.
- 19. Pairwise Comparison Method Rank your choices for president: Clinton McCain Obama We will make a table to compare these rankings similar to ex 3.5 on pg 150
- 20. Pairwise Comparison Method Voters rank all candidates. For each pair of candidates X and Y, determine how many voters prefer X to Y and vice versa. If X is preferred to Y by more voters, then X receives 1 point. If Y is preferred to X by more voters, then Y receives 1 point. If the candidates tie, then each receives 1/2 point.
- 21. Pairwise Comparison Method The candidate who receives the most points is selected. This method is also call the Condercet method after the French mathematician who analyzed and studied this method.
- 22. Pairwise Comparison Method Analyze our presidential candidates and determine a winner based on the Pairwise Comparison Method.
- 23. Section 3.1 Voting Systems Pg. 154 (1,3,6,9,13,14,15,25,33) You will need to show some work on each, maybe totals and/or tables
- 24. Flaws in Voting Systems Majority Criterion Head-to-Head Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion One more voting system called Approval Voting
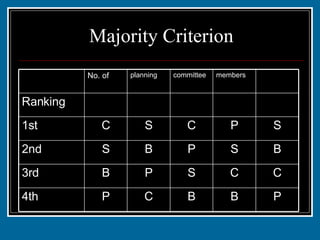
- 25. Majority Criterion If a candidate is the first choice of a majority of voters, then that candidate should be elected.
- 26. Majority Criterion P B B C P 4th C C S P B 3rd B S P B S 2nd S P C S C 1st 1 1 2 2 3 Ranking members committee planning No. of
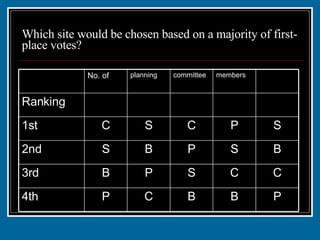
- 27. Which site would be chosen based on a majority of first-place votes? P B B C P 4th C C S P B 3rd B S P B S 2nd S P C S C 1st 1 1 2 2 3 Ranking members committee planning No. of
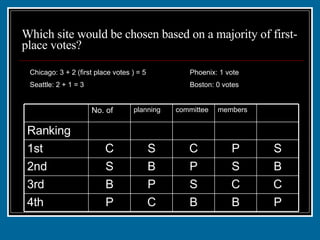
- 28. Which site would be chosen based on a majority of first-place votes? Chicago: 3 + 2 (first place votes ) = 5 Phoenix: 1 vote Seattle: 2 + 1 = 3 Boston: 0 votes P B B C P 4th C C S P B 3rd B S P B S 2nd S P C S C 1st 1 1 2 2 3 Ranking members committee planning No. of
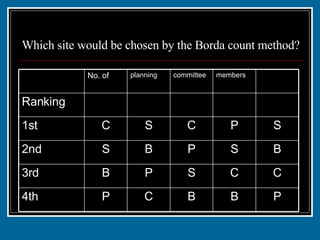
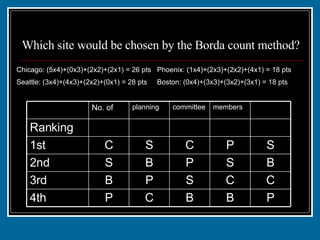
- 29. Which site would be chosen by the Borda count method? P B B C P 4th C C S P B 3rd B S P B S 2nd S P C S C 1st 1 1 2 2 3 Ranking members committee planning No. of
- 30. Which site would be chosen by the Borda count method? Chicago: (5x4)+(0x3)+(2x2)+(2x1) = 26 pts Phoenix: (1x4)+(2x3)+(2x2)+(4x1) = 18 pts Seattle: (3x4)+(4x3)+(2x2)+(0x1) = 28 pts Boston: (0x4)+(3x3)+(3x2)+(3x1) = 18 pts P B B C P 4th C C S P B 3rd B S P B S 2nd S P C S C 1st 1 1 2 2 3 Ranking members committee planning No. of
- 31. Majority Criterion The Borda count method yielded a winner other than the one that received the majority of first-place votes. Many would consider this unfair. The Borda count method may violate the Majority Criterion Did our candy selection violate the majority criterion?
