Obstetric sepsis presentation by Dr. ranjana khanna.
- 1. OBSTETRIC SEPSIS Dr Ranjana Khanna - Prayagraj Dr Sujata Dalvi - Mumbai
- 3. Dr Sujata Dalvi ’üĄ Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist ŌĆō Mumbai Gleneagles / Saifee / Bhatia / St Elizabeth Hospitals ’üĄ Hon Clinical Associate ŌĆō Nowrosjee Wadia Maternity Hospital ’üĄ Treasurer ŌĆō Mumbai Obstetrics & Gynaecological Society (MOGS) ’üĄ Associate Editor of JOGI (Journal of Ob Gyn of India) ’üĄ President ŌĆō Mumbai Menopause Society ’üĄ Imm Past Secretary ŌĆō AMOGS (Association of Maharashtra Ob Gyn Societies)
- 4. Panelists ’üĄ Dr Komal Chavan ’üĄ Dr Rahul Mayekar ’üĄ Dr Preeti Lewis ’üĄ Dr Pradnya Changede ’üĄ Dr Prema Kania ’üĄ Dr Pradnya Supe ’üĄ Dr Reena Wani ’üĄ Dr Tarini Taneja
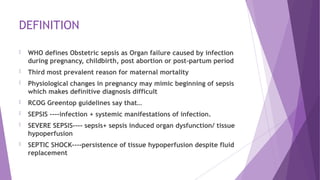
- 5. DEFINITION ’üĄ WHO defines Obstetric sepsis as Organ failure caused by infection during pregnancy, childbirth, post abortion or post-partum period ’üĄ Third most prevalent reason for maternal mortality ’üĄ Physiological changes in pregnancy may mimic beginning of sepsis which makes definitive diagnosis difficult ’üĄ RCOG Greentop guidelines say thatŌĆ” ’üĄ SEPSIS ----infection + systemic manifestations of infection. ’üĄ SEVERE SEPSIS---- sepsis+ sepsis induced organ dysfunction/ tissue hypoperfusion ’üĄ SEPTIC SHOCK----persistence of tissue hypoperfusion despite fluid replacement
- 6. Clinical response arising from a nonspecific insult, including >=2 of the following: o Temperature >= 38┬░C or <=36┬░C o HR >= 90 beats/min o Respirations >= 20/min, PC02< 32 o WBC count>=12,000/mm3 or <=4,000/mm3 or >10% immature neutrophils (Band Forms) SIRS with a presumed or confirmed infectious process Severe sepsis with persistent refractory hypo tension Sepsis with >=1 sign of organ failure o Cardiovascular o Renal o Respiratory o Hepatic o Hematologic/ DIC o CNS o Metabolic acidosis What is Sepsis? A spectrum of body response and changes SIRS ŌĆō Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Bone RC, et al. Chest 1992;101:1644 Opal SM,et al. Crit Care Med 2000;28:S81; Levy M, et al. Crit Care Med 31:2003
- 7. ETIOLOGY OF OBSTETRIC SEPSIS ’üĄ Septic abortion ’üĄ PROM / PPROM ’üĄ Chorioamnionitis ’üĄ Postpartum endometritis ’üĄ Wound sepsis ’üĄ RTI ’üĄ UTI ’üĄ Necrotising fasciitis ’üĄ Acute appendicitis / pancreatitis / cholecystitis
- 8. What are the risk factors for Obstetric Sepsis?
- 9. RISK FACTORS FOR OBSTETRIC SEPSIS ’üĄ Obesity ’üĄ Impaired glucose tolerance/diabetes ’üĄ Impaired immunity/ on immunosuppressive medication ’üĄ Anaemia ’üĄ Vaginal discharge ’üĄ H/O Pelvic infection ’üĄ H/O gr B streptococcal infection ’üĄ Amniocentesis/ other invasive procedures ’üĄ Cervical cerclage ’üĄ PROM ’üĄ GAS infection in close contacts / family members ’üĄ Black or other minority ethnic gr origin
- 10. What is the pathophysiology of obstetric sepsis?
