OMFS Neck Swelling g.pptx
- 2. What Causes Head and Neck Swellings ? ’üČInflammatory / Infectious conditions. ’üČCystic lesions, thyroid masses, vascular masses, & salivary gland masses. ’üČEnlargement of lymph nodes ’üČBenign & Malignant masses.
- 3. Symptoms Associated with Neck Lumps ’üČ Change in the voice including hoarseness persists for > 2 weeks ’üČ Growth in the mouth ’üČ Swollen tongue ’üČ Blood in the saliva or phlegm ’üČ Swallowing problems
- 4. History
- 5. 5 Students & 3 Teachers go for CAMPFIRE 1- Shape 1- Tenderness 2- Size 2- Transillumination 3- Site 3- Temperature 4- Surface 5- Scar Consistency - Attachment - Mobility - Pulsation - Fluctuancy - Irreducibility - Regional lymph nodes - Edge Physical Examination
- 6. ŌĆó MRI ŌĆó C.T SCAN ŌĆó PET/CT Radiographic investigations of Head and Neck Swelling
- 7. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology ’üČSafe ’üČRapid ’üČInexpensive ’üČPresurgical Planning ’üČAvoid surgical biopsy
- 8. What Causes Head and Neck Swellings ? ’üČCystic lesions, thyroid masses, vascular masses, & salivary gland masses. ’üČEnlargement of lymph nodes ’üČInflammatory / Infectious conditions. ’üČBenign & Malignant masses.
- 12. Inflammatory / Infectious Swelling Cervical Adenitis secondary to acute URTI, tonsillitis, & EBV . Chronic inflammatory disease like Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis, Cat Scratch disease, Shaving. These disease processes have to be treated medically.
- 13. Cystic swelling
- 14. Dermoid and Epidermoid Cysts An essential difference between Dermoid cyst and Epidermoid cyst is the presence of dermal appendages such as sebaceous glands, hair follicles, & sweat glands Clinical appearance of Dermoid and Epidermoid cysts of the neck ’ā╝a midline suprahyoid growing mass ’ā╝The mass is soft, mobile, and unattached to the overlying skin. ’ā╝Unlike thyroglossal duct cysts, the Dermoid are not intimately associated with the hyoid bone and thus do not move on protrusion of the tongue On CT scan the central cavity is usually filled with homogeneous, hypoattenuated fluid material. Discrete intracystic foci ŌĆ£marbles,ŌĆØ with moderate hyperintensity due to coalescence of fat into small nodules within a fluid matrix Surgical Management >> Complete surgical excision
- 16. Thyroglossal Duct Cyst The thyroid primordium originates at the level of the foramen cecum at the junction of the anterior 2/3 & posterior 1/3 of the tongue located in the midline or slightly paramedian The cysts usually manifest as an enlarging painless fluctuant mass ranges from 0.5 to 6 cm in diameter Approximately 80% of the cysts occur either at or below the level of the hyoid bone. Characteristically the lesion moves upward on tongue protrusion, a reflection of the origin of the duct at the foramen cecum CT scans >> smooth, well-circumscribed mass anywhere along the vertical course of the vestigial thyroglossal duct
- 17. Surgical Management >> Sistrunk procedure involves en bloc excision of the entire thyroglossal duct tract to the foramen cecum, as well as the central 1 to 2 cm of the hyoid bone
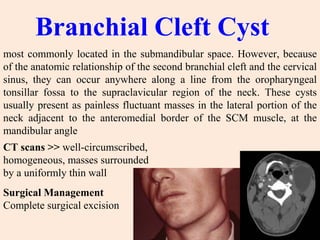
- 19. Branchial Cleft Cyst most commonly located in the submandibular space. However, because of the anatomic relationship of the second branchial cleft and the cervical sinus, they can occur anywhere along a line from the oropharyngeal tonsillar fossa to the supraclavicular region of the neck. These cysts usually present as painless fluctuant masses in the lateral portion of the neck adjacent to the anteromedial border of the SCM muscle, at the mandibular angle CT scans >> well-circumscribed, homogeneous, masses surrounded by a uniformly thin wall Surgical Management Complete surgical excision
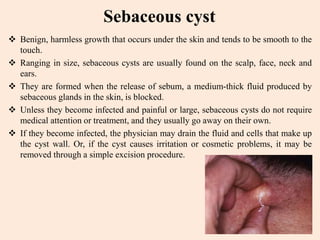
- 20. Sebaceous cyst ’üČ Benign, harmless growth that occurs under the skin and tends to be smooth to the touch. ’üČ Ranging in size, sebaceous cysts are usually found on the scalp, face, neck and ears. ’üČ They are formed when the release of sebum, a medium-thick fluid produced by sebaceous glands in the skin, is blocked. ’üČ Unless they become infected and painful or large, sebaceous cysts do not require medical attention or treatment, and they usually go away on their own. ’üČ If they become infected, the physician may drain the fluid and cells that make up the cyst wall. Or, if the cyst causes irritation or cosmetic problems, it may be removed through a simple excision procedure.
