Objective primary algebra
- 1. Objective Brownian Algebra PICTORIAL SYMBOLIZATION OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
- 2. FOREWORD FOREWORD In 1970-s George Spencer-Brown wrote the controversial book titled The Laws of Form. It is controversial because he used the VOID in the algebraic equations in his new algebra. The other strange symbol he used is the half box he called the CROSS. With the new symbols he constructed an arithmetic based on the Law of Cancelation and the Law of Condensation. Based on the arithmetic he developed a Primary Algebra with two primitives: the law of Position and the Law of transposition. In the later part of his book he interpreted his primary algebra as a new planar symbolization of Boolean algebra. Next, Louis Kauffman replaced the CROSS with the complete BOX to develop his semi pictorial Box Algebra as the symbolization of Boolean algebra. In this book we replace the letters in the Box Algebra with colored object to construct a totally pictorial planar symbolization of Boolean Algebra called Objective Brownian Algebra.
- 3. PRIMITIVES of the OBJECTIVE BROWNIAN ALGEBRA The Objective Brownian Algebra, as the symbolization of the Boolean Agebra of Logic, is based on two primitive concepts: VOID BOX represents FALSE and represents TRUE. The primitive operations are Juxtaposition BOX enclosure represents a OR b represents NOT a The primitives of logical arithmetic are Cancelation Condensation The primitives of logical algebra are Position Transposition
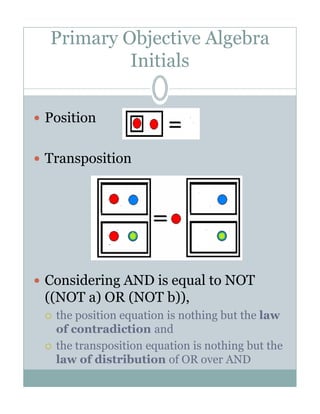
- 4. Primary Objective Algebra Initials Position Transposition Considering AND is equal to NOT ((NOT a) OR (NOT b)), the position equation is nothing but the law of contradiction and the transposition equation is nothing but the law of distribution of OR over AND
- 5. Primary algebra Rules of Inference Using the algebraic rules and we can derive all the boolean tautologies, from the position and transposition axioms, as consequences.
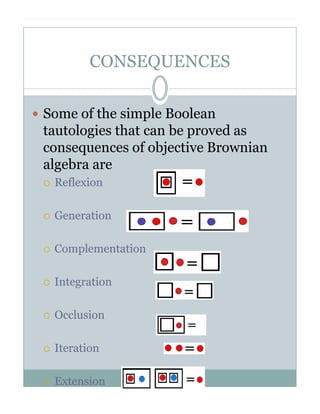
- 6. CONSEQUENCES Some of the simple Boolean tautologies that can be proved as consequences of objective Brownian algebra are Reflexion Generation Complementation Integration Occlusion Iteration Extension
- 14. AFTERWORD Brownian algebra is not the simplest axiom system for the Boolean algebra of logic. In fact, if we take the Occlusion, the Reflexion and the Generation laws as axioms to build the Boundary Logic of William Bricken as another simple axiomatic formulation of the Boolean Algebra Ultimately, we can simply use the Extension law as the only axiom for the Box Algebra as the simplest axiomatization of the Boolean Algebra All of them can be made Objective by using colored objects as variable names, the box as NOT operator and juxtaposition as OR connection. Objective Algebra can also represent logical system based on AND and NOT operation such as Peircean Existential Graph System.
- 15. References Aristotle : Non-Mathematical Verbal Logic http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/prior.1.i.html George Boole: Algebraic Symbolic Logic (Algebra of Logic) http://www.freeinfosociety.com/media/pdf/4708.pdf Charles Sanders Peirce: Algebraic Graphical Logic (Existential Graph) http://www.jfsowa.com/peirce/ms514.htm George Spencer-Brown: Algebraic Graphical Logic (Laws of Form) http://www.4shared.com/document/bBAP7ovO/G-spencer-Brown-Laws-of-Form1.html Louis Kauffman: Algebraic Pictorial Logic (Box Algebra) http://www.math.uic.edu/~kauffman/Arithmetic.htm