- 11. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ’üĄ Common organisms involved are.. ’üĄ Ecoli ’üĄ Klebsiella ’üĄ Group A beta haemolytic streptococcus ’üĄ GBS ’üĄ Staphylococcus ’üĄ Bacteroids ’üĄ N.Gonorrhoea ’üĄ C.Trachomatis ’üĄ Cl. Welchi ’üĄ Mycoplasma hominis ’üĄ H.Influenzae
- 12. MECHANISM ’üĄ These inflammatory mediatorsŌĆ” ’üĄ Endothelial dysfunction ’üĄ Increased vascular permeability ’üĄ Myocardial suppression ’üĄ Activation of coagulation cascade leading to DIC
- 13. EVOLUTION OF SEPSIS In Early Stages of Sepsis Released Vasoactive Mediators cause: ’üĄ Vasodilation ’üĄ Platelet Aggregation ’üĄ Capillary Plugging ’üĄ Endothelial Damage resulting in o Cellular Hypoxia o Lactic Acidosis o Worsening of Tissue Perfusion In Late Stages of Sepsis Poor tissue perfusion causes: Ō¢¬ Decreased Vascular resistance Ō¢¬ Decreased cardiac output Ō¢¬ Vasoconstriction Ō¢¬ Further decrease in tissue perfusion Ō¢¬ End organ damage Many cytokines cause global myocardial dysfunction, which results in septic shock
- 14. What Should Prompt recognition of Obstetric Sepsis ’üĄ Clinical signs suggesting sepsis includes ŌĆ”.pyrexia, hypothermia, tachycardia, tachypnoea, hypoxia, hypotension, oliguria, impaired consciousness &failure to respond to tt. But these signs may not always be present & are not related to severity of sepsis. ’üĄ Regular observations of P/R, B.P, R/R Temp should be recorded on MODIFIED EARLY OBSTETRIC WARNING SCORES ( MEOWS ) chart. ’üĄ Disease progression may be more rapid than non-pregnant state. ’üĄ Sepsis may cause Abdominal pain & tenderness. ’üĄ Severe infection may result in Preterm Labour. ’üĄ Toxic shock syndrome may produce confusing symptoms eg NVD, severe pain, watery discharge, rash.
- 15. What are the four pillars of sepsis?
- 16. Four pillars of septic shock management 1. Early recognition of shock state and identification of source of infection 2. Resuscitation and rapid establishment of tissue reperfusion 3. Providing support to failing organs 4. Source control including early adequate antibiotics and drainage/ debridement
- 17. Prognosis in OBSTETRIC SEPSIS ’üĄ SOFA score in ObstetricsŌĆ”..assesses the degree of organ system dysfunction of a patientŌĆ”This score has a score for six major organs of the bodyŌĆ”.respiratory, cardiovascular, hepatic, coagulation, CNS, renal ..Each organ received a score ranging from 0 (normal ) to 4 ( most abnormal ) with minimum SOFA score of 0 & maximum of 24 ’üĄ qSOFA score in pregnancy evaluates presence of 3 clinical criteria: systolic BP <100ŌĆ”.respiratory rate>22 & altered mental status
- 18. Red flag symptoms of sepsis ’üĄ High temperature ’üĄ New onset of confusion or altered mental state
- 19. SEPSIS SIX CARE BUNDLE ’üĄ GIVE 3 ’üĄ 1ŌĆ”OXYGENŌĆöTitrate O2 to saturations of 94-98% or 88- 92% in chronic lung disease. ’üĄ FLUIDSŌĆō Start IV fluid resuscitation if hypovolaemiaŌĆö500 ml bolus of isotonic crystalloids over 15 min & 30ml/kg reassessing signs of hypovolaemia. ’üĄ ANTIMICROBIALSŌĆöIV antibiotics according to local guidelines.