- 21. ’üČRanula presents as a Cystic swelling in the floor of mouth. ’üČ It occurs as a mucous extravasation from sublingual salivary gland. ’üČ Plunging Ranula may extend through the mylohyoid muscles into the neck. ’üČ Surgical treatment is by removal of the Sublingual gland.
- 22. Pharyngeal pouch pocket that forms in the upper part of the esophagus. Food collects in the pouch instead of going down the esophagus causing difficulty in swallowing and loss of weight. Some food may regurgitate (comes back undigested) in the throat and mouth causing coughing and chest infections. Etiology ’üČ Upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. ’üČ When the upper esophageal sphincter doesnŌĆÖt open all the way, it puts pressure on an area of the pharynx wall. ’üČ This excess pressure gradually pushes the tissue outward.
- 23. Clinical picture ŌĆó Left side swelling ŌĆó Soft, tender ŌĆó Pain, dysphagia ŌĆó Recurrent respiratory infection ŌĆó Halitosis ŌĆó Food regurgitation Diagnosis Barium swallow, is a special X-ray that highlights the inside of your mouth, pharynx, and esophagus.
- 24. Goitre
- 26. Neoplasms
- 27. Benign tumors Pleomorphic adenoma 1- Parotid > submandibular & palatal S.G 2- Painless, firm, slowly growing swelling 3- With Submucosal bluish discoloration 4- Not invade facial n.& no metastasis 5- ItŌĆÖs dump-bell shaped tumor
- 28. Treatment Complete excision with a surrounding normal tissue 1- if in Superficial lobe Superficial parotidectomy (lateral lobectomy) 2- if in superficial and deep lobe Total parotidectomy with preservation of facial nerve.
- 29. WarthinŌĆÖs tumor ŌĆó in parotid & minor glands in palate ŌĆó slowly growing round painless movable mass ŌĆó Bilateral ŌĆó If multiple & irregular >>> high recurrence rate ŌĆó Superficial parotidectomy
- 30. Malignant tumors Malignant pleomorphic adenoma ’üČPrimary malignant pleomorphic adenoma ’üČMalignant transformation of benign pleomorphic adenoma
- 32. Squamous Cell Carcinoma ŌĆó 6th most common cancer worldwide ŌĆó HNSCC ~ 5% all cancers ŌĆó S.C.C most common upper aero digestive tract malignancy ŌĆó Smoking ŌĆó 50% HNSCC occur in oral cavity ŌĆó Management presents considerable functional and aesthetic problems ŌĆó Multidisciplinary approach imperative ’ā╝ Removal of Primary tumor + cervical nodes ’ā╝ Surgery / Radiation / Chemotherapy ’ā╝ Sometimes palliation ’ā╝ Cervical neck disease reduces survival by 50%