Nuclear energy
- 1. Nuclear Power Made by Matt Howse with OpenOffice 3.3
- 2. What is Nuclear Power? Nuclear Power is electricity that is made by harnessing the internal power of some types of atoms. There are two types of nuclear power-producing methods. Nuclear fission, which involves splitting the nucleus of a large atom, and nuclear fusion, which is about fusing two small nuclei together and is only in experimental stages. Nuclear fission reactors involving Uranium-235 are very common throughout the world.
- 3. Uses in the past Nuclear energy has been harnessed before in both devastating and enlightening ways. Nuclear bombs, sometimes called ânukesâ, are extremely dangerous due to the following: Explosion of a nuclear warhead produces a very large and hot blast.
- 4. Radiation, or ânuclear falloutâ, can cause DNA mutations and death.
- 5. The first successful chain reaction was achieved in a graphite-uranium reactor in a squash court under the west stands of the athletic at the University of Chicago. It was rebuilt in 1943 at a site southwest of Chicago then was decommissioned in 1954. This was the first use of nuclear energy to generate power. In 1956, the first major nuclear power plant was opened in England.
- 6. Future uses In the future, it is likely that fusion reactors will be common while fission reactors won't. Fission reactors are much more dangerous than fusion reactors, and they require slightly more complex processes to produce the fuel. Fusion fuel is found rather abundantly in water, while fission fuel is a rare isotope of Uranium that's produced by reactions of other radioactive elements. Our world may be powered by fusion reactors on earth, and solar power made by the sun's fusion reactions.
- 7. Advantages Nuclear reactions produce lots of energy-One pound of Uranium has the heat power content of 2,300,000 pounds of coal.
- 8. Nuclear plants can be dual purpose-It is possible to desalinate water by the reaction process.
- 9. Little or no air pollution.
- 10. One plant can generate power for a huge amount of people.
- 11. The Earth has limited amounts of coal, oil, and other fossil fuels. Nuclear energy could still produce electricity after fossil fuels become scarce.
- 12. Disadvantages Fission reactors produce nasty nuclear waste, a byproduct which is radioactive and deadly.
- 13. Meltdowns are disasters that occur by uncontrolled reactions or uncontained heat spreading. They can result in fires, explosions, and release of nuclear fallout into the atmosphere.
- 14. Nuclear fuel is radioactive. It can be dangerous to process and ship.
- 15. Nuclear fission fuel is nonrenewable, although fusion fuel is common.
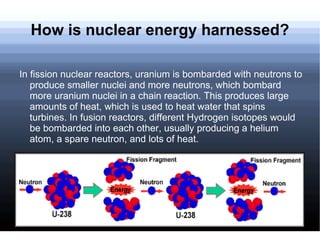
- 16. How is nuclear energy harnessed? In fission nuclear reactors, uranium is bombarded with neutrons to produce smaller nuclei and more neutrons, which bombard more uranium nuclei in a chain reaction. This produces large amounts of heat, which is used to heat water that spins turbines. In fusion reactors, different Hydrogen isotopes would be bombarded into each other, usually producing a helium atom, a spare neutron, and lots of heat.
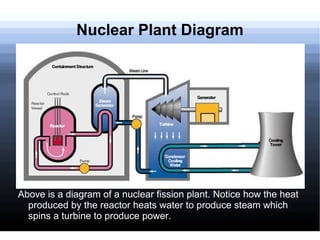
- 17. Nuclear Plant Diagram Above is a diagram of a nuclear fission plant. Notice how the heat produced by the reactor heats water to produce steam which spins a turbine to produce power.
- 18. Nuclear plants in the world There were 435 nuclear plants in the world in 1998, with 30 under construction.
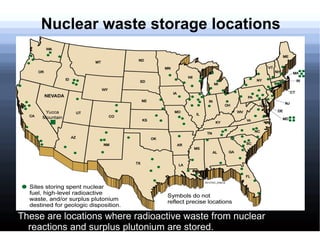
- 19. Nuclear waste storage locations These are locations where radioactive waste from nuclear reactions and surplus plutonium are stored.
- 20. Presentation end Sources used: Wikipedia, Funk and Wagnall's Encyclopedia, Thinkquest.com, Bing image search. Thank you for viewing this production!