Object Oriented Programming Concepts for beginners
- 1. Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Vibhawa Nirmal Wijerathna
- 2. What is Object Oriented Programming ? • Object oriented Programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of “Objects”. • The main aim of object-oriented programming is to implement real-world entities, for example, object, classes, abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism, etc.
- 3. Why Object-Oriented Programming ? • Easy for troubleshooting • Cades can be able to reuse • Flexible • Low cost of development • Increase Maintainability
- 4. Why not Object-Oriented Programming ? • Complex with Planning • Programmer should be skilled with technology • Flexible
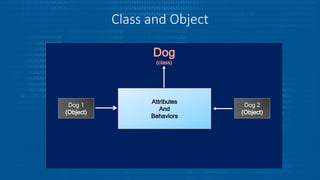
- 5. What is a Class? • A Class is group of objects which have common features • Also class is a "blueprint" for creating objects.
- 6. What is an Object ? • An entity that has state and behavior Example: Chair, Bike , Car • Object has three characteristics • State • Behavior • Identity Example: Pen is an object. Its name is Reynolds; color is white; known as its state. It is used to write; writing is its behavior.
- 7. Class and Object Dog (class) Dog 1 (Object) Dog 2 (Object) Attributes And Behaviors
- 8. Object-Oriented Programming Concepts • Inheritance • Polymorphism • Abstraction • Encapsulation
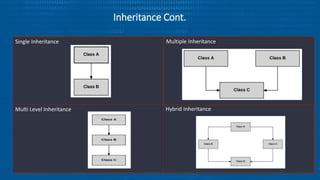
- 9. Inheritance • Inheritance is possible to inherit attributes and the methods from one class to another class. • There are two types of classes • Super Class – the class being inherited from • Sub Class - the class that inherits from another class • Types of Inheritance • Single • Multiple • Multi- Level • Hierarchical
- 10. Inheritance Cont. Single Inheritance Multi Level Inheritance Hybrid Inheritance Multiple Inheritance
- 11. Encapsulation • Principle of wrapping variables and codes together as a single unit. • It is a mechanism that binds the code and the variables together. • Encapsulation supports to • Hide Data • Testing easily • Reusability • Increased Flexibility
- 12. Abstraction • Abstraction is the process of hiding certain details and showing only essential information to the user. • Also defined as the process of identifying only the required characteristics of an object ignoring the irrelevant details.
- 13. Polymorphism • Polymorphism means "many forms”. • Polymorphism allows us to perform a single action in different ways.