Obesity
- 2. What is Obesity? ’éŚObesity is that, you have a high amount of fat in your body, and from that definition you can notice that, obesity is not about more weight, it's about more fat . ’éŚ To understand this you may weight more because you are tall. And this is normal.
- 3. Body mass index (BMI) ’éŚ is far more commonly used to define obesity and has been found to closely correlate with the degree of body fat in most settings . ’éŚ all you want is to measure your weight in Kilograms (kg) and your height in meters (m), and then use this form ’éŚ Underweight = <18.5 Normal weight = 18.5ŌĆō24.9
- 5. ’éŚ World Health Organization (WHO) criteria based on BMI. for adults: ’éŚ GRADE 1 : (overweight ) BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2. ’éŚ GRADE 2 : overweight (obesity) BMI of 30-39.9 kg/m2. ’éŚ GRADE 3 : overweight (severe obesity) BMI greater than or equal to 40 kg/m2. ’éŚ Some people like the muscular athletes find their (BMI) higher than normal, when they most likely have a normal amounts of fat in their bodies, and the answer is that, they weight more not because of fat, but because of muscles.
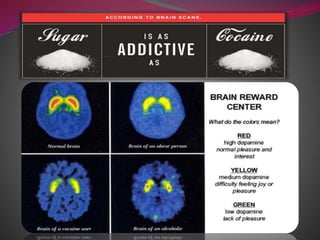
- 7. Causes of obesity : ŌĆó Not just the activities need to burn calories, also many metabolic reactions in the body need the energy from food, such as to warm up in cold weather and to sweat in the hot days. ŌĆó But when our food calories amounts exceed the body need, they will be stored in the body as fat.
- 8. ’ü▒PHYSICAL ACTIVITY : ’āś If you are not active enough, you do not use the energy provided by the food you eat, and the extra energy you consume is stored by the body as fat. ’āś Levels of physical activity have declined, in parallel with increased use of television and computer games ’ü▒ GENETICS: It may be true that certain genetic traits inherited from your parents ŌĆō such as having a large appetite ŌĆō may make losing weight more difficult, but it certainly doesn't make it impossible.
- 9. ’ü▒DIETS: ’éŚ eating large amounts of fast food ’éŚ drinking too much alcohol ’éŚ sugary drinks ’éŚ eating larger portions than you need ’éŚ comfort eating ŌĆō if you feel depressed or have low self-esteem, you may eat to make yourself feel better ’ü▒Lack of sleep ’ü▒Pregnancy ’ü▒Age : obesity could occur at any age, but when we get age we lose more amount of muscles built. more amount of muscles give higher rate of metabolism and calories burning. When we lose them we reduce the calories burning and tend to fill the body with fat
- 10. ’ü▒MEDICAL REASONS : ’éŚ In some cases, underlying medical conditions may contribute to weight gain. These include : an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) Cushing's syndrome ŌĆō a rare disorder that causes the over-production of steroid hormones. ’ü▒ DRUGS : ’éŚ some medications lead the body to gain more weight, these drugs include, diabetes medications, steroids and beta blockers, and antidepressants drugs. ’ü▒LEPTIN : ’éŚ is a hormone made by adipose cells that helps to regulateenergy balance by inhibiting hunger. In obesity, a decreased sensitivity to leptin occurs, resulting in an inability to detect satiety despite high energy stores.
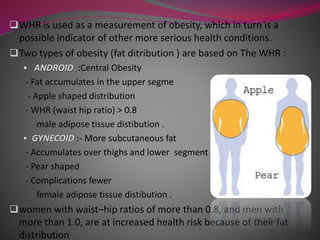
- 11. WaistŌĆōhip ratio ’ü▒is the ratio of the circumference of the waist to that of the hips. ’ü▒This is calculated as waist measurement divided by hip measurement (W ├Ę H). For example, a person with a (64 cm) waist and (97 cm) hips has a waistŌĆōhip ratio of about 0.66. ’ü▒ The WHR has been used as an indicator or measure of health, and the risk of developing serious health conditions. Research shows that people with "apple-shaped" bodies (with more weight around the waist) face more health risks than those with "pear-shaped" bodies who carry more weight around the hips.
