OCCUPATIONAL HAZARDS.pptx
- 1. 1 Ikiriza Antony OCCUPATIONAL HAZARDS
- 2. 2 By the end of this lectures students should be able; ÔÇó Differentiate between hazard and risks ÔÇó Describe the Classifications of occupational health and safety hazards ÔÇó To Identify the occupational health and safety hazards in various workplaces ÔÇó Discuss the range of hazards in LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- 3. 3 ´éó Hazard: is a condition or set of circumstances that has a potential of causing harm or contributing to injury or death. ´éó Safety hazards: hazards that can cause accidents, injuries, and sometimes even death ´éó Heath hazards: those hazards that can cause occupational disease or illness ´éó Risk: A combination of likelihood that injury or damage to peopleÔÇÖs health, or property will occur and the severity OCCUPATIONAL HAZARDS
- 4. 4 ´éóPlanning and Design (people involved in planning and design activities may create hazards) ´éóProduction and Distribution (production, process, distribution can result in hazards) ´éóMaintenance and Repair (hazards may come from insufficient, delayed and improper maintenance) ´éóCommunication (poor communication or failures in communications can introduce hazards) SOURCES OF HAZARDS
- 5. 5 ´éóChemical hazards ´éóPhysical hazards ´éóBiological hazards ´éóErgonomic hazards ´éóPsycho-social hazards TYPES OF OCCUPATIONAL HAZARDS
- 6. 6 Classification of dangerous chemicals ´éù Carcinogens ´éù Corrosion ´éù Oxidizing ´éù Harmful ´éù Very toxic and toxic ´éù Irritant ´éù Highly flammable ´éù Explosive CHEMICAL HAZARDS
- 7. 7 Hazard warning signs and symbols Source: Barbara A. Plog, Fundamentals of Industrial hygiene, 4th. Edition, 1996
- 8. 8 ´éóThese are agents that cause cancer ´éóThese can be identified in epidemiological studies ´éóThey include: Asbestos, Benzene, Rubber Manufacture, Coke Oven Emissions, Lead, Chromium, Wood Dusts, Vinyl Chloride, Chloroform, DDT, Beryllium, Asbestos,Cadmi CARCINOGENS
- 9. 9 1. Asphyxiation 2. Systemic intoxication 3. Pneumoconiosis (occupational lung disease due to inhalation of dust usually in mines) 4. Cancers 5. Irritation 6. Mutagenicity 7.Teratogenicity EFFECTS OF CHEMICALS
- 10. 10 ÔÇó Extremes of temperature ÔÇó Ionizing radiation ÔÇó Non ionizing radiation ÔÇó Excessive noise ÔÇó Vibrations PHYSICAL HAZARDS
- 11. 11 ´éóAny living organism with potential to caus e harm to humans ´éóThey can be transmitted via inhalation, co ntact, ingestion and Injection ´éóThey include: ´éù Bacteria ´éù Viruses ´éù Fungi ´éù Mold ´éù Protozoa ´éù Animals and insects BIO HAZARDS (BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS)
- 12. BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS VIRUSES FUNGI BACTERIA PARASITES 12
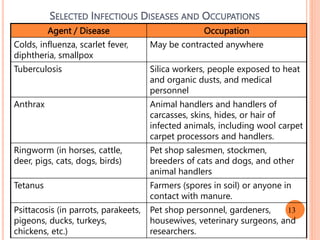
- 13. SELECTED INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND OCCUPATIONS Agent / Disease Occupation Colds, influenza, scarlet fever, diphtheria, smallpox May be contracted anywhere Tuberculosis Silica workers, people exposed to heat and organic dusts, and medical personnel Anthrax Animal handlers and handlers of carcasses, skins, hides, or hair of infected animals, including wool carpet carpet processors and handlers. Ringworm (in horses, cattle, deer, pigs, cats, dogs, birds) Pet shop salesmen, stockmen, breeders of cats and dogs, and other animal handlers Tetanus Farmers (spores in soil) or anyone in contact with manure. Psittacosis (in parrots, parakeets, pigeons, ducks, turkeys, chickens, etc.) Pet shop personnel, gardeners, housewives, veterinary surgeons, and researchers. 13
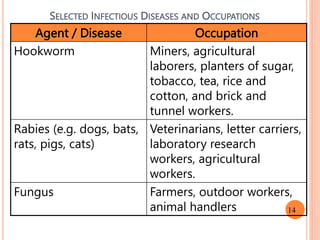
- 14. SELECTED INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND OCCUPATIONS Agent / Disease Occupation Hookworm Miners, agricultural laborers, planters of sugar, tobacco, tea, rice and cotton, and brick and tunnel workers. Rabies (e.g. dogs, bats, rats, pigs, cats) Veterinarians, letter carriers, laboratory research workers, agricultural workers. Fungus Farmers, outdoor workers, animal handlers 14
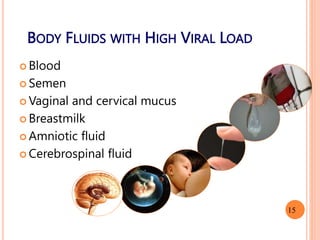
- 15. BODY FLUIDS WITH HIGH VIRAL LOAD ´éó Blood ´éó Semen ´éó Vaginal and cervical mucus ´éó Breastmilk ´éó Amniotic fluid ´éó Cerebrospinal fluid 15
- 16. 16 ´éóIn summary exposure to Biohazards can be thro ugh; ´éó Laboratory research ´éó Hospitals ´éó Laundry ´éó Housekeeping ´éó Health care ´éó Diet ´éó Contact with the skin EXPOSURES TO BIO HAZARDS