- 32. Head-to-Head Criterion If a candidate is favored when compared separately with each of the other candidates, then the favored candidate should be elected.
- 33. Head-to-Head Criterion 3 options for a meal given by an accounting department: P (picnic), C (catered), R (restaurant) P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
- 34. Head-to-Head Criterion Which option would the dept select using the plurality method? (greatest number of first place votes) P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
- 35. Head-to-Head Criterion Which option would the dept select using the plurality method? (greatest number of first place votes) A Picnic with 3 first place votes. P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
- 36. Head-to-Head Criterion Which option is the winner in a head-to-head competition? P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
- 37. Head-to-Head Criterion 3 members prefer P to R (column 1) 4 members prefer R to P (columns 2 and 3) R is preferred to C by 5 to 2 (see columns 1 and 2) R is preferred to both P and C. R is called a Condorcet option P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
- 38. Head-to-Head Criterion R is preferred to both P and C. R is called a Condorcet option Since R is now the winner and P was the winner for the plurality method the Head-to-Head Criterion has been violated. P P C 3rd R C R 2nd C R P 1st 2 2 3 Ranking members Accounting dept. Number of
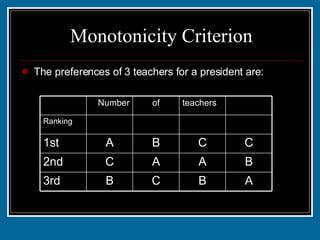
- 39. Monotonicity Criterion Suppose a particular candidate X, is selected in an election. If, hypothetically, the election were to be held again and each voter who changes his or her preferences does so by switching the positions of X and the candidate one position above X in that voterŌĆÖs preference ranking, then the candidate X should still be elected.
- 40. Monotonicity Criterion The preferences of 3 teachers for a president are: A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 5 12 14 Ranking teachers of Number
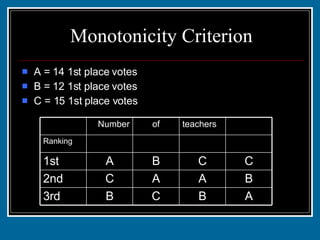
- 41. Monotonicity Criterion Who will be elected using the plurality with elimination method? A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 5 12 14 Ranking teachers of Number
- 42. Monotonicity Criterion A = 14 1st place votes B = 12 1st place votes C = 15 1st place votes Did anyone receive a majority? A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 5 12 14 Ranking teachers of Number
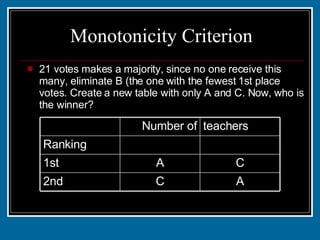
- 43. Monotonicity Criterion 21 votes makes a majority, since no one receive this many, eliminate B (the one with the fewest 1st place votes. Create a new table with only A and C. Now, who is the winner? A C 2nd C A 1st 15 26 Ranking teachers Number of
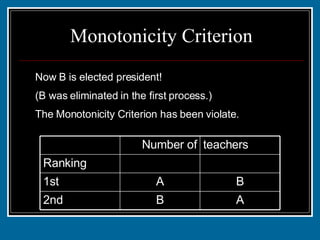
- 44. Monotonicity Criterion Suppose that 4 of the 5 teacher who originally ranked the candidates in the the order CAB reconsidered and ranked them ACB instead. Would this change affect the outcome of the election? A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 5 12 14 Ranking teachers of Number
- 45. Monotonicity Criterion Suppose that 4 of the 5 teacher who originally ranked the candidates in the the order CAB reconsidered and ranked them ACB instead. Would this change affect the outcome of the election? New chart A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 1 12 18 Ranking teachers of Number
- 46. Monotonicity Criterion New chart - Now who wins using the plurality with elimination method? A = 18 1st place B = 12 1st place C = 11 1st place Now we eliminate C A B C B 3rd B A A C 2nd C C B A 1st 10 1 12 18 Ranking teachers of Number
- 47. Monotonicity Criterion Now B is elected president! (B was eliminated in the first process.) The Monotonicity Criterion has been violate. A B 2nd B A 1st 22 19 Ranking teachers Number of
- 48. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion Suppose a particular alternative, X, is selected in an election. If, hypothetically, this election were to be held again, but with one or more of the unselected alternatives removed from consideration, then the alternative X should still be selected.
