Ofirmev Results 1 to 400 data points
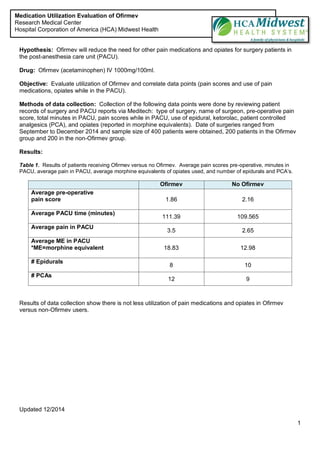
- 1. Updated 12/2014 1 Hypothesis: Ofirmev will reduce the need for other pain medications and opiates for surgery patients in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU). Drug: Ofirmev (acetaminophen) IV 1000mg/100ml. Objective: Evaluate utilization of Ofirmev and correlate data points (pain scores and use of pain medications, opiates while in the PACU). Methods of data collection: Collection of the following data points were done by reviewing patient records of surgery and PACU reports via Meditech: type of surgery, name of surgeon, pre-operative pain score, total minutes in PACU, pain scores while in PACU, use of epidural, ketorolac, patient controlled analgesics (PCA), and opiates (reported in morphine equivalents). Date of surgeries ranged from September to December 2014 and sample size of 400 patients were obtained, 200 patients in the Ofirmev group and 200 in the non-Ofirmev group. Results: Table 1. Results of patients receiving Ofirmev versus no Ofirmev. Average pain scores pre-operative, minutes in PACU, average pain in PACU, average morphine equivalents of opiates used, and number of epidurals and PCAŌĆÖs. Ofirmev No Ofirmev Average pre-operative pain score 1.86 2.16 Average PACU time (minutes) 111.39 109.565 Average pain in PACU 3.5 2.65 Average ME in PACU *ME=morphine equivalent 18.83 12.98 # Epidurals 8 10 # PCAs 12 9 Results of data collection show there is not less utilization of pain medications and opiates in Ofirmev versus non-Ofirmev users. Medication Utilization Evaluation of Ofirmev Research Medical Center Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Midwest Health
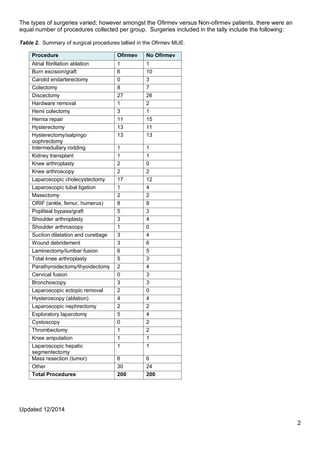
- 2. Updated 12/2014 2 The types of surgeries varied; however amongst the Ofirmev versus Non-ofirmev patients, there were an equal number of procedures collected per group. Surgeries included in the tally include the following: Table 2. Summary of surgical procedures tallied in the Ofirmev MUE. Procedure Ofirmev No Ofirmev Atrial fibrillation ablation 1 1 Burn excision/graft 6 10 Carotid endarterectomy 0 3 Colectomy 8 7 Discectomy 27 26 Hardware removal 1 2 Hemi colectomy 3 1 Hernia repair 11 15 Hysterectomy 13 11 Hysterectomy/salpingo oophrectomy 13 13 Intermedullary rodding 1 1 Kidney transplant 1 1 Knee arthroplasty 2 0 Knee arthroscopy 2 2 Laparoscopic cholecystectomy 17 12 Laparoscopic tubal ligation 1 4 Masectomy 2 2 ORIF (ankle, femur, humerus) 8 8 Popliteal bypass/graft 5 3 Shoulder arthroplasty 3 4 Shoulder arthroscopy 1 0 Suction dilatation and curettage 3 4 Wound debridement 3 6 Laminectomy/lumbar fusion 6 5 Total knee arthroplasty 5 3 Parathyroidectomy/thyoidectomy 2 4 Cervical fusion 0 3 Bronchoscopy 3 3 Laparoscopic ectopic removal 2 0 Hysteroscopy (ablation) 4 4 Laparoscopic nephrectomy 2 2 Exploratory laparotomy 5 4 Cystoscopy 0 2 Thrombectomy 1 2 Knee amputation 1 1 Laparoscopic hepatic segmentectomy 1 1 Mass resection (tumor) 6 6 Other 30 24 Total Procedures 200 200