- 20. ’üĄ TAKE 3 ’üĄ CULTURESŌĆöTake blood cultures before starting antibiotics & consider source control. ’üĄ BLOODSŌĆöLactate measurement , FBC ,U&E , LFT ,coag factors. ’üĄ URINE OUTPUTŌĆöAssess urine output & cathetrise.. ’üĄ GOLDEN HOUR OF SEPSIS---stresses the relation between timely initiation of antibiotics & outcomeŌĆ” each hour delay in Tt reduces sepsis survival by 7.6%.
- 21. Golden Hour of Sepsis ’üĄ ŌĆ£Golden hourŌĆØ of sepsis is the idea that starting antibiotic treatment promptly can improve outcomes ’üĄ For each hour that treatment is delayed, sepsis survival decreases by 7.6% ’üĄ The ŌĆ£golden hourŌĆØ refers to early recognition, early administration of antibiotics, and early reversal of shock state
- 22. Incidence ’üĄ Sepsis ŌĆō leading cause of maternal mortality ŌĆō morbidity ’üĄ Pregnancy related sepsis ŌĆō 11 % ’üĄ 25 ŌĆō 40 % maternal deaths - worldwide ’üĄ Global ŌĆō National ’üĄ WHO ŌĆō 4.4 % (puerperal sepsis ŌĆō alone in live births) ’üĄ Severe sepsis ŌĆō acute organ dysfunction (MM ŌĆō 20 to 40 % - up to 60% if septic shock develops)
- 23. Why is pathophysiology different in pregnancy during sepsis ?
- 24. Pathophysiology - Sepsis ’üĄ In Pregnancy ŌĆō ’üĄ Maternal Immune system adaptation for development of fetus ŌĆō may impair maternal system to fight infection ’üĄ Physiological Hyperventilation ŌĆō due to pregnancy ŌĆō may cause respiratory alkalosis ŌĆō may not be able to buffer metabolic acidosis caused by sepsis ’üĄ Some of the physiological changes ŌĆō may mimic early septic changes ŌĆō making diagnosis little difficult
- 25. Investigations ’üĄ CULTURESŌĆöTake blood cultures before starting antibiotics & consider source control ’üĄ BLOODSŌĆöLactate measurement , FBC ,U&E , LFT ,RFTs, coag profile ’üĄ USG ŌĆō Abdomen / Pelvis ’üĄ MRI ’üĄ Chest / Cardiac evaluation
- 26. Role of Bio Markers ??
- 27. Bio markers ’üĄ Identify patients at early stage ’üĄ Differentiate sepsis from non-inflammatory pathologies ’üĄ Severity of condition ’üĄ Guiding treatment ’üĄ Total WBC Count ŌĆō CRP (C reactive protein) ŌĆō Procalcitonin levels ’üĄ WBC & CRP (non-specific for inflammation) ’üĄ PCT (specific for bacterial infection) ’üĄ Elevated Lactate levels ŌĆō poor prognosis
- 28. Antibiotics ??
- 29. Choice of Antibiotics ’üĄ Broad spectrum preferred ŌĆō start ASAP ’üĄ Depend upon culture report ŌĆō change ’üĄ Gram positive / negative / anaerobes ’üĄ If no improvement ŌĆō addition of higher antibiotics ’üĄ Occasionally ŌĆō Fungal infection ’üĄ Resistance to antibiotics ??
- 30. Management Bundle of Care approach ??