- 17. 17 ´éó There are numerous psychosocial factors, which operate at workplace. ´éó These are the human relationships among workers themselves and those in authorities over them. ´éó Examples of psychosocial factors include:- ´éóThe type and rhythm of work. ´éóWork stability. ´éóSexual and other forms of harassment ´éóJob satisfaction. ´éóLeadership style. ´éó Security. ´éó Workers` participation and communication. ´éóMotivation and incentives. PSYCHOSOCIAL HAZARDS
- 18. STRESS Manifestations of Stress PHYSIOLOGICAL ´â╝ Heart rate ´â╝ Blood pressure ´â╝ Indigestion BEHAVIORAL ´â╝ Drug use ´â╝ Alcohol intake ´â╝ Heavy smoking ´â╝ Impulsive emotiona l behavior ´â╝ Poor work & family relationship ´â╝ Social isolation ´â╝ Family abandonme nt ´â╝ Sleep problems PSYCHOLOGICAL ´â╝ Fatigue ´â╝ Anxiety ´â╝ Tension ´â╝ Irritability ´â╝ Depression ´â╝ Boredom ´â╝ Inability to concentrat e ´â╝ Low esteem 18
- 19. ÔÇó Ergonomics, also known as human engineering or human factors engineering. ÔÇó The science of designing machines, products, and systems to maximize the safety, comfort, and efficiency of the people who use them. ERGONOMIC HAZARDS 19
- 20. ÔÇó As result of improper designing of work systems. ÔÇó May cause musculoskeletal injuries. ÔÇó The main areas of concern for ergonomic hazards include: ÔÇó equipment layout and operation ÔÇó lifting, pushing and pulling (manual handling) ÔÇó systems and computer programs ÔÇó task, job and workplace design ÔÇó workstation design and height. ERGONOMIC HAZARDS 20
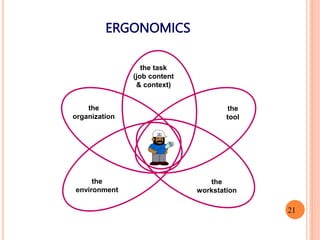
- 21. ERGONOMICS the tool the workstation the task (job content & context) the organization the environment 21
- 23. Forceful exertion Risk Factor: ERGONOMICS 23
- 24. RISK FACTOR: ERGONOMICS Repetitive movement 24
- 25. RISK FACTOR: ERGONOMICS Extreme range of motion 25
- 26. RISK FACTOR: ERGONOMICS Awkward posture 26
- 27. OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES ´üÁ Occupational diseases are adverse health conditions in the human being, the occurrence or severity of which is related to exposure to factors on the job or in the work environment. ´üÁ Such factors can be: ´üÁPhysical: e.g. heat, noise, radiation ´üÁChemical: e.g. solvents, pesticides, heavy metals, dust ´üÁBiological: e.g. tuberculosis, hepatitis B virus, HIV ´üÁErgonomic: e.g. improperly designed tools or work areas, repetitive motions ´üÁPsychosocial stressors: e.g. lack of control over work, inadequate personal support ´üÁMechanical: these mainly cause work accidents and injuries rather than occupational diseases. 27
- 28. OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES ´éóOccupational diseases are slow to develop, less dramatic and even less obvious. ´éóDue to their gradual effects they do not receive publicity. ´éóLosses attributable to occupational diseases over time are more difficult to describe compared to injuries. 28
- 29. MOST COMMON OCC DISEASES ´éó Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) ´éó Pneumoconioses (mining operations) ´éó Respiratory eg. Occupational asthma (paints) ´éó Occupational dermatoses (skin disorders) ´éó MSDs (lack of ergonomics) ´éó Psychiatric disorders (post-traumatic stress), drug abuse ´éó Hepatitis B and C, TB, HIV, anthrax, etc (health care, vet) ´éó Occupational cancer (chemical, pesticides, dyes) ´éó Cardiovascular disorders ´éó Gasto-intestinal disorders ´éó Visual disorders ´éó Neurological disorders ´éó Reproductive disorders 29
- 30. SUMMARY ´éóThere is an unlimited number of hazards that can be found in almost every workplace. ´éóThese include both obvious unsafe working conditions and insidious, less obvious hazards. ´éóHazards often are built into the workplace. Therefore, workplace managers must ensure that hazards are removed, rather than trying to get workers to adapt to unsafe conditions. ´éóThe most effective accident and disease prevention begins when work processes are still in the design stage, when safe conditions can be built into the work process. 30
- 31. ACTIVITY ´éóRead and make notes about identification of occupational health and safety hazards ´éóDiscuss the different occupational hazards in your workplace. ´Ç┐ 31
Editor's Notes
- #4: Risk- chance that harm (illness, injury, disorder, impairment) will arises due to exposure to an occupation hazard