odometer & some terms in a instrumentation
- 1. NAME : ADRI RAHADIAN S CLASS : 2-A NIM : 111611003 http://www.slideshare.net/adri_rahadian
- 2. Task 1 Odometer : An odometer or odograph is an instrument that indicates distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or automobile. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two. Tripmeter : Most modern cars include a trip meter (trip odometer). Unlike the odometer, a trip meter is reset at any point in a journey, making it possible to record the distance traveled in any particular journey or part of a journey.
- 3. Odometer & Tripmeter After reaching the maximum reading, an odometer or trip meter restarts from zero, called odometer rollover.
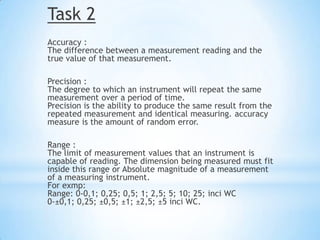
- 5. Task 2 Accuracy : The difference between a measurement reading and the true value of that measurement. Precision : The degree to which an instrument will repeat the same measurement over a period of time. Precision is the ability to produce the same result from the repeated measurement and identical measuring. accuracy measure is the amount of random error. Range : The limit of measurement values that an instrument is capable of reading. The dimension being measured must fit inside this range or Absolute magnitude of a measurement of a measuring instrument. For exmp: Range: 0-0,1; 0,25; 0,5; 1; 2,5; 5; 10; 25; inci WC 0-┬▒0,1; 0,25; ┬▒0,5; ┬▒1; ┬▒2,5; ┬▒5 inci WC.
- 6. Subdivision : Subdivision is an area or part of something which is itself a part of something larger. Subdivision in measurement system is an units smaller than other units in the same process variable. Example : an angle have number of 360 degree of in one complete rotation. At each level have 60 subdivision called minute and at each minute have 60 subdivision called second. Error : The amount of deviation from a standard or specification. Errors should be eliminated in the measuring process.
- 7. Hysteresis : The delay between the action and reaction of a measuring instrument. Hysteresis is the amount of error that results when this action occurs. Stability : The ability of a measuring instrument to retain its calibration over a long period of time. Stability determines an instrument's consistency over time. Repeatability : The ability to obtain consistent results when measuring the same part with the same measuring instrument.
- 8. Sensitivity : Sensitivity is the smallest change in a measurement that an instrument is capable of detecting. Resolution : The smallest change in a measured value that the instrument can detect. Resolution is also known as sensitivity.
- 9. Thermocouple : A thermocouple consists of two conductors of different materials (usually metal alloys) that produce a voltage in the vicinity of the point where the two conductors are in contact. The voltage produced is dependent on, but not necessarily proportional to, the difference of temperature of the junction to other parts of those conductors. Thermocouples are a widely used type of temperature sensor for measurement and control and can also be used to convert a temperature gradient into electricity. RTD : Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature by correlating the resistance of the RTD element with temperature. The RTD element is made from a pure material whose resistance at various temperatures has been documented. The material has a predictable change in resistance as the temperature changes; it is this predictable change that is used to determine temperature.
- 10. Thermocouple connected to a multimeter displaying room temperature in ┬░C.
- 11. Pressure Transmitter : A pressure transmitter helps to accomplish two specific goals. First, pressure instruments monitor the amount of pressure applied to a part of the process that is required in order to achieve the desired result. Data logging : The process of using a computer to collect data through sensors, analyze the data and save and output the results of the collection and analysis. Data logging also implies the control of how the computer collects and analyzes the data.
- 13. Valve : Mechanical or electromechanical device by which the flow of a gas, liquid, slurry, or loose dry material can be started, stopped, diverted, and/or regulated. The type of valve (looked from function) include : Hidraulic Valve Pneumatic Valve Manual Valve Selenoid Valve Motor Valve
- 15. ADC : An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC, A/D or A to D) is a device that uses sampling to convert a continuous quantity to a discrete time representation in digital form. The reverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). DAC : a digital-to-analog converter (DAC or D-to-A) is a device that converts a digital (usually binary) code to an analog signal (current, voltage, or electric charge). An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse operation.
- 16. 4-channel stereo multiplexed 8-channel digital-to-analog analog-to-digital converter converterCirrus Logic CS4382 WM8775SEDS made as used in a soundcard. by Wolfson Microelectronics placed on an X-Fi Fatal1ty Prosound card.