nuclear envelope
- 1. Nuclear receptors Emilie Lilford Group 11
- 2. Biochemical definition of a receptor
- 3. Chemical change ï physiological change ï biological function Ligand Receptor
- 4. Types of receptors and locations: âĒ Cell surface receptors âĒ Receptors located in the cytoplasm âĒ Nuclear receptors
- 5. Ligands of nuclear receptors
- 6. Structures of some nuclear receptor ligands and their corresponding receptors name.
- 9. Sandwich filling model of ligand binding domain (LBD) LBD
- 10. DNA binding domain (DBD) â structure of the human progesterone receptor DBD
- 11. What is a Domain? âĒ Independent subunits of proteins. âĒ Between 25 -500 amino acids in length. âĒ Independently stable and folded. âĒ Can diverge and converge. âĒ Domain represents function.
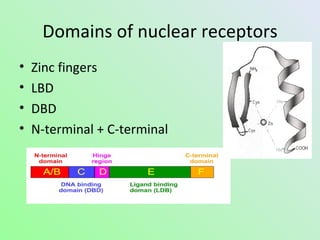
- 12. Domains of nuclear receptors âĒ Zinc fingers âĒ LBD âĒ DBD âĒ N-terminal + C-terminal
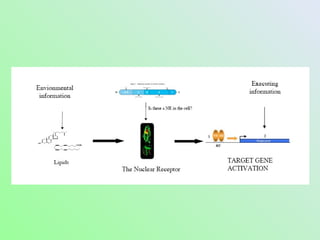
- 13. How nuclear receptors work.