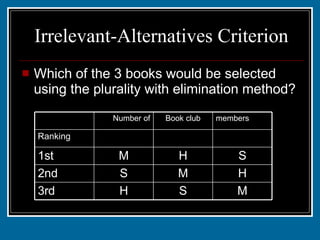
- 49. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion A book club is choosing from 3 types of book. Preferences are: M S H 3rd H M S 2nd S H M 1st 2 1 2 Ranking members Book club Number of
- 50. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion Which of the 3 books would be selected using the plurality with elimination method? M S H 3rd H M S 2nd S H M 1st 2 1 2 Ranking members Book club Number of
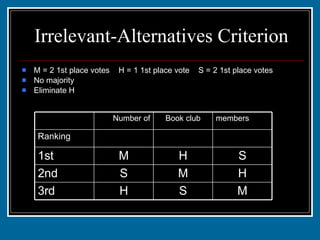
- 51. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion M = 2 1st place votes H = 1 1st place vote S = 2 1st place votes No majority Eliminate H M S H 3rd H M S 2nd S H M 1st 2 1 2 Ranking members Book club Number of
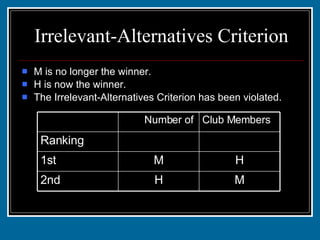
- 52. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion M is the winner because M received the majority of votes. M S 2nd S M 1st 2 3 Ranking Club Members Number of
- 53. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion The club decides to eliminate choice S. Would M still be the winner? M H 2nd H M 1st 3 2 Ranking Club Members Number of
- 54. Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion M is no longer the winner. H is now the winner. The Irrelevant-Alternatives Criterion has been violated. M H 2nd H M 1st 3 2 Ranking Club Members Number of
- 55. Flaws in Voting Systems Does a system exist that is always fair?
- 56. Flaws in Voting Systems Does a system exist that is always fair? NO! The Arrow impossibility theorem says that there is no voting method that always satisfies these criterion: Majority Head-to-Head Monotonicity Irrelevant-Alternatives
- 57. Approval Voting One more system Each candidate votes for all the candidates he or she considers acceptable. The candidate with the greatest number of votes is selected. Can be used to select top two candidates. Members of the Baseball Hall of Fame are chosen using a variation of this method. A player must receive 75% of the votes cast to elected.
- 58. Section 3.2 Flaws of Voting Systems Pg 172 (1,3,7,13,19,23)
- 59. Weighted Voting Systems The Electoral College: Each state has a number of votes equal to the number of its U.S. senators plus the number of its U.S. representatives, with a minimum of three votes. The District of Columbia also has three votes. We currently have 538 electoral votes and 270 votes are needed to win.
- 60. Weighted Voting Systems The Electoral College: Generally, all the electoral college votes of a particular state go to the same presidential candidate. This method does not always choose a president who received the majority of the popular vote - the election of 2000.
- 61. Weighted Voting Systems The table at the right can be converted to the following notation: [12,11,9,8] 11 Darrell 8 Carlos 12 Roberta 9 Angie Weight Voter
- 62. Weighted Voting Systems [12,11,9,8] To win an election 21 votes are needed. The new notation becomes: [21 | 12,11,9,8] 11 Darrell 8 Carlos 12 Roberta 9 Angie Weight Voter
- 63. Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [21 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass?
- 64. Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [21 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass? 10 + 7 + 4 = 21 Yes, the motion passes with just enough votes. Voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 make up a winning coalition .
- 65. Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [30 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass? 10 + 7 + 4 = 21 No, the winning quota is higher (called a superquota ) and the motion does not pass.
- 66. Winning and Losing Coalitions For [8 | 6, 5, 4] list all possible coalitions and determine whether each coalition is a winning or a losing coalition.