- 12. ’ü▒WHR is used as a measurement of obesity, which in turn is a possible indicator of other more serious health conditions. ’ü▒Two types of obesity (fat ditribution ) are based on The WHR : ’é¦ ANDROID :Central Obesity - Fat accumulates in the upper segme - Apple shaped distribution - WHR (waist hip ratio) > 0.8 male adipose tissue distibution . ’é¦ GYNECOID :- More subcutaneous fat - Accumulates over thighs and lower segment - Pear shaped - Complications fewer female adipose tissue distibution . ’ü▒women with waistŌĆōhip ratios of more than 0.8, and men with more than 1.0, are at increased health risk because of their fat distribution
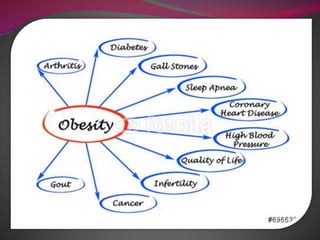
- 14. What are the complications of obesity? ’āśHypertension . ’āśType 2 diabetes: Most people who have type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese. You can cut your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by losing weight, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and exercising more. ’āśSexual problems. ’āśSocial isolation. ’āśStroke. ’āśPhysical disability. ’āśGallbladder disease.
- 15. ’āśSleep apnea (dangerous sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts). ’āśOsteoarthritis. ’āśHigh cholesterol and triglycerides. ’āśMetabolic syndrome. ’āśCancer.
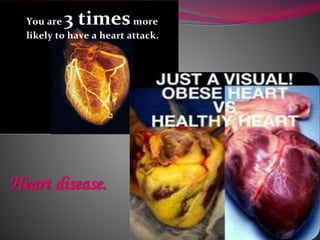
- 16. Heart disease.
- 17. Cancer: Cancers of the colon, breast (after menopause), endometrium, kidney, and esophagus
- 19. Childhood obesity ’ü▒Childhood obesity is often the result of an interplay between many genetic and environmental factors. ’ü▒The effects of eating habits on childhood obesity are difficult to determine. ’ü▒Calorie-rich drinks and foods are readily available to children. Consumption of sugar-laden soft drinks may contribute to childhood obesity.
- 20. ’üČPhysical activity :Many children fail to exercise because they are spending time doing immobile activities such as computer usage, playing video games or watching television. ’üČmedications : There are no medications currently approved for the treatment of obesity in children. - Sibutramine is approved for adolescents older than 16
- 22. Treatment the healthy weight is the main goal for obesity treatment. and you can reach that by making a good treatment plan with your doctor and may be a big team of nutritionist, dietitian, obesity specialist and nurse. This plan include: ’ü▒Dietary changes. ’ü▒Exercise and activity. ’ü▒Behavior change. ’ü▒Prescription medication. ’ü▒Weight-loss surgery.
- 23. ’āśMore exercise: ’āś 150 to 250 minutes of moderate intensity activity every week is helpful to keep you away from obesity, and these activities such as fast walking and swimming. ’āś Due to the large size of leg muscles, walking, running, and cycling are the most effective means of exercise to reduce body fat. ’āś A 1.5 kilogram loss was observed with a greater degree of exercise. ’āśDiet : ’āś eat colorful vegetables and fruit. ’āś eat dark chocolate. ’āś drink at least 4 litres of water daily. ’āś Avoid saturated and trans fat. ’āś Drinking green.
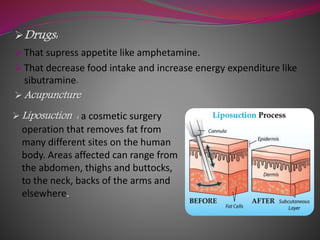
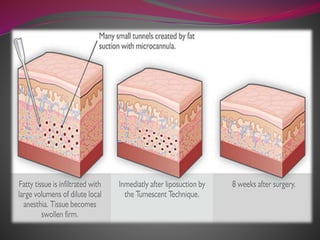
- 25. ’āśDrugs: ’āś That supress appetite like amphetamine. ’āś That decrease food intake and increase energy expenditure like sibutramine. ’āś Acupuncture ’āś Liposuction : a cosmetic surgery operation that removes fat from many different sites on the human body. Areas affected can range from the abdomen, thighs and buttocks, to the neck, backs of the arms and elsewhere.
- 27. :Gastrectomy ’üČ There are three main types of gastrectomy: ’ü▒A partial gastrectomy is the removal of a part of the stomach. ItŌĆÖs usually the lower half thatŌĆÖs removed. ’ü▒A full gastrectomy is the removal of the entire stomach. ’ü▒A sleeve gastrectomy is the removal of the left side of the stomach. This is usually performed as part of a surgery for weight loss ’üČ Removing your stomach doesnŌĆÖt take away your ability to digest liquids and foods. However, you may need to make several lifestyle changes after the procedure. Gastrectomy is the removal of part or all of the stomach.