NSAIDs classification & mechanism of action
- 1. KHWAJA YUNUS ALI UNIVERSITY QUEST FOR KNOWLEDGE……… Assignment On NSAIDs Course Name: Advanced Medicinal Chemistry Course Code: BPH 4101 Submitted By: Submitted To: Date of Submission: 10-08-2020 Naznin Shahria Senior Lecturer Department Of Pharmacy Khwaja Yunus Ali University Quazi Istiaque Bari ID No: 2017301030007 4th year 1st semester Batch- 8th Department Of Pharmacy Khwaja Yunus Ali University
- 2. NSAIDs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are members of a drug class that reduces pain, decreases fever, prevents blood clots, and in higher doses, decreases inflammation. Example- Aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, diclofenac etc. Classification of NSAIDs: A. Nonselective COX inhibitors (traditional NSAIDs) 1. Salicylates: Aspirin. 2. Propionic acid derivatives: Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Ketoprofen, Flurbiprofen. 3. Fenamate: Mephenamic acid. 4. Enolic acid derivatives: Piroxicam, Tenoxicam. 5. Acetic acid derivatives: Ketorolac, Indomethacin, Nabumetone 6. Pyrazolone derivatives: Phenylbutazone, Oxyphenbutazone. B. Preferential COX-2 inhibitors ď‚· Nimesulide, ď‚· Diclofenac, ď‚· Aceclofenac, ď‚· Meloxicam, ď‚· Etodolac. C. Selective COX-2 inhibitors ď‚· Celecoxib, ď‚· Etoricoxib, ď‚· Parecoxib D. Analgesic-antipyretics with poor antiinflammatory action 1. Paraaminophenol derivative: Paracetamol (Acetaminophen). 2. Pyrazolone derivatives: Metamizol (Dipyrone), Propiphenazone. 3. Benzoxazocine derivative: Nefopam.
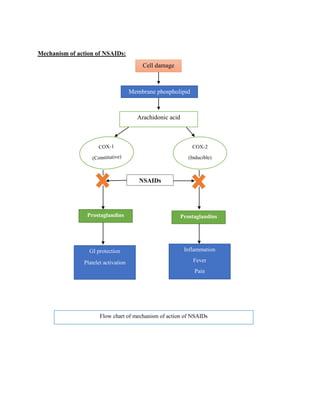
- 3. Mechanism of action of NSAIDs: COX-2 (Inducible) NSAIDs Prostaglandins Prostaglandins GI protection Platelet activation Inflammation Fever Pain Cell damage Membrane phospholipid Arachidonic acid Flow chart of mechanism of action of NSAIDs