- 67. Winning and Losing Coalitions [8 | 6, 5, 4] Winning 6+5+4=15 {P 1 ,P 2 ,P 3 } Winning 5+4=9 {P 2 ,P 3 } Winning 6+4=10 {P 1 ,P 3 } Winning 6+5=11 {P 1 ,P 2 } Losing 4 {P 3 } Losing 5 {P 2 } Losing 6 {P 1 } Winning or Losing Sum of Weights Coalition
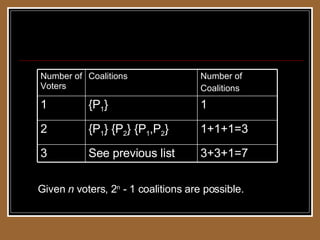
- 68. Winning and Losing Coalition Given n voters, 2 n - 1 coalitions are possible. 3+3+1=7 See previous list 3 1+1+1=3 {P 1 } {P 2 } {P 1 ,P 2 } 2 1 {P 1 } 1 Number of Coalitions Coalitions Number of Voters
- 69. Weighted Voting Systems How many coalitions are possible in a weighted voting system with seven voters?
- 70. Weighted Voting Systems How many coalitions are possible in a weighted voting system with seven voters? 2 7 - 1 = 128 -1 = 127
- 71. Weighted Voting Systems Dictators Dummies Voters with Veto Power Critical voters
- 72. Weighted Voting Systems Dictators [10 | 10, 5, 4] P 1 has enough votes to pass a motion no matter how the other two vote
- 73. Weighted Voting Systems Dummies A voter without power. His vote has no influence on the outcome of a vote. See table 3.2 on pg 188
- 74. Weighted Voting Systems Voters with Veto Power See table on pg 187 - if P 1 is not in a coalition, the coalition is a losing coalition. P 1 is said to have veto power
- 75. Section 3.3 Weighted Voting Systems Pg 193 (1,3,5,7,11,12,15,16,17a,31,32)
- 76. Contemporary Math Chapter 3 Assignments This assignment is due Tuesday June 3. You will need to show some work on each, maybe totals and/or tables Section 3.1 Pg. 154 (1,3,6,9,13,14,15,25,33) Section 3.2 Pg 172 (1,3,7,13,19,23) Section 3.3 Pg 193 (1,3,5,7,11,12,15,16,17a,31,32)












































![Weighted Voting Systems The table at the right can be converted to the following notation: [12,11,9,8] 11 Darrell 8 Carlos 12 Roberta 9 Angie Weight Voter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-61-320.jpg)
![Weighted Voting Systems [12,11,9,8] To win an election 21 votes are needed. The new notation becomes: [21 | 12,11,9,8] 11 Darrell 8 Carlos 12 Roberta 9 Angie Weight Voter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-62-320.jpg)
![Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [21 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-63-320.jpg)
![Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [21 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass? 10 + 7 + 4 = 21 Yes, the motion passes with just enough votes. Voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 make up a winning coalition .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-64-320.jpg)
![Weighted Voting Systems Given the weighted voting system [30 | 10,8,7,7,4,4], suppose that voters P 1 , P 3 , and P 5 vote yes on a certain motion. Does the motion pass? 10 + 7 + 4 = 21 No, the winning quota is higher (called a superquota ) and the motion does not pass.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-65-320.jpg)
![Winning and Losing Coalitions For [8 | 6, 5, 4] list all possible coalitions and determine whether each coalition is a winning or a losing coalition.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-66-320.jpg)
![Winning and Losing Coalitions [8 | 6, 5, 4] Winning 6+5+4=15 {P 1 ,P 2 ,P 3 } Winning 5+4=9 {P 2 ,P 3 } Winning 6+4=10 {P 1 ,P 3 } Winning 6+5=11 {P 1 ,P 2 } Losing 4 {P 3 } Losing 5 {P 2 } Losing 6 {P 1 } Winning or Losing Sum of Weights Coalition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-67-320.jpg)



![Weighted Voting Systems Dictators [10 | 10, 5, 4] P 1 has enough votes to pass a motion no matter how the other two vote](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nossi-ch-3-1212026181186934-8/85/Nossi-ch-3-72-320.jpg)