Nursing care of spinal cord injury
- 1. NURSING CARE OF PATIENT WITH SPINAL CORD INJURIES Dr. A.Seethalakshmi Reader, Faculty of Nursing, SRIHER(DU).
- 3. INCIDENCE INDIA 20/million ŌĆó Jaipur ŌĆó Falls-66% ŌĆó RTA-18% ŌĆó Weights-15% US 32/ million ŌĆó 2,35,000 ŌĆó 11,000 annually ŌĆó 77.8% men ŌĆó 38 yrs ŌĆó Ōåæ 60 yrs-11.5%
- 4. ETIOLOGY ŌĆó Motor vehicle accidents ŌĆó Falls ŌĆó Violence ŌĆó Sporting injuries
- 5. EXTENT ŌĆó Incomplete quadriplegia- 34.1% ŌĆó Complete quadriplegia - 18.3% ŌĆó Incomplete paraplegia - 18.1% ŌĆó Complete paraplegia - 23%
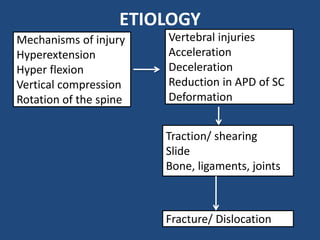
- 6. ETIOLOGY Mechanisms of injury Hyperextension Hyper flexion Vertical compression Rotation of the spine Vertebral injuries Acceleration Deceleration Reduction in APD of SC Deformation Traction/ shearing ║▌║▌▀Ż Bone, ligaments, joints Fracture/ Dislocation
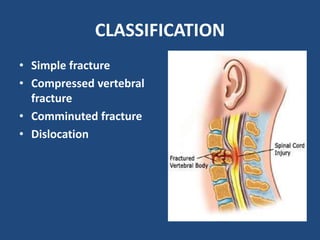
- 7. CLASSIFICATION ŌĆó Simple fracture ŌĆó Compressed vertebral fracture ŌĆó Comminuted fracture ŌĆó Dislocation
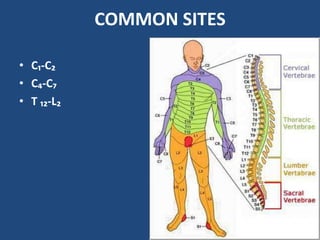
- 8. COMMON SITES ŌĆó CŌéü-CŌéé ŌĆó CŌéä-CŌéć ŌĆó T ŌéüŌéé-LŌéé
- 9. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Microscop ic heamorrh ages-GM Edema- WM Impairs microcircu lation Ischemic Areas Cellular and subcellular alterations Tissue necrosis 4hrs myelin disruption, axonal degeneration and ischemic endothelial injury Chemical and metabolic changes Necrosis-40% of cross sectional cord in 4hrs 70% in 24 hrs Cord swelling- diaphragm and medulla oblongata Phagocytes 36-48 hrs after injury Microglia and astrocytes Resorption of hemorrhage Acellular collagenous tissue in 3-4 weeks
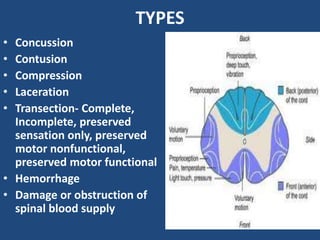
- 10. TYPES ŌĆó Concussion ŌĆó Contusion ŌĆó Compression ŌĆó Laceration ŌĆó Transection- Complete, Incomplete, preserved sensation only, preserved motor nonfunctional, preserved motor functional ŌĆó Hemorrhage ŌĆó Damage or obstruction of spinal blood supply
- 11. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS SPINAL SHOCK: ŌĆó 7-20 days up to 3 mths ŌĆó Skeletal muscles, bladder, bowel, sexual function and autonomic control. ŌĆó Paralysis and flaccidity, absence of sensation, loss of bladder and rectal control, drop in BP, ŌĆó Poor venous circulation ŌĆó SNS- Thermal control ŌĆó Sweating and capillary dilation
- 12. Cont.d NEUROGENIC SHOCK loss of sympathetic outflow: vasodilation, hypotension, bradycardia and hypothermia.
- 13. AUTONOMICHYPERREFLEXIA ŌĆó Syndrome ŌåæBP at any time after spinal shock resolves. ŌĆó CVS response to SNS stimulation. ŌĆó Paroxysmal HT, pounding headache, blurred vision, sweating, flushing of skin, nasal congestion, nausea, piloerection and bradycardia ŌĆó Cause : Distended bladder or rectum
- 15. DIAGNOSIS ŌĆó Physical ŌĆó Radiologic- chest and spine ŌĆó Myelographic examination ŌĆó Somatosensory evoked potential ŌĆó PFT ŌĆó ABGŌĆÖs ŌĆó CT scan, ŌĆó MRI
- 16. MANAGEMENT ŌĆó Immobilization ŌĆó Decompression ŌĆó Corticosteroids ŌĆó Nutrition ŌĆó Lung function ŌĆó Skin integrity ŌĆó Bowel and bladder management
- 17. NURSING PROCESS IN REHABILITATION ŌĆó Ineffective breathing pattern ŌĆó Risk for trauma ŌĆó Impaired physical mobility ŌĆó Disturbed sensory perception ŌĆó Acute pain ŌĆó Anticipatory grieving ŌĆó Bowel incontinence/ constipation ŌĆó Impaired urinary elimination
- 18. Cont.d.. ŌĆó Risk for autonomic dysreflexia ŌĆó Risk for impaired skin/ tissue integrity ŌĆó Inadequate knowledge regarding condition, prognosis, complications, treatment self care and discharge needs.