- 31. Bundle of Care approach ’üĄ Resuscitation bundle within first 6 hours ŌĆō associated with reduced mortality from sepsis ’üĄ Early recognition ’üĄ Essential investigations / monitoring (culture ŌĆō UO ŌĆō inv) ’üĄ Essential treatment (O2 ŌĆō IV Fluids ŌĆō Antibiotics) ’üĄ Sepsis 6 ŌĆō O2, blood culture, antibiotics, IV Fluids, lactate ŌĆō Hb, UO ’üĄ All within first 1 hour
- 32. Management ’üĄ IV Fluids ’üĄ Crystalloids ŌĆō primary choice ’üĄ Initial 30 ml/kg ----- later 20 ml/kg ’üĄ No improvement ŌĆō Sr lactate levels / hypotension ’üĄ Shift to ICU ’üĄ Broad spectrum antibiotics ’üĄ Remove sepsis ’üĄ Plan for Birth with ICU support
- 34. Monitoring Patient ’üĄ Maternal ŌĆō Fetal monitoring ’üĄ Examinations ’üĄ Investigations ’üĄ Central venous line ŌĆō ICU ’üĄ USG ŌĆō NST ’üĄ Discuss Birth plan ŌĆō ICU in charge / Anaesthetist / NN / Colleagues
- 35. Role of Surgical Therapy ?
- 36. Surgical therapy ’üĄ Retained products ’üĄ I & D ŌĆō abscess ’üĄ Debridement ŌĆō necrotic tissue ’üĄ Pelvic mass removal ŌĆō SOS Hysterectomy ’üĄ To remove source of infection
- 37. Delivery ??
- 38. Delivery of Fetus ’üĄ Decision ŌĆō complex ’üĄ Source of infection ŌĆō gestational age ŌĆō fetal well- being - maternal well being ’üĄ Treat maternal status first ŌĆō stabalize ’üĄ Fetal monitoring (gestational age) ’üĄ Deliver ŌĆō where ?
- 39. Transfer to ICU ??
- 40. Indications ŌĆō ICU transfer ’üĄ Cardio-vascular ’üĄ Respiratory ’üĄ Renal ’üĄ GI ŌĆō liver related ’üĄ Neurological ’üĄ Miscellaneous
- 41. Managing Maternal Sepsis ’üĄ High degree of suspicion ’üĄ Quick detect maternal deterioration (bed side) ’üĄ Implement sepsis bundle immediately ’üĄ Fluid resuscitation ŌĆō Antibiotics ŌĆō Investigations (lactate) ŌĆō O2 ŌĆō UO ŌĆō neck-line ’üĄ Once stabilized ŌĆō find source of infection ’üĄ Anticipate ŌĆō prevent adverse pregnancy outcome
- 42. SEPTIC ABORTION ’üĄ Septic abortion is a serious infection of the uterus that occurs during, shortly before, or after an abortion or miscarriage. ’üĄ It is uncommon but may be life threateningŌĆ”fatality rate 0.4-0.6/100000 first trimester pregnancy losses.S/SŌĆ”Rise in temp.,leukocytosis, lower abdominal tenderness,cervical tenderness & purulent vaginal discharge. ’üĄ Infection goes from endometrium---myometrium---parametrium---peritoneum. ’üĄ Cause is polymicrobial
- 43. Septic Abortion ?? ’üĄ GRADE 1ŌĆ”.Infection localised to uterus. ’üĄ GRADE 2ŌĆ”.Infection spreads beyond uterus to parametrium, tubes, ovaries, pelvic peritoneum. ’üĄ GRADE 3ŌĆ”Generalised peritonitis, endotoxic shock, jaundice, acute renal failure ’üĄ Preventive Measures: ’üĄ Access to effective & acceptable contraception ’üĄ Access to safe legal abortion ’üĄ Appropriate medical management of abortion
- 44. Take Home Message ’üĄ Sepsis ŌĆō leading cause maternal mortality / morbidity ’üĄ Pregnant women ŌĆō more susceptible ’üĄ Physiological changes mimic changes ŌĆō delays diagnosis & optimal treatment ’üĄ Identification ŌĆō pathogens with proper antibiotics ŌĆō main key ’üĄ Removal of source of infection ŌĆō important
- 46. Thank You