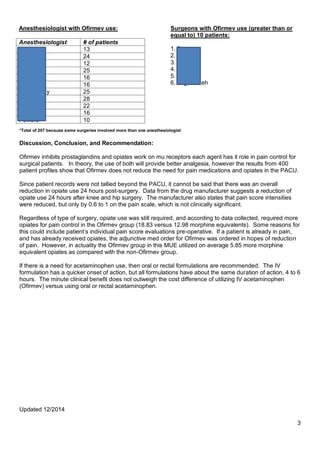
- 3. Updated 12/2014 3 *Total of 207 because some surgeries involved more than one anesthesiologist Discussion, Conclusion, and Recommendation: Ofirmev inhibits prostaglandins and opiates work on mu receptors each agent has it role in pain control for surgical patients. In theory, the use of both will provide better analgesia, however the results from 400 patient profiles show that Ofirmev does not reduce the need for pain medications and opiates in the PACU. Since patient records were not tallied beyond the PACU, it cannot be said that there was an overall reduction in opiate use 24 hours post-surgery. Data from the drug manufacturer suggests a reduction of opiate use 24 hours after knee and hip surgery. The manufacturer also states that pain score intensities were reduced, but only by 0.6 to 1 on the pain scale, which is not clinically significant. Regardless of type of surgery, opiate use was still required, and according to data collected, required more opiates for pain control in the Ofirmev group (18.83 versus 12.98 morphine equivalents). Some reasons for this could include patientŌĆÖs individual pain score evaluations pre-operative. If a patient is already in pain, and has already received opiates, the adjunctive med order for Ofirmev was ordered in hopes of reduction of pain. However, in actuality the Ofirmev group in this MUE utilized on average 5.85 more morphine equivalent opiates as compared with the non-Ofirmev group. If there is a need for acetaminophen use, then oral or rectal formulations are recommended. The IV formulation has a quicker onset of action, but all formulations have about the same duration of action, 4 to 6 hours. The minute clinical benefit does not outweigh the cost difference of utilizing IV acetaminophen (Ofirmev) versus using oral or rectal acetaminophen. Surgeons with Ofirmev use (greater than or equal to) 10 patients: 1. Basta 2. Blatt 3. Cates 4. Garcia 5. Hicks 6. Taghizadeh Anesthesiologist with Ofirmev use: Anesthesiologist # of patients Armstrong 13 Berenson 24 Bernard 12 Bruening 25 Freund 16 Gassin 16 Ludwikosky 25 Moncure 28 Moore 22 Novak 16 Powers 10
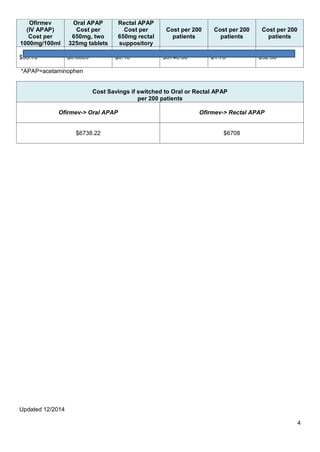
- 4. Updated 12/2014 4 Ofirmev (IV APAP) Cost per 1000mg/100ml Oral APAP Cost per 650mg, two 325mg tablets Rectal APAP Cost per 650mg rectal suppository Cost per 200 patients Cost per 200 patients Cost per 200 patients $33.70 $0.0089 $0.16 $6740.00 $1.78 $32.00 *APAP=acetaminophen Cost Savings if switched to Oral or Rectal APAP per 200 patients Ofirmev-> Oral APAP Ofirmev-> Rectal APAP $6738.